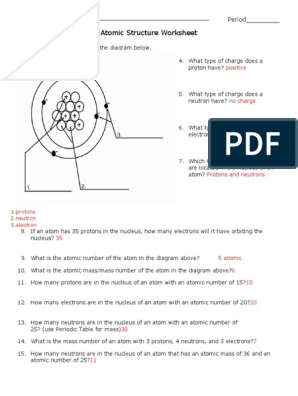
Atomic Structure: Chapter Test B
Atomic Structure: Chapter Test B
Uploaded by
Teegin HackerCopyright:
Available Formats
Atomic Structure: Chapter Test B
Atomic Structure: Chapter Test B
Uploaded by
Teegin HackerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Atomic Structure: Chapter Test B
Atomic Structure: Chapter Test B
Uploaded by
Teegin HackerCopyright:
Available Formats
Name Date Class
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Chapter Test B
A. Matching
Match each term in Column B with the correct description in Column A. Write the letter of the correct term on the
line.
Column A Column B
1. the number of protons in the nucleus of an a. electron
element
2. the smallest particle of an element that retains its b. mass number
identity in a chemical reaction
3. the total number of protons and neutrons in the c. atomic number
nucleus of an atom
4. a positively charged subatomic particle d. atomic mass
5. atoms with the same number of protons but e. neutron
different numbers of neutrons
6. a negatively charged subatomic particle f. atomic mass unit
1
7. the mass of a carbon-12 atom g. proton
12
8. an arrangement of elements in which the h. isotopes
elements are separated into groups based on a set
of repeating properties
9. a subatomic particle with no charge i. atom
10. the weighted average of the mass of the atoms in j. periodic table
a naturally occurring sample of an element
B. Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line.
11. Which of these statements is included in Dalton’s atomic theory?
a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged.
b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms.
c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons.
d. Atoms are divisible.
12. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Electrons are positively charged.
b. Protons are negatively charged.
c. Neutrons have no charge.
d. Atoms are positively charged.
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 97
Name Date Class
13. Which of the following correctly lists the particles in order from least massive to most massive?
a. proton, electron, hydrogen atom, helium atom
b. proton, helium atom, hydrogen atom, electron
c. hydrogen atom, electron, helium atom, proton
d. electron, proton, hydrogen atom, helium atom
14. Which of the following statements is not consistent with the results obtained in Rutherford’s gold foil
experiment?
a. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged.
b. The nucleus of an atom contains almost all the mass of the atom.
c. Atoms are composed mainly of empty space.
d. Electrons are contained in the nucleus of an atom.
15. The identity of an element can be determined on the basis of which of the following?
a. the number of protons in an atom of the element
b. the number of neutrons in an atom of the element
c. the mass number of the element
d. the atomic mass of the element
16. What is the atomic number and the mass number of an atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons?
a. atomic number = 11 and mass number = 12
b. atomic number = 12 and mass number = 11
c. atomic number = 11 and mass number = 23
d. atomic number = 23 and mass number = 12
17. An atom of hydrogen-2 contains
a. 2 protons, 2 electrons, and 2 neutrons.
b. 2 protons, 2 electrons, and 4 neutrons.
c. 1 proton, 1 electron, and 1 neutron.
d. 1 proton, 1 electron, and 2 neutrons.
18. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Each vertical column of elements in the periodic table is called a period.
b. The elements in any group of the periodic table have similar physical and chemical properties.
c. Group 1A contains the elements hydrogen and helium.
d. In the modern periodic table, elements are listed in order of increasing atomic mass.
19. Isotopes of the same element have
a. the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
b. the same number of protons but different numbers of electrons.
c. the same number of neutrons but different numbers of protons.
d. the same number of neutrons but different numbers of electrons.
20. Which symbol correctly represents an element (D) whose atoms contain 15 protons and 20 neutrons?
20 35
a. 15 D c. 15 D
15 15
b. 20 D d. 35 D
98 Core Teaching Resources
Name Date Class
21. If Z is the symbol for an element, which pair among the following represents isotopes of the same
element?
a. 51 51
25 Z and 26 Z c. 50 50
25 Z and 27 Z
51 50 51 50
b. 25 Z and 25 Z d. 26 Z and 25 Z
22. The relative abundance of each isotope of an element determines its
a. atomic number. c. number of electrons.
b. atomic mass. d. number of protons.
