The Delhi high court has recently censured the state government for its failure to place 14 reports of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) before the legislative assembly.
Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) is a constitutional authority responsible for auditing and reporting on the financial operations of the government at the Union and State levels.
| Aspect | CAG in India | CAG in Britain |
| Status | Constitutional authority under Article 148. | Appointed as part of the executive branch. |
| Role | Independent auditor of public accounts and spending. | Auditor and consultant to Parliament on public spending. |
| Reporting | Reports directly to the President or Governors, who table them in Parliament or State Legislatures. | Reports to the UK Parliament through the Public Accounts Committee. |
| Scope of Audit | Audits all receipts, expenditures, and accounts of the Union, States, and Public Sector Enterprises. | Primarily focuses on central government accounts, public corporations, and local bodies. |
| Tenure | Fixed tenure of 6 years or until the age of 65, whichever is earlier. | Tenure is not constitutionally fixed, depending on contractual terms. |
| Vinod Rai, the former Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India, suggested several reforms to strengthen the institution and enhance its effectiveness in ensuring transparency and accountability.
Key reforms include:
These reforms aim to make the CAG more dynamic, proactive, and aligned with the challenges of modern governance. |
|---|
Relationship between Comptroller And Auditor General of India (CAG) and Public Accounts Committee (PAC):
|
|---|
CAG reports are essential tools for promoting transparency, accountability, and efficient governance. However, challenges like insufficient debate, lack of follow-up mechanisms, and public apathy hinder their impact. By drawing on global best practices and modernizing India’s audit the government can strengthen democratic accountability and ensure better utilization of public resources.
ISRO successfully conducted the Space Docking Experiment (SPADEX) to demonstrate in-orbit docking technology, a critical capability for refueling, satellite servicing, and future space station missions.
ISRO’s Space Farming Trial (2023)
|
|---|
ISRO’s recent achievements, including Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, SPADEX, and space farming trials, showcase India’s growing capability in space exploration. By addressing challenges through increased funding, technological innovation, and global collaboration, ISRO can further enhance its contribution to scientific discovery, economic growth, and global sustainability.
A transient “ghost island” which was born from a mud volcano eruption in the Caspian Sea has been reported in the news. This island emerged in early 2023 and receded into the sea by the end of 2024.
A “ghost island” refers to a temporary landmass that appears and disappears due to natural geological or environmental phenomena, such as mud volcano eruptions, sediment accumulation, or tidal and erosion processes.
A geological phenomenon where gases, liquids, and sediments erupt to the surface, creating temporary landforms. Often found in tectonic zones, they can expel methane and mud, sometimes causing fiery eruptions. They often form in tectonically active regions with high subsurface pressures.
About Caspian SeaThe Caspian Sea is the world’s largest land locked reservoir, covering an area of 392,600 km2. Countries Bordering the Caspian Sea
Major Rivers: The Caspian Sea receives water primarily from three major rivers:
|
The devastating wildfires in Los Angeles were driven by rare meteorological conditions known as ‘hydroclimate whiplash’ and exacerbated by climate change and human activities.
Recently, the Commerce Ministry has requested the Finance Ministry to extend the ₹3,000 crore Interest Equalisation Scheme, prioritizing MSMEs involved in exports.
Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises
|
|---|
| Type of Enterprise | Investment in Plant and Machinery/Equipment | Annual Turnover |
| Micro | Up to ₹1 crore | Up to ₹5 crore |
| Small | Up to ₹10 crore | Up to ₹50 crore |
| Medium | Up to ₹50 crore | Up to ₹250 crore |
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced the list of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in the Upper Layer (UL) under Scale Based Regulation (SBR) for the year 2024-25
The NBFC Upper Layer (UL) list for 2024-25 includes Tata Sons Private Ltd, Bajaj Finance Ltd, LIC Housing Finance Ltd, and Aditya Birla Finance Ltd, among others.
