Your intelligent pair programmer directly within your tmux sessions.



Screenshots |
Report Bug |
Request Feature
Tmux Cheat Sheet |
Tmux Getting Started |
Tmux Config Generator
- About The Project
- Installation
- Post-Installation Setup
- TmuxAI Layout
- Observe Mode
- Prepare Mode
- Watch Mode
- Knowledge Base
- Model Configuration
- Squashing
- Core Commands
- Command-Line Usage
- Configuration
- Contributing
- License
TmuxAI is an intelligent terminal assistant that lives inside your tmux sessions. Unlike other CLI AI tools, TmuxAI observes and understands the content of your tmux panes, providing assistance without requiring you to change your workflow or interrupt your terminal sessions.
Think of TmuxAI as a pair programmer that sits beside you, watching your terminal environment exactly as you see it. It can understand what you're working on across multiple panes, help solve problems and execute commands on your behalf in a dedicated execution pane.
TmuxAI's design philosophy mirrors the way humans collaborate at the terminal. Just as a colleague sitting next to you would observe your screen, understand context from what's visible, and help accordingly, TmuxAI:
- Observes: Reads the visible content in all your panes
- Communicates: Uses a dedicated chat pane for interaction
- Acts: Can execute commands in a separate execution pane (with your permission)
This approach provides powerful AI assistance while respecting your existing workflow and maintaining the familiar terminal environment you're already comfortable with.
TmuxAI requires only tmux to be installed on your system. It's designed to work on Unix-based operating systems including Linux and macOS.
The fastest way to install TmuxAI is using the installation script:
# install tmux if not already installed
curl -fsSL https://get.tmuxai.dev | bashThis installs TmuxAI to /usr/local/bin/tmuxai by default. If you need to install to a different location or want to see what the script does before running it, you can view the source at get.tmuxai.dev.
You can also download pre-built binaries from the GitHub releases page.
After downloading, make the binary executable and move it to a directory in your PATH:
chmod +x ./tmuxai
sudo mv ./tmuxai /usr/local/bin/To install the latest development version directly from the main branch:
go install github.com/alvinunreal/tmuxai@mainNote: The main branch contains the latest features and fixes but may be less stable than official releases.
TmuxAI reads its configuration from ~/.config/tmuxai/config.yaml. To get running, create the file with a model entry that points at the provider you use.
-
Create the config path
mkdir -p ~/.config/tmuxai vim ~/.config/tmuxai/config.yaml
-
Add a minimal config
models: primary: provider: openrouter # openrouter, openai or azure model: anthropic/claude-haiku-4.5 api_key: sk-your-api-key
Swap the provider name and fill in the model/API key required by your account.
-
Start TmuxAI
tmuxai
See Model Configuration for more details.
TmuxAI is designed to operate within a single tmux window, with one instance of TmuxAI running per window and organizes your workspace using the following pane structure:
-
Chat Pane: This is where you interact with the AI. It features a REPL-like interface with syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and readline shortcuts.
-
Exec Pane: TmuxAI selects (or creates) a pane where commands can be executed.
-
Read-Only Panes: All other panes in the current window serve as additional context. TmuxAI can read their content but does not interact with them.
