Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL GROUPING SETS operator to generate multiple grouping sets.
Setup a sample table
Let’s set up a new table named inventory to demonstrate the functionality of the GROUPING SETS.
First, create a new table named inventory :
CREATE TABLE inventory (
warehouse VARCHAR(255),
product VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
model VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
quantity INT,
PRIMARY KEY (warehouse,product,model)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert data into the inventory table:
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Jose', 'iPhone','6s',100);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Fransisco', 'iPhone','6s',50);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Jose','iPhone','7',50);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Fransisco', 'iPhone','7',10);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Jose','iPhone','X',150);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Fransisco', 'iPhone','X',200);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Jose','Samsung','Galaxy S',200);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Fransisco','Samsung','Galaxy S',200);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Fransisco','Samsung','Note 8',100);
INSERT INTO inventory(warehouse, product, model, quantity)
VALUES('San Jose','Samsung','Note 8',150);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Third, query data from the inventory table:
SELECT
*
FROM
inventory;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Introduction to SQL GROUPING SETS
A grouping set is a set of columns by which you group using the GROUP BY clause. Normally, a single aggregate query defines a single grouping set.
The following example defines a grouping set (warehouse, product). It returns the number of stock keeping units (SKUs) stored in the inventory by warehouse and product.
SELECT
warehouse,
product,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
warehouse,
product;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The following query finds the number of SKUs by the warehouse. It defines the grouping set (warehouse):
SELECT
warehouse,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
warehouse;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)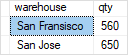
The following query returns the number of SKUs by the product. It defines the grouping set (product):
SELECT
product,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
product;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The following query finds the number of SKUs for all warehouses and products. It defines an empty grouping set ().
SELECT
SUM(quantity) qty
FROM
inventory;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
So far, we have four grouping sets: (warehouse, product), (warehouse), (product), and (). To return all grouping sets using a single query, you can use the UNION ALL operator to combine all the queries above.
The UNION ALL requires all result sets to have the same number of columns, therefore, you need to add NULL to the select list to of each query as shown below:
SELECT
warehouse,
product,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
warehouse,
product
UNION ALL
SELECT
warehouse,
null,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
warehouse
UNION ALL
SELECT
null,
product,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
product
UNION ALL
SELECT
null,
null,
SUM(quantity) qty
FROM
inventory;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
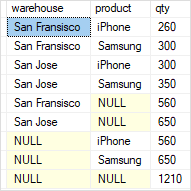

As you can see clearly from the output, the query generated a single result set with the aggregates for all grouping sets.
Even though the query works as expected, it has two main issues:
- First, the query is difficult to read because it is lengthy.
- Second, it has a performance issue because the database system has to scan the inventory table multiple times.
To resolve these issues, SQL provides us with the GROUPING SETS.
The GROUPING SETS is an option of the GROUP BY clause. The GROUPING SETS defines multiple grouping sets within the same query.
The following illustrates the general syntax of the GROUPING SETS option:
SELECT
c1,
c2,
aggregate (c3)
FROM
table
GROUP BY
GROUPING SETS (
(c1, c2),
(c1),
(c2),
()
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This query defines four grouping sets (c1,c2), (c1), (c2), and ().
You can apply the GROUPING SETS to rewrite the query with the UNION ALL clauses above:
SELECT
warehouse,
product,
SUM (quantity) qty
FROM
inventory
GROUP BY
GROUPING SETS(
(warehouse,product),
(warehouse),
(product),
()
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
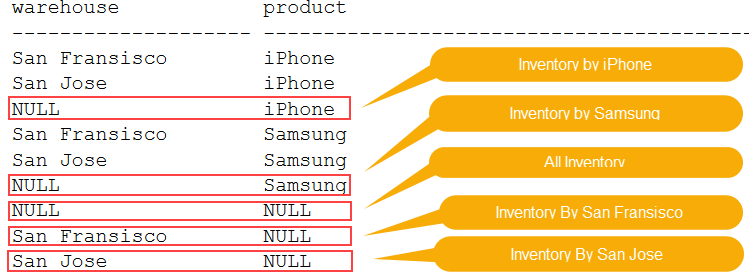

This query is more readable and performed faster than the query above because the database system does not have to read the inventory table multiple times.
Now, you should know how to use the SQL GROUPING SETS to generate multiple grouping sets using a single query.