23. Three isotopes of oxygen occur in nature: oxygen-16, oxygen-17, and oxygen-18. If the atomic mass of
oxygen is 15.9994, which of the three isotopes, if any, is the most abundant?
a. oxygen-16 c. oxygen-18
b. oxygen-17 d. All are equally abundant.
24. Element Z has two naturally occurring isotopes: Z-20 and Z-22. If the atomic mass of Z is 21.5 amu, what
is the relative abundance of each isotope in nature?
a. one Z-20 to one Z-22 c. two Z-20s to one Z-22
b. one Z-20 to two Z-22s d. one Z-20 to three Z-22s
C. Problems
Solve the following problems in the space provided. Show your work.
25. The element argon contains three naturally occurring isotopes:
36 38 40
18 Ar 18 Ar 18 Ar
The relative abundances and atomic masses are 0.337% (mass = 35.978 amu), 0.063% (mass = 37.963 amu), and
99.600% (mass = 39.962 amu), respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass of argon.
26. List the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of the following atoms.
Protons Neutrons Electrons
19
9 F
27
13 Al
40
18 Ar
65
30 Zn
108
47 Ag
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 99
Name Date Class
27. Complete the following table.
Atomic Mass Number of Number of Number of
Symbol
Number Number Protons Neutrons Electrons
24
12 12 Mg
39 20
30 26
80
35 Br
197 79
D. Essay
Write a short essay for the following.
28. Explain how the isotopes of one element are alike and how they are different. Give at least two examples of each.
100 Core Teaching Resources
You might also like
- General Organic and Biochemistry An Applied Approach 2nd Edition Armstrong Test BankDocument14 pagesGeneral Organic and Biochemistry An Applied Approach 2nd Edition Armstrong Test BankJeffreyThomasfgiam100% (14)
- Characteristics of Living Things - QuizizzDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things - QuizizzArina KhusnaNo ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation WorksheetDocument2 pagesFractional Distillation Worksheetdodo100% (1)
- Isotopes Worksheet Answer KeyDocument2 pagesIsotopes Worksheet Answer KeyJhey Em0% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesAtomic StructureTeang LamNo ratings yet
- Module On The Mole Concept Suggested Time Allotment: 3-4 Hours Prepared By: Luisita L. Ely, PHDDocument12 pagesModule On The Mole Concept Suggested Time Allotment: 3-4 Hours Prepared By: Luisita L. Ely, PHDEl GardeneroNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Worksheet: Name PeriodDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure Worksheet: Name Periodapi-496534295100% (1)
- Atomic History Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageAtomic History Worksheet Answer KeyRhuvy Ramos50% (2)
- Average Atomic Mass Worksheet 2Document1 pageAverage Atomic Mass Worksheet 2api-320485715No ratings yet
- Reviewer - College ExamDocument6 pagesReviewer - College ExamAyey Dy100% (10)
- Abs Esp SystemDocument19 pagesAbs Esp SystemdjtomcraftNo ratings yet
- Octet Rule Practice-FDocument4 pagesOctet Rule Practice-FDavid Leonardo Justinico CastroNo ratings yet
- Worksheet13 VSEPR KeyDocument4 pagesWorksheet13 VSEPR KeyBrent DawnNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Atomic - Structure - QuizDocument4 pagesQuiz 3 Atomic - Structure - QuizMustufa KhalilNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding WorksheetDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding WorksheetAnbiya FathimaNo ratings yet
- History and Models of The Atom: Click On MeDocument26 pagesHistory and Models of The Atom: Click On MeRon Adrian Sarte SebastianNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetRoxy LificNo ratings yet
- Atomic Model WorksheetDocument2 pagesAtomic Model WorksheetTelle Telle100% (1)
- (10E) Worksheet 1.2 - Electronic ConfigurationDocument2 pages(10E) Worksheet 1.2 - Electronic ConfigurationkrisnuNo ratings yet
- Cycles WorksheetDocument4 pagesCycles WorksheetRose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model ActivityDocument2 pagesBohr Model ActivityAnonymous 7QjNuvoCpINo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter: Practice Questions - Paper 2Document8 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter: Practice Questions - Paper 2Agastya ArasuNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS - Review The AtomDocument5 pagesANSWERS - Review The AtomDayana MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 GuideDocument39 pagesGrade 8 GuideBreeza Marie VeralloNo ratings yet