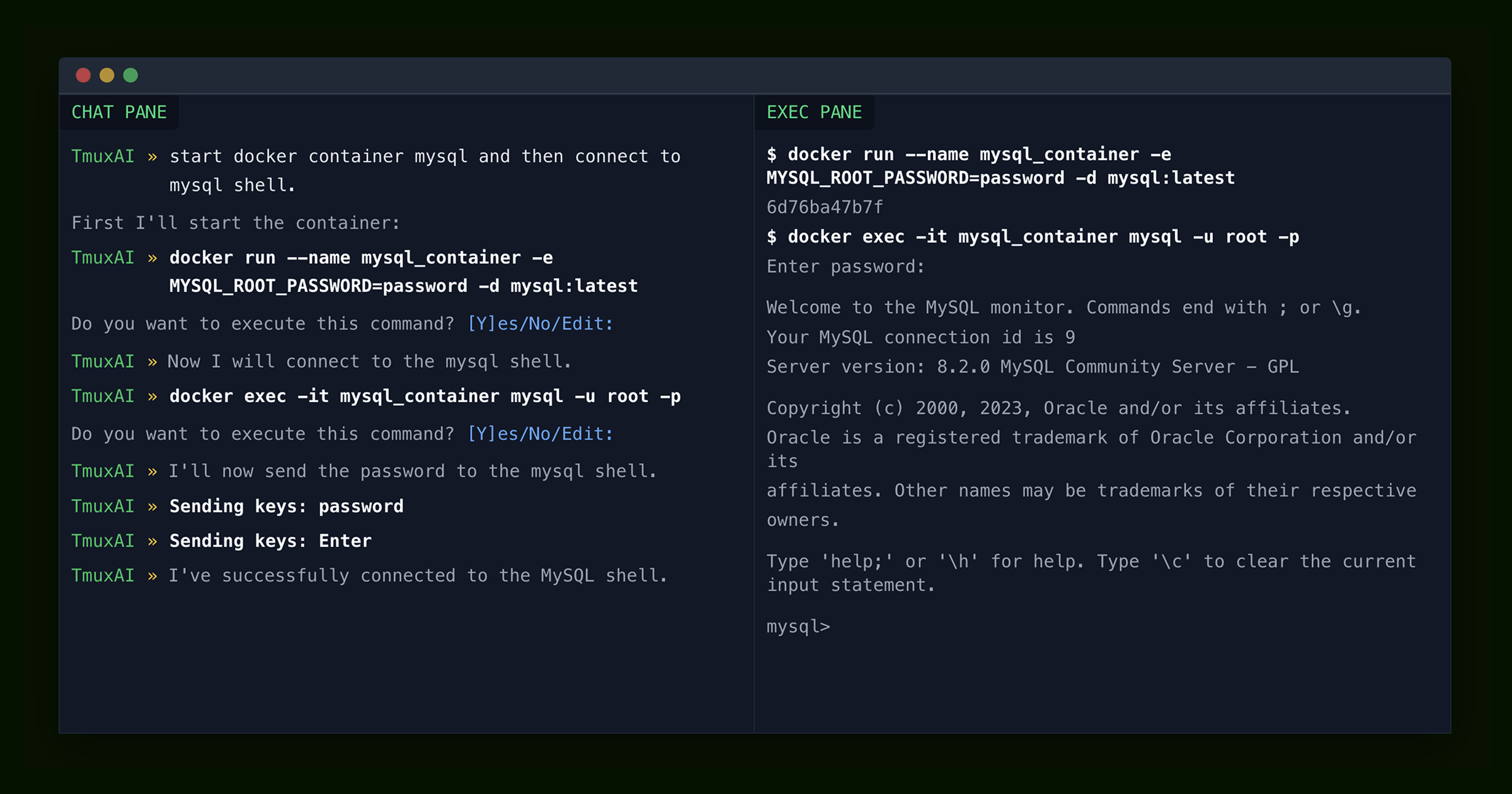
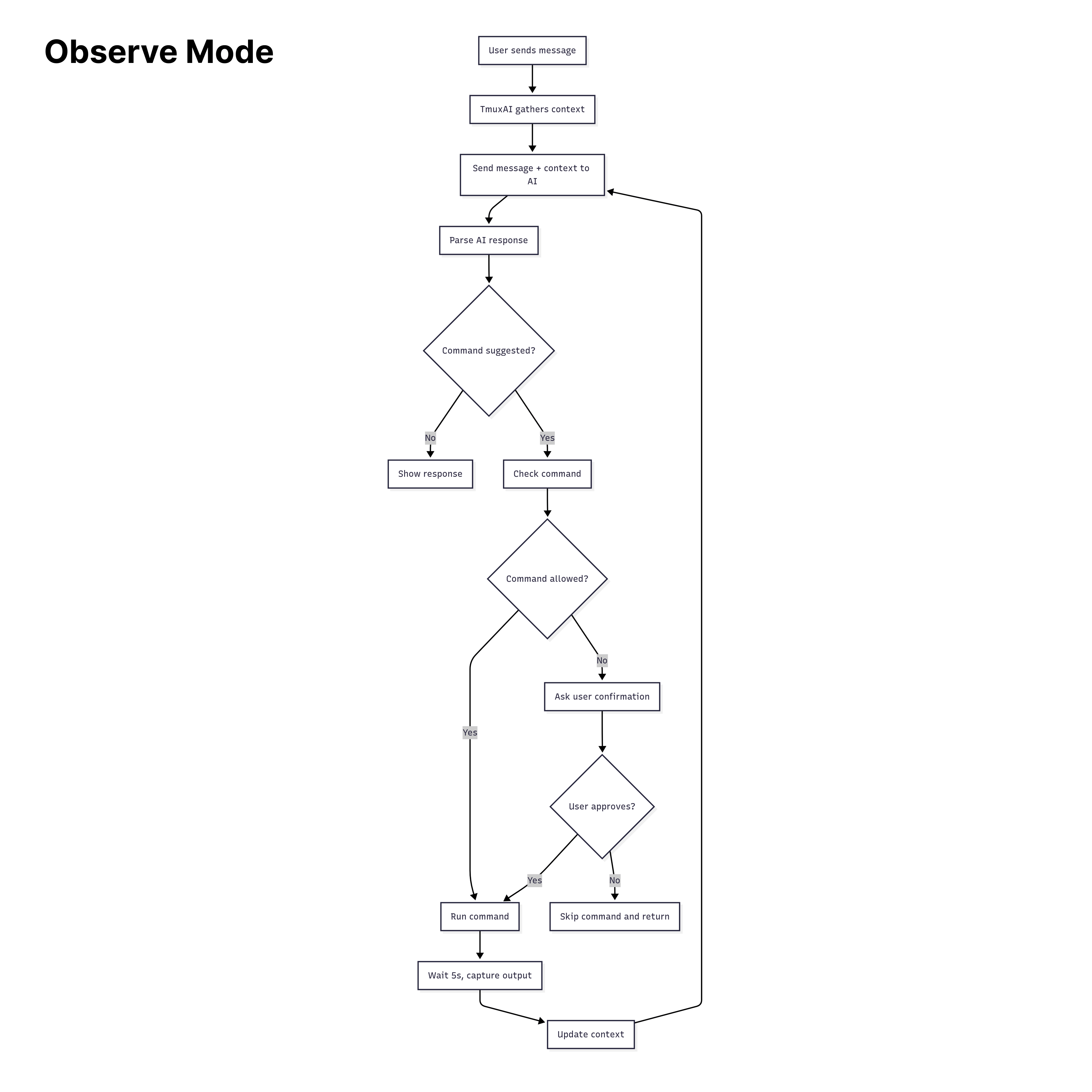
TmuxAI operates by default in "observe mode". Here's how the interaction flow works:
-
User types a message in the Chat Pane.
-
TmuxAI captures context from all visible panes in your current tmux window (excluding the Chat Pane itself). This includes:
- Current command with arguments
- Detected shell type
- User's operating system
- Current content of each pane
-
TmuxAI processes your request by sending user's message, the current pane context, and chat history to the AI.
-
The AI responds with information, which may include a suggested command to run.
-
If a command is suggested, TmuxAI will:
- Check if the command matches whitelist or blacklist patterns
- Ask for your confirmation (unless the command is whitelisted)
- Execute the command in the designated Exec Pane if approved
- Wait for the
wait_interval(default: 5 seconds) (You can pause/resume the countdown withspaceorenterto stop the countdown) - Capture the new output from all panes
- Send the updated context back to the AI to continue helping you
-
The conversation continues until your task is complete.

