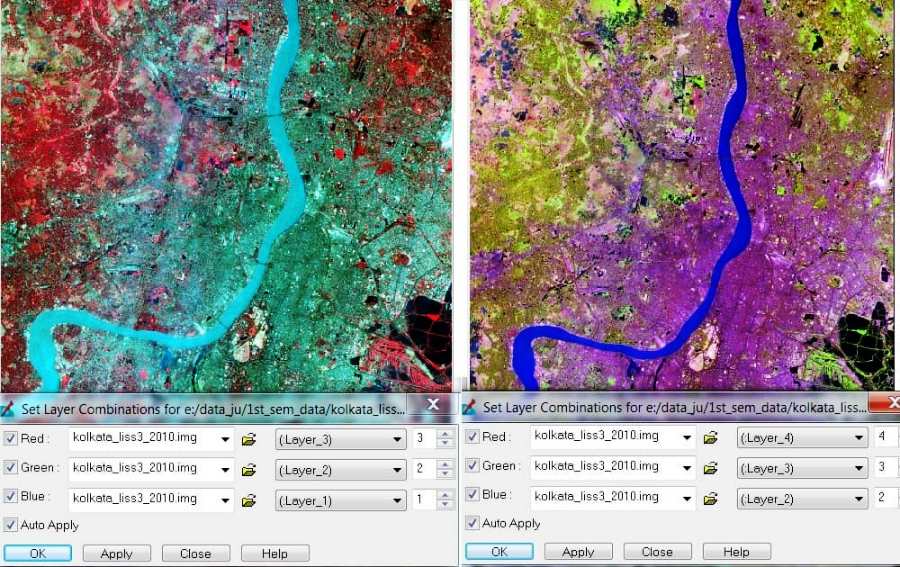
False Color Composite (FCC)
A false color satellite image is one in which the Red (R), Green (G), and Blue (B) values do not correspond to the true colors of red, green and blue. A standard False Color Composite (FCC) blue is assigned to green radiations (0.5 to 0.6 μm), green is assigned to red radiations (0.6 to 0.7 μm and red is assigned to Near Infrared radiation (0.7 to 0.8 μm).
In other words, a false color composite is a multi-spectral image interpretation using the standard visual RGB band range. FCC imagery can be produced using different color combinations. The choice of a color scheme depends on the type of objects that need to be emphasized in the image.
False Color Composite Vegetation
This false color composite scheme allows vegetation to be detected readily in the image. Vegetation appears in different shades of red depending on the types and conditions of the vegetation, since it has a high reluctance in the NIR band.
False Color Composite Band Combination
| FCC Band Combination (RGB) | Description |
|---|---|
| 4,3,2 | Standard “false-color” combination. Vegetation shows in red. |
| 3,