- Names and Formulas of Complex Ions (A Lesson Plan)Document3 pagesNames and Formulas of Complex Ions (A Lesson Plan)MarkNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Weather Matter Assessment Studentand Teacher VersionsDocument34 pagesWater Cycle Weather Matter Assessment Studentand Teacher VersionsJulia Meirelles100% (2)
- Pure Substances and MixturesDocument19 pagesPure Substances and MixturesMaria Florence Ybonne Sagot-InocentesNo ratings yet
- 7 Elements in The Human BodyDocument2 pages7 Elements in The Human BodyCris CorsinoNo ratings yet
- MYP4 Chemistry Periodic TrendsDocument31 pagesMYP4 Chemistry Periodic TrendsAref Dahabrah100% (1)
- Forces and Motion Unit TestDocument14 pagesForces and Motion Unit TestRonald TranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Atomic Structure Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 2-Atomic Structure Worksheet AnswershomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Worksheet Study On AlkanesDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Worksheet Study On AlkanesThee-Great Arthur N'SamaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Activity SheetDocument17 pages2nd Quarter Activity SheetMarilyn OngkikoNo ratings yet
- Groups, Noble Gases, Metals, Non-Metals and Metalloids. Transition ElementDocument3 pagesGroups, Noble Gases, Metals, Non-Metals and Metalloids. Transition ElementEman Tan DuNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table - QuizDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table - QuizLeriMarianoNo ratings yet
- Examview - Chemistry Applications Yearly AssessmentDocument25 pagesExamview - Chemistry Applications Yearly Assessmentapi-232424041No ratings yet
- Worksheet On Quantum NumbersDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Quantum NumbersJannah Mae IsioNo ratings yet
- Atoms Periodic Table Pop QuizDocument2 pagesAtoms Periodic Table Pop QuizAlrianne BatonghinogNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory ReviewDocument5 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory ReviewTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Isotopes WorksheetDocument1 pageIsotopes WorksheetBrentRJones100% (1)
- SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY 8Document4 pagesSCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY 8ANDJELYN M. ABALOSNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument19 pagesTopic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration TestDocument1 pageElectron Configuration TestSri HartonoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 ChemistryDocument40 pagesGrade 9 ChemistryCartano fam100% (1)
- (2.1) E, C, & M (Without Answer)Document2 pages(2.1) E, C, & M (Without Answer)Rose Ann Saldivia AgramonNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 Q1 Properties of SolutionsDocument2 pagesLas Science 7 Q1 Properties of SolutionsJonah Santos-PinedaNo ratings yet
- Forces in Fluids Sample TestDocument13 pagesForces in Fluids Sample Testgrace_lo_1No ratings yet
- Atomic Spectra Worksheet Answer Key 05-06Document3 pagesAtomic Spectra Worksheet Answer Key 05-06Anonymous E9ESAecw8x33% (3)
- Climate Change Exercise Grade 7 PDFDocument5 pagesClimate Change Exercise Grade 7 PDFMaria Isabella Harsono100% (1)
- Matter QUIZ RESULTSDocument4 pagesMatter QUIZ RESULTScjNo ratings yet
- 1020-Lewis and Shapes PDFDocument4 pages1020-Lewis and Shapes PDFJaya Chitra Degala RamaluNo ratings yet
- Particle Nature of MatterDocument45 pagesParticle Nature of MatterDina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Gas Laws ExercisesDocument6 pagesChemistry Gas Laws Exercisesjag1231No ratings yet
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistDocument12 pagesIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786No ratings yet