Prepare mode is an optional feature that enhances TmuxAI's ability to work with your terminal by customizing your shell prompt and tracking command execution with better precision. This enhancement eliminates the need for arbitrary wait intervals and provides the AI with more detailed information about your commands and their results.
When you enable Prepare Mode, TmuxAI will:
- Detects your current shell in the execution pane (supports bash, zsh, and fish)
- Customizes your shell prompt to include special markers that TmuxAI can recognize
- Will track command execution history including exit codes, and per-command outputs
- Will detect command completion instead of using fixed wait time intervals
To activate Prepare Mode, simply use:
TmuxAI » /prepare
By default, TmuxAI will attempt to detect the shell running in the execution pane. If you need to specify the shell manually, you can provide it as an argument:
TmuxAI » /prepare bash
Prepared Fish Example:
$ function fish_prompt; set -l s $status; printf '%s@%s:%s[%s][%d]» ' $USER (hostname -s) (prompt_pwd) (date +"%H:%M") $s; end
username@hostname:~/r/tmuxai[21:05][0]»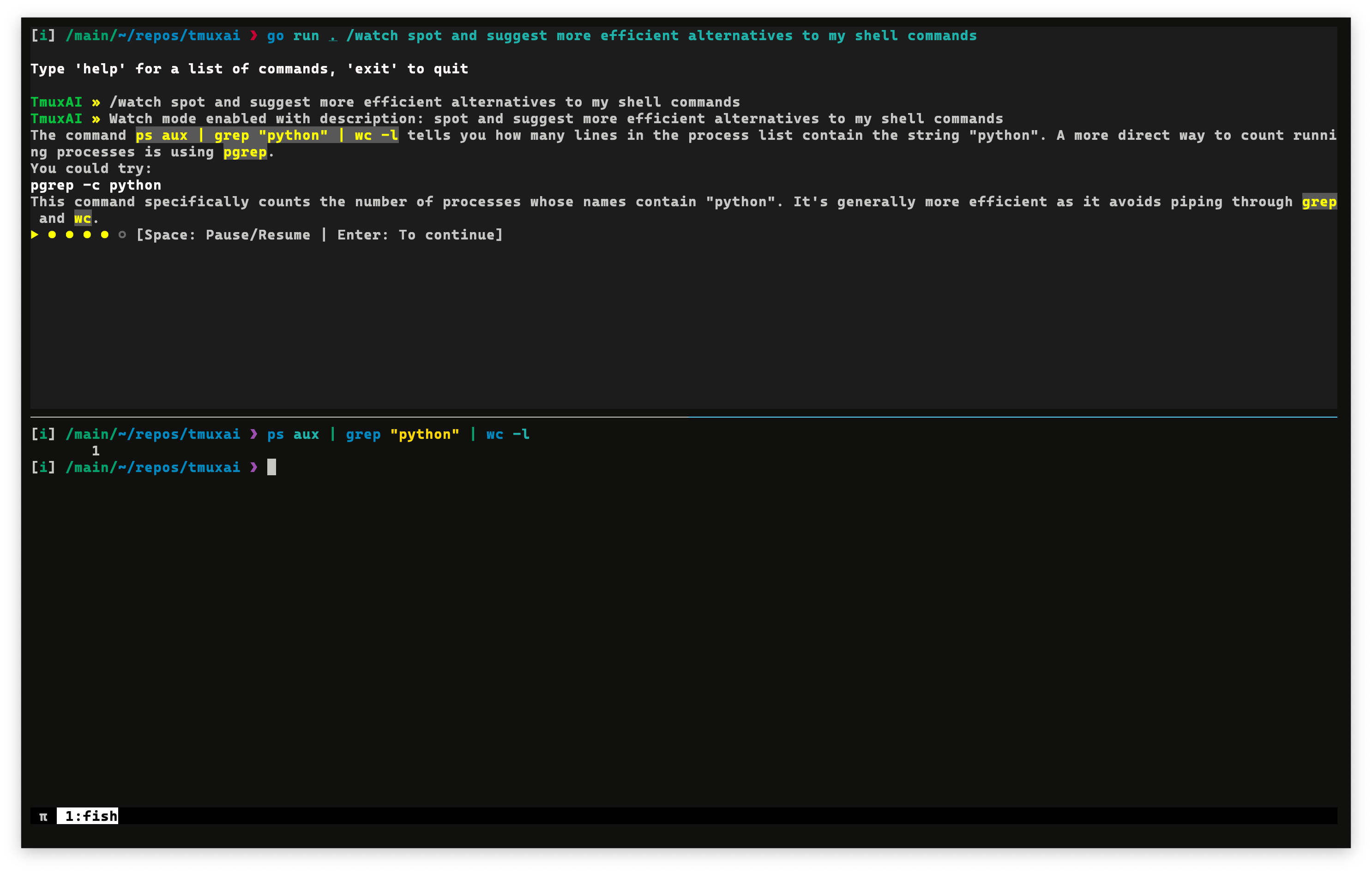
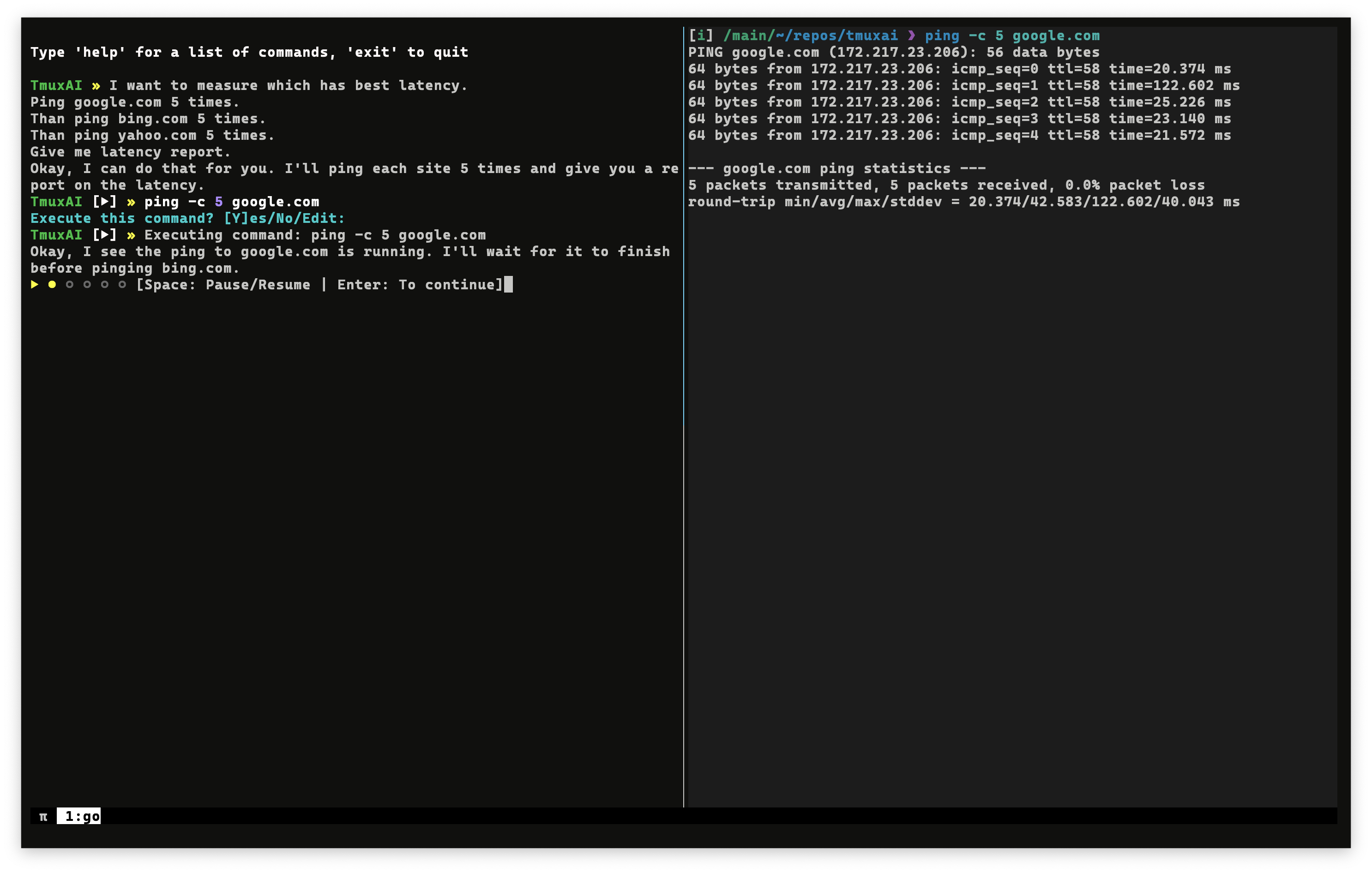
