Swan ganz intro
- 2. Why use the Pulmonary Artery Catheter? Gives Diagnostic information on critically ill patients… Helps diagnose the cause of hypotension Helps in fluid status maintenance Give critical cardiac function data
- 3. Equipment Swan-Ganz pulmonary artery catheter 2 Transducer set-ups: CVP PA Cardiac monitor Multiple waveforms Cardiac output capabilities
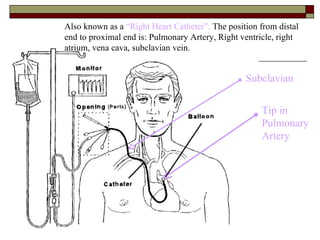
- 7. Also known as a “Right Heart Catheter”. The position from distal end to proximal end is: Pulmonary Artery, Right ventricle, right atrium, vena cava, subclavian vein. Subclavian Tip in Pulmonary Artery
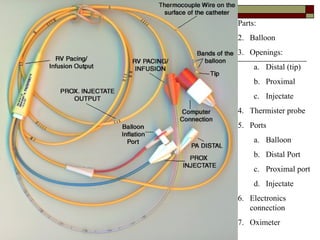
- 8. Parts: 2. Balloon 3. Openings: a. Distal (tip) b. Proximal c. Injectate 4. Thermister probe 5. Ports a. Balloon b. Distal Port c. Proximal port d. Injectate 6. Electronics connection 7. Oximeter
- 9. Information given by the “Swan” Pulmonary Artery (PA) Pressure Central Venous Pressure (CVP) Pressure Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP or “Wedge”) Cardiac Output (in Liters/minute) SVO2 Systemic Vascular Resistance Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Cardiac Index
- 10. Information given by the “Swan” This data can be subdivided into the following areas: Continuously Monitored Intermittently Monitored Derived by calculations
- 11. Information given by the “Swan” Continuously Monitored Parameters: Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PA) Central Venous Pressure (CVP) SvO2 Measurements recorded in “mmHg” These values are a measurement of the fluid pressure in the Pulmonary Artery, and Vena Cava respectively. These values are useful in quantifying and diagnosing cardiopulmonary disease.
- 12. Monitor showing continuously monitored PA and CVP
- 13. Also continuously monitored…. Although optional SvO2 Saturation of Venous Oxygen Measured in the Pulmonary Artery This reading is the Only TRUE mixed venous.
- 14. Intermittently monitored Pulmonary Capillary Wedge pressure (PCWP) Balloon is inflated, a pressure reading is taken, the balloon is deflated. Leaving the balloon inflated with INFARCT the lung!
- 15. Intermittently monitored, cont…. Cardiac output by “Thermo dilution” Cold fluid is injected into the “Injectate port” of the catheter. The temperature of the fluid is measured at two points by the thermistor on the catheter and calculated to cardiac output.
- 16. Calculations Systemic Vascular Resistance How hard is it get blood through the vascular system? Pulmonary Vascular Resistance How hard does the right heart have to work to get blood through the lungs and back to the left heart? Cardiac Index Careful! These calculations are subject to error!
- 17. The Measured Values CVP: Low pressure reading - ~5 mmHg PA: Systolic/diastolic- ~20/10 SvO2 ~75%
- 18. The intermittent values PCWP ~8 mmHg Cardiac Output: normally ~6 l/m