Patch Graft
- 1. Dr . Amar Karkhanis DNB,FRCS, MRCOphth Karkhanis Super-speciality Hospital Thane
- 3. Aim Tectonic Patch Grafts are performed in certain indicated sight threatening situations Reinforcement of thin or perforated sclera or Cornea, especially when the choroid is exposed, to prevent prolapse of ocular contents and secondary infection.
- 4. Advantages Readily available from donor eyes Can be easily preserved for months Strong, flexible, and easy to handle Sclera has a natural curvature allowing it to neatly blend with host sclera Avascular and is well tolerated with little inflammatory reaction
- 5. Indications Necrotizing scleritis following Pterygium surgery Trauma Infections Post Glaucoma Surgery Auto-immune disorders
- 6. Methods & Intervention 2 types of grafts: Full thickness: preferred for infective etiologies Lamellar: preferred for non infective situations Intervention : (1) removal of all devitalized or infected scleral tissue surrounding the melt (2) use of lamellar or full-thickness donor corneal/ scleral tissue, fashioned to fit the scleral defect exactly or a 0.25-mm diameter larger (3) placement of a pedicled conjunctival flap or AMG over the patch graft
- 7. Limbal Patch Grafts After measuring the corneal diameter the widest point of the lesion is measured A corneal rim is fashioned with the the help of 2 trephines or Free hand. Extent of lesions (schematic)
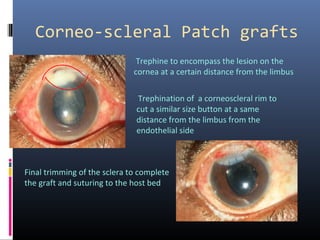
- 9. Corneo-scleral Patch grafts Trephine to encompass the lesion on the cornea at a certain distance from the limbus Trephination of a corneoscleral rim to cut a similar size button at a same distance from the limbus from the endothelial side Final trimming of the sclera to complete the graft and suturing to the host bed
- 10. Scleral Patch Grafts • Conjunctiva, Tenon's capsule, and episcleral tissue are dissected to expose the area of scleral defect. • After defining the borders of the surgical bed to be reinforced, the donor sclera graft is fashioned to the appropriate size and thickness. • The graft is then secured using 8-0 Vicryl sutures on the scleral side & 10-0 nylon sutures on the corneal side • The repaired sclera is then covered with a conjunctival flap or an amniotic membrane graft (AMG, using 10-0 nylon sutures.
- 12. Corneal patch grafts Effective in emergency situations Tissue loss in large corneal perforations
- 13. Conclusion Patch graft is a useful therapeutic option in emergency sight threatening situations of corneal or scleral thinning and perforations as Effectively restores the integrity of the eye Allows acceptable visual rehabilitation
- 14. Thank you