Watch Mode transforms TmuxAI into a proactive assistant that continuously monitors your terminal activity and provides suggestions based on what you're doing.
To enable Watch Mode, use the /watch command followed by a description of what you want TmuxAI to look for:
TmuxAI » /watch spot and suggest more efficient alternatives to my shell commands
When activated, TmuxAI will:
- Start capturing the content of all panes in your current tmux window at regular intervals (
wait_intervalconfiguration) - Analyze content based on your specified watch goal and provide suggestions when appropriate
Watch Mode could be valuable for scenarios such as:
-
Learning shell efficiency: Get suggestions for more concise commands as you work
TmuxAI » /watch spot and suggest more efficient alternatives to my shell commands -
Detecting common errors: Receive warnings about potential issues or mistakes
TmuxAI » /watch flag commands that could expose sensitive data or weaken system security -
Log Monitoring and Error Detection: Have TmuxAI monitor log files or terminal output for errors
TmuxAI » /watch monitor log output for errors, warnings, or critical issues and suggest fixes
As you work with TmuxAI, your conversation history grows, adding to the context provided to the AI model with each interaction. Different AI models have different context size limits and pricing structures based on token usage. To manage this, TmuxAI implements a simple context management feature called "squashing."
Squashing is TmuxAI's built-in mechanism for summarizing chat history to manage token usage.
When your context grows too large, TmuxAI condenses previous messages into a more compact summary.
You can check your current context utilization at any time using the /info command:
TmuxAI » /info
Context
────────
Messages 15
Context Size~ 82500 tokens
████████░░ 82.5%
Max Size 100000 tokensThis example shows that the context is at 82.5% capacity (82,500 tokens out of 100,000). When the context size reaches 80% of the configured maximum (max_context_size in your config), TmuxAI automatically triggers squashing.
If you'd like to manage your context before reaching the automatic threshold, you can trigger squashing manually with the /squash command:
TmuxAI » /squashThe Knowledge Base feature allows you to create pre-defined context files in markdown format that can be loaded into TmuxAI's conversation context. This is useful for sharing common patterns, workflows, or project-specific information with the AI across sessions.