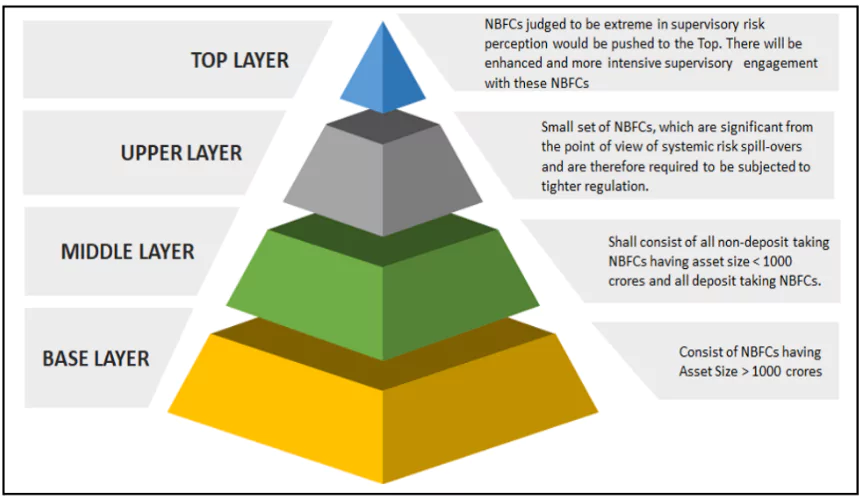 Categorization of NBFCs
Categorization of NBFCs
| Parameter | Banks | NBFCs |
| Demand Deposits | Can accept demand deposits | Cannot accept demand deposits |
| Payment and Settlement System (PSS) | Part of PSS; can issue cheques | Not part of PSS; cannot issue cheques |
| Deposit Insurance | Deposits insured by Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation | No deposit insurance facility available |
| Reserve Ratios (CRR, SLR) | Must maintain Reserve Ratios prescribed by RBI | Not required to maintain Reserve Ratios |
| Regulation Act | Regulated under Banking Regulation Act, 1949 | Regulated under Companies Act, 1956 |
| Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) | Up to 74% FDI allowed for private sector banks (49% under automatic route) | 100% FDI allowed |
Recent research challenges the conventional understanding that iron deficiency is the primary cause of anaemia in India, suggesting a need for diversified policy interventions to address the issue effectively.
Anaemia is a medical condition where the number of red blood cells (RBCs) or the haemoglobin levels in the blood are below normal, leading to reduced oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
6x6x6 strategy Under AMB
|
|---|
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has recommended capping internet tariffs for Wi-Fi service providers under the PM-WANI scheme at twice the retail broadband rate.
Recently, the Lokpal, India’s first anti-corruption ombudsman, revealed data showcasing its limited productivity since its establishment.
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has unveiled the Sanchar Saathi mobile app designed to streamline the reporting of suspected fraudulent communications.
A new method to manage ecological risks from DDT by binding it with biochar has been developed by the researchers of Sweden’s Chalmers University of Technology.
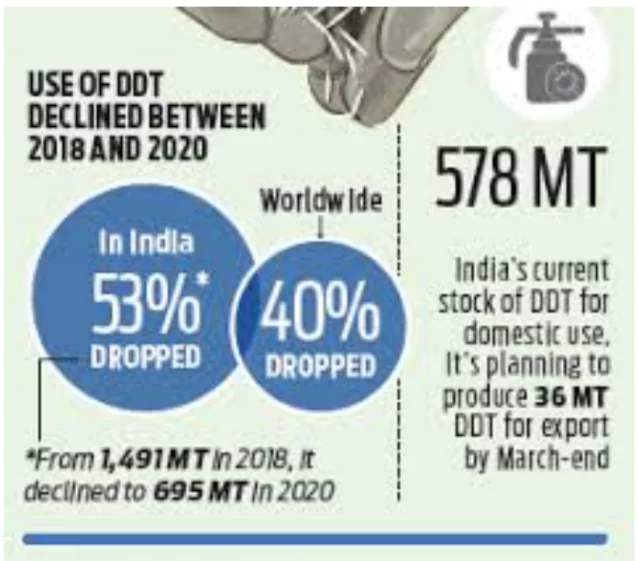 India banned the agricultural use of DDT by 1972.
India banned the agricultural use of DDT by 1972.
Biochar
|
The Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU-IND) and the National Housing Bank (NHB) have signed an MoU as part of efforts in effective implementation of requirements of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act and Rules.
About Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND)
National Housing Bank (NHB)
|
|---|
Context: Blue Origin has launched its New Glenn rocket on its first test flight sending up a prototype satellite to orbit thousands of miles above Earth.
Context: The QS World Future Skills Index 2025 has been released recently.
More Than Ever, The World Needs To Listen to Mahat...
An Opportunity to Settle Sri Lanka’s Ethnic Prob...
The Science is Clear, Crowd Disasters are Preventa...
In DeepSeek Breakthrough, Lessons for India
UN Urges to Save Glaciers, Secure The Planet
Bridge the Milk Divide For a Nutritionally Secure ...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>