Guarijio people
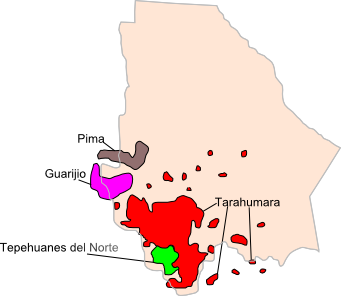 Guarijío territory in magenta | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 2,100 (2020) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
( | |
| Languages | |
| Guarijio language, Spanish[2] | |
| Religion | |
| Traditional tribal religion | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Mayo,[1] Tarahumara[3] |
The Guarijío (Spanish: Guarijío) are an indigenous people of Mexico. They primarily live in 17 villages near the West Sierra Madre Mountains in Chihuahua and the Sonoran border.[2] Their homelands are remote and reached either on foot or horseback.[4] Their traditional Guarijio language has about 2100 speakers.
Name
[edit]The Guarijío people are also known as the Huarijío, Maculái, Macurái, Macurawe, Varihío, Varijío, Varohio, or Vorijío people.[2]
Language
[edit]The Guarijío language is a Tarahumaran language of the Uto-Aztecan language family, written in the Latin script. A dictionary and grammar have been published for the language.[2] Children primarily learn Spanish in school.[4]
History
[edit]Guarijíos lived between the Tarahumara to the south and east and Mayo to the west. Spanish Jesuit missionaries arrived in their territory in the 1620s. The Jesuits established a mission in Chínipas, where some Guarijío and Guazapare people rebelled against them. After the Spanish military retaliated, the Guarijío dispersed and split into two distinct communities—one in Sonora and the other in Chihuahua[1]
Culture
[edit]These people enjoy seclusion in spacious villages. A festival, called tuburada, brings them together socially on momentous occasions, including the planting and harvesting of maize.[5] A tubrada includes feasting, ceremonial smoking of Nicotiana rustica, processions with fireworks, and dancing.[6]
Subsistence
[edit]Guarijío adapted farming to their dry climate and grow amaranth, beans, maize, and squash. They supplement these crops with wild plants harvested from the forest.[4]
See also
[edit]- Jean Bassett Johnson (1915–1944), American anthropologist who studied the Guarijío in the 1930s
- Wimmeria mexicana, a plant used by Guarijío people for medicinal tea
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- Lenguas indígenas y hablantes de 3 años y más, 2020 INEGI. Censo de Población y Vivienda 2020
- Yetman, David (2002). The Guarijios of the Sierra Madre: Hidden People of Northwestern Mexico. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. ISBN 978-0826322340.