Intron
Intron je nukleotidna sekvenca unutar gena koja se uklanja putem RNK splajsovanja tokom formiranja finalnog RNK proizvoda.[1][2] Termin intron se odnosi na DNK sekvencu unutar gena, i odgovarajuću sekvencu RNK transkripta.[3] Sekvence koje se spajaju u finalnu maturiranu RNK nakon RNK splajsovanja su eksoni. Introni su prisutni u genima većine organizama i mnogim virusima. Oni se mogu naći u širokom nizu gena, uključujući one koji kodiraju proteine, ribozomsku RNK (rRNK), i transportnu RNK (tRNK). Tokom formirana proteina iz gena koji sadrže introne, dolazi do RNK splajsovanja nakon transkripcije i pre translacije.
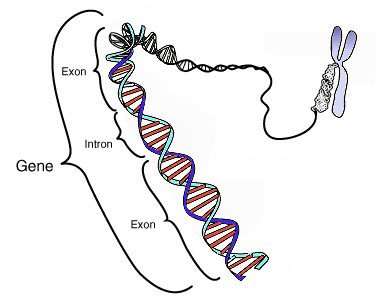
Reč intron je izvedena iz termina intrageni region, i.e. region unutar gena.
Reference
uredi- ↑ Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garlard Science. ISBN 0-8153-3218-1.
- ↑ Stryer, Lubert; Berg, Jeremy Mark; Tymoczko, John L. (2007). Biochemistry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-6766-X.
- ↑ Kinniburgh Alan, Mertz, J. and Ross, J. (July 1978). „The precursor of mouse β-globin messenger RNA contains two intervening RNA sequences”. Cell 14 (3): 681–693. DOI:10.1016/0092-8674(78)90251-9. PMID 688388.
Literatura
uredi- Stryer, Lubert; Berg, Jeremy Mark; Tymoczko, John L. (2007). Biochemistry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-6766-X.
- Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, and Peter Walter Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2007, ISBN 978-0-8153-4105-5. Fourth edition is available online through the NCBI Bookshelf: link
- Jeremy M Berg, John L Tymoczko, and Lubert Stryer, Biochemistry 5th edition, 2002, W H Freeman. Available online through the NCBI Bookshelf: link