Table of Contents
CaCO3 in Chemistry
Calcium carbonate or CaCO3 is One of the most well-known compounds in the field of chemistry. CaCO3 can be found as colorless crystals or as a white, odorless powder. There is a wide range of applications in chemistry as well as in commercial fields. It is located in the crust of the planet. It can also be found in a variety of materials, including marble, limestone, etc. In this article, we are going to learn more about CaCO3, its Properties, its preparation, Reaction, and uses.
CaCO3 Chemical Name
The chemical name of CaCO3 is Calcium carbonate. The most famous form of CaCO3 is limestone. Chalk, which is a type of CaCO3 is very common in classrooms. Calcite, Vaterite, and Aragonite are a few examples of pure calcium carbonate minerals. Snail shells, eggshells, oyster shells, and other biological sources of calcium carbonate. It can be found in a variety of materials, including marble, limestone, and more. Despite coming in various forms, they are chemically equivalent and only physically different from one another. They go by the name calcite as well.
CaCO3 Common Name- Calcium Carbonate common name
CaCO3 The Common and famous name of CaCO3 is limestone and Chalk.
CaCO3 Compound Name
The compound CaCO3 is commonly known as calcium carbonate.
CaO Common Name
Calcium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula CaO. It is commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime and is a white, caustic, and alkaline crystalline solid at room temperature. Calcium oxide is often used in various industrial applications, including as a desiccant, in the production of cement, and as a chemical reagent.
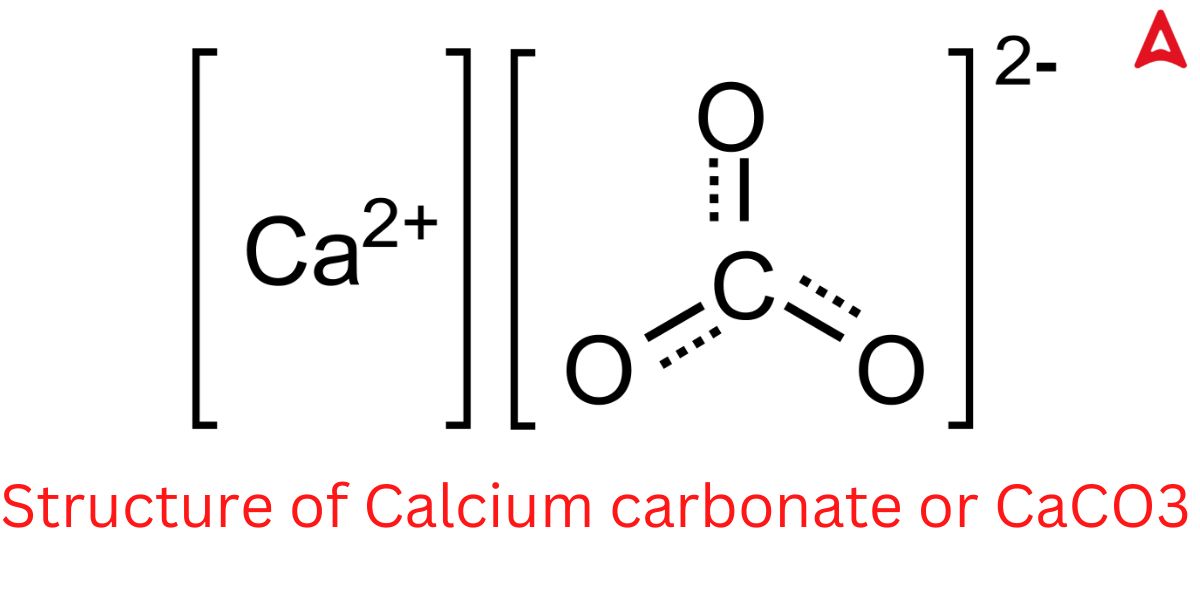
CaCO3 Structure
CaCo3 Structure is given below in this image. Check all Bonds of CaCo3
CaCo3 Molecular Weight
Calcium carbonate or CaCO3 has no smell. non-toxic and water-insoluble which occurs widely in rocks all throughout the planet. The white mineral CaCO3 is a naturally occurring component of chalks, limestones, and marbles. It is a typical material found in the minerals calcite and aragonite in rocks.
CaCO3 Molecular weight Calculation: Oxygen has an atomic mass of 16u, carbon has an atomic mass of 12u, calcium has an atomic mass of 40u,
The formula of CaCO3 has three Oxygen, one calcium, and one carbon atom. Hence the total molecular weight of CaCO3 =(40+12+16×3)= 40+ 48+12= 100 g/mol
CaCO3 has a molecular mass of 100 u or 100 g/mol.
Preparation of CaCO3
CaCO3 can be prepared in various ways.
1. Slaked lime and carbon dioxide are used as the raw components to produce CaCO3. Calcite is produced when carbon dioxide is allowed to pass through slaked lime.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
2. Calcium oxide is used to prepare calcium carbonate on a big scale for commercial application. After adding water to make calcium hydroxide, carbon dioxide is then filtered through the resulting solution. It is carried out to precipitate the necessary calcium carbonate.
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
3. Calcium chloride and sodium carbonate solutions are used to create calcium carbonate as an alternative method of producing CaCO3.
CaCl2+ Na2CO3→ CaCO3 + 2NaCl
Properties of CaCO3
The properties of Calcium Carbonate or CaCO3 are:
- Calcium Carbonate is a white, odourless powder with colourless crystals.
- The density of CaCO3 is 2.71 g/mL.
- CaCO3 has a 1,339 °C melting point.
- CaCO3 has a molecular weight of 100.0869 grammes per mole.
- Calcium carbonate breaks down into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide at a temperature of 1200 K.
- Calcium carbonate reacts with weak acids to form carbon dioxide.
- Due to the calcium ion’s presence, calcium carbonate is the salt of a strong base and a weak acid (due to the presence of the carbonate ion, usually derived from carbonic acid). As a result, this salt has a somewhat basic composition.
Reactions of CaCO3
1. As a byproduct of CaCO3 reaction with diluted acid, carbon dioxide is produced.Using this reaction, carbon dioxide is produced for use in chemicals or in the commercial sector,
CaCO3+H2SO4 → CaSO4+H2O+CO2
2. Calcium carbonate breaks down at 1200 K to produce calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaO + CO2 = CaCO3
3. When CaCO3 reacts with acids, carbon dioxide is released (technically, carbonic acid, but that quickly breaks down to CO2 and H2O:
CaCO3 + 2H+ = Ca2+ H2O+CO2
4. Carbon dioxide is produced when calcium carbonate reacts with dilute acids.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O +CO2
5. Calcium carbonate reacts with carbon dioxide-saturated water to produce soluble calcium bicarbonate.
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 ↔ Ca(HCO3)2↓
CaCO3 Uses
CaCO3 has a wide range of applications as follows
- CaCO3 is utilized in the construction of buildings and roads as aCaCO3 is a component of cement.
- CaCO3 is used as a building material (marble) in the construction industry.
- It is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry to make antacid pills from basic components.
- The main component of agricultural lime is calcium carbonate, which is produced when calcium ions in hard water combine with carbonate ions to form limescale.
- It is used in medicine to purify iron from iron ore and as an antacid or calcium supplement.
- Most of the businesses that use paper, paint, and pulp also use calcium carbonate.
- In water and wastewater treatment facilities, calcium carbonate is used to eliminate pollutants and acidity.