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDocument10 pagesPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- UAM Grade 9Document1 pageUAM Grade 9Sheila Marie AmigoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Integrated Science Test Term One For Externals - 2018Document2 pagesGrade 9 Integrated Science Test Term One For Externals - 2018Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ExamDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Examapi-375738241No ratings yet
- 5021354-Class 9 - Science - Chem - Structure of The Atom - WS With Ans. - ShyniDocument7 pages5021354-Class 9 - Science - Chem - Structure of The Atom - WS With Ans. - ShyniSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesPractice Exam QuestionsEamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Atomic ConceptsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Atomic ConceptsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Abaqus Tutorial 1Document11 pagesAbaqus Tutorial 1Dg IRfan100% (1)
- Backward EulerDocument2 pagesBackward EulerCherry JyotshnaNo ratings yet
- Vortex FlowDocument2 pagesVortex Flowbachayadav0% (1)
- Advanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergyDocument1 pageAdvanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergySyed Hafeez Peeran QuadriNo ratings yet
- Exploring Black Holes Chapter 3Document43 pagesExploring Black Holes Chapter 3maria solNo ratings yet
- 10 - Imperfection in Solids Point Defects in MetalsDocument12 pages10 - Imperfection in Solids Point Defects in MetalshussainNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Physics-1. Electric Charges and Field & Potential and CapacitorsDocument16 pagesHsslive-Xii-Physics-1. Electric Charges and Field & Potential and CapacitorsAdith DeepakNo ratings yet
- RRB JE ME CBT 2 Full Test 1 - 150 Questions MCQ TestDocument94 pagesRRB JE ME CBT 2 Full Test 1 - 150 Questions MCQ TestS KousikNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 AsolnsDocument7 pagesExam 2 AsolnsLogesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Centroid of VolumeDocument10 pagesCentroid of VolumeDianne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Seismic DesignDocument24 pagesSeismic DesignKiranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department: Adamson University College of EngineeringDocument13 pagesChemical Engineering Department: Adamson University College of EngineeringKarl RodernoNo ratings yet
- 33 ch3Document15 pages33 ch3vivek chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 23 - SPH ModellingDocument11 pagesTutorial 23 - SPH Modellingjs kalyana rama100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics II - Homework Assignment 8: Alejandro G Omez Espinosa April 15, 2013Document4 pagesQuantum Mechanics II - Homework Assignment 8: Alejandro G Omez Espinosa April 15, 2013Ale GomezNo ratings yet
- Higher TG Based On Triple Hydrogen Bond Interactions - Jean Claude MBULU AGALIADocument20 pagesHigher TG Based On Triple Hydrogen Bond Interactions - Jean Claude MBULU AGALIAabhijeetanand2010No ratings yet
- III Semester SPECTROS PDFDocument11 pagesIII Semester SPECTROS PDFArangaNo ratings yet
- The Calculus of VariationsDocument52 pagesThe Calculus of VariationsKim HsiehNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument1 pageActivityTomy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 06 Stoichiometry 2b PDFDocument4 pages06 Stoichiometry 2b PDFchewazableNo ratings yet
- Acid Base NotesDocument98 pagesAcid Base NotesTasniiem KhmbataNo ratings yet
- 5cuttingconditions 170204214737Document93 pages5cuttingconditions 170204214737ramadanNo ratings yet
- Metrical Dimensional Relations of The Aether" by E.P.Dollard - Gestalt RealityDocument33 pagesMetrical Dimensional Relations of The Aether" by E.P.Dollard - Gestalt Realitywangha6No ratings yet
- 13.07.22 Bitsat Full Test-2 Paper Solutions PDFDocument37 pages13.07.22 Bitsat Full Test-2 Paper Solutions PDFNishitaNo ratings yet
- Operator Product Expansion in Quantum Field TheoryDocument11 pagesOperator Product Expansion in Quantum Field TheoryDennisNo ratings yet
- Teks in Focus Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument3 pagesTeks in Focus Physical and Chemical Propertiesabcde2811No ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Section 02 Particles and Radiation - AQA Physics A-LevelDocument14 pagesDetailed Notes - Section 02 Particles and Radiation - AQA Physics A-LevelHector KennerleyNo ratings yet