Knowledge bases are markdown files stored in ~/.config/tmuxai/kb/. To create one:
-
Create the knowledge base directory if it doesn't exist:
mkdir -p ~/.config/tmuxai/kb -
Create a markdown file with your knowledge base content:
cat > ~/.config/tmuxai/kb/docker-workflows.md << 'EOF' # Docker Workflows ## Common Commands - Always use `docker compose` (not `docker-compose`) - Prefer named volumes over bind mounts for databases - Use `.env` files for environment-specific configuration ## Project Structure - Development: `docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up` - Production: `docker compose -f docker-compose.prod.yml up -d` EOF
Once created, you can load knowledge bases into your TmuxAI session:
# List available knowledge bases
TmuxAI » /kb
Available knowledge bases:
[ ] docker-workflows
[ ] git-conventions
[ ] testing-procedures
# Load a knowledge base
TmuxAI » /kb load docker-workflows
✓ Loaded knowledge base: docker-workflows (850 tokens)
# List again to see loaded status
TmuxAI » /kb
Available knowledge bases:
[✓] docker-workflows (850 tokens)
[ ] git-conventions
[ ] testing-procedures
Loaded: 1 KB(s), 850 tokens
# Unload a knowledge base
TmuxAI » /kb unload docker-workflows
✓ Unloaded knowledge base: docker-workflows
# Unload all knowledge bases
TmuxAI » /kb unload --all
✓ Unloaded all knowledge bases (2 KB(s))You can also load knowledge bases directly from the command line when starting TmuxAI:
# Load single knowledge base
tmuxai --kb docker-workflows
# Load multiple knowledge bases (comma-separated)
tmuxai --kb docker-workflows,git-conventionsYou can configure knowledge bases to load automatically on startup by adding them to your ~/.config/tmuxai/config.yaml:
knowledge_base:
auto_load:
- docker-workflows
- git-conventions
# path: /custom/path # Optional: use custom KB directoryImportant Notes:
- Loaded knowledge bases consume tokens from your context budget
- Use
/infoto see how many tokens your loaded KBs are using - Knowledge bases are injected after the system prompt but before conversation history
- Unloading a KB removes it from future messages immediately
TmuxAI supports configuring multiple AI model configurations and easily switching between them. This allows you to define different AI providers, models, and settings for various use cases.
Configure multiple AI models in your ~/.config/tmuxai/config.yaml:
# Optional: specify which model to use by default
# If not set, the first model in the list will be used automatically
default_model: "fast"
models:
fast:
provider: "openrouter"
model: "anthropic/claude-haiku-4.5"
api_key: "sk-or-your-openrouter-key"
smart:
provider: "openrouter"
model: "google/gemini-2.5-prod"
api_key: "sk-or-your-openrouter-key"
# You can use any chat completion compatible endpoint as base_url
anthropic:
provider: "openrouter"
model: "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022"
api_key: "your-anthropic-api-key"
base_url: "https://api.anthropic.com"
local-llama:
provider: "openrouter"
model: "gemma3:1b"
api_key: "sk-or-your-openrouter-key"
base_url: http://localhost:11434/v1
# Responses API
codex:
provider: "openai"
model: "gpt-5-codex"
api_key: "sk-or-your-openrouter-key"
azure-gpt4:
provider: "azure"
model: "gpt-4o"
api_key: "your-azure-openai-api-key"
api_base: "https://your-resource.openai.azure.com/"
api_version: "2025-04-01-preview"
deployment_name: "gpt-4o"Supported Providers:
openai- OpenAI Responses API (GPT-4, GPT-5, etc.)openrouter- Universal OpenAI-Compatible Gateway (access to any OpenAI-compatible provider)azure- Azure OpenAI Chat Completions API
OpenRouter Universal Access Examples:
models:You can switch between configured models in multiple ways:
CLI Flag:
# Use a specific model for the session
tmuxai --model gpt4
tmuxai --model claude-sonnet "Help me debug this code"Interactive Commands:
# List available models and see current selection
TmuxAI » /model
Available Models
[ ] claude-sonnet (openrouter: anthropic/claude-3.5-sonnet)
[ ] fast (openrouter: anthropic/claude-haiku-4.5)
[✓] smart (openrouter: google/gemini-2.5-prod)
[ ] local-llama (openrouter: meta-llama/llama-3.1-8b-instruct:free)
Current Model:
Configuration: smart
Provider: openrouter
Model: google/gemini-2.5-prod
# Switch to a different model
TmuxAI » /model claude-sonnet
✓ Switched to claude-sonnet (openrouter: anthropic/claude-3.5-sonnet)
# Status bar shows current model when using non-default
TmuxAI [claude-sonnet] [▶] »Environment Variables:
export TMUXAI_DEFAULT_MODEL="gpt4"- Auto-selection: First model in list is used automatically when no default is set
- Status Indicator: Current model appears in status bar when using non-default model
- Seamless Switching: No need to restart - models switch instantly during your session
- No Setup Required: TmuxAI starts without any configuration
- Configure When Ready: Add your first message to see helpful setup instructions
- Add Models: Configure multiple models in
~/.config/tmuxai/config.yaml - Start Using: Switch models with
/model <name>ortmuxai --model <name>
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
/info |
Display system information, pane details, and context statistics |
/clear |
Clear chat history. |
/reset |
Clear chat history and reset all panes. |
/config |
View current configuration settings |
/config set <key> <value> |
Override configuration for current session |
/model |
List available models and show current active model |
/model <name> |
Switch to a different model configuration |
/squash |
Manually trigger context summarization |
/prepare [shell] |
Initialize Prepared Mode for the Exec Pane (e.g., bash, zsh) |
/watch <description> |
Enable Watch Mode with specified goal |
/kb |
List available knowledge bases with loaded status |
/kb load <name> |
Load a knowledge base into conversation context |
/kb unload <name> |
Unload a specific knowledge base |
/kb unload --all |
Unload all knowledge bases |
/exit |
Exit TmuxAI |
You can start tmuxai with an initial message, task file, model configuration, or knowledge bases from the command line:
-
Direct Message:
tmuxai your initial message
-
Task File:
tmuxai -f path/to/your_task.txt
-
Specify Model:
# Use a specific model configuration tmuxai --model gpt4 "Write a Go function" tmuxai --model claude-sonnet
-
Load Knowledge Bases:
# Single knowledge base tmuxai --kb docker-workflows # Multiple knowledge bases tmuxai --kb docker-workflows,git-conventions
-
Combine Options:
tmuxai --model gpt4 --kb docker-workflows "Debug this Docker issue"
The configuration can be managed through a YAML file, environment variables, or via runtime commands.
TmuxAI looks for its configuration file at ~/.config/tmuxai/config.yaml.
For a sample configuration file, see config.example.yaml.
All configuration options can also be set via environment variables, which take precedence over the config file. Use the prefix TMUXAI_ followed by the uppercase configuration key:
# General settings
export TMUXAI_DEBUG=true
export TMUXAI_MAX_CAPTURE_LINES=300
export TMUXAI_MAX_CONTEXT_SIZE=150000
# Quick setup with environment variables (alternative to model configurations)
export TMUXAI_OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-api-key-here"
export TMUXAI_OPENAI_MODEL="gpt-4"
export TMUXAI_OPENROUTER_API_KEY="your-openrouter-api-key-here"You can also use environment variables directly within your configuration file values. The application will automatically expand these variables when loading the configuration:
# Example config.yaml with environment variable expansion
openai:
api_key: "${OPENAI_API_KEY}"
model: "${OPENAI_MODEL:-gpt-4}"
openrouter:
api_key: "${OPENROUTER_API_KEY}"
base_url: "${OPENROUTER_BASE_URL:-https://openrouter.ai/api/v1}"You can override configuration values for your current TmuxAI session using the /config command:
# View current configuration
TmuxAI » /config
# Override a configuration value for this session
TmuxAI » /config set max_capture_lines 300
TmuxAI » /config set wait_interval 3These changes will persist only for the current session and won't modify your config file.
If you have a suggestion that would make this better, please fork the repo and create a pull request.
You can also simply open an issue.
Don't forget to give the project a star!
Distributed under the Apache License. See Apache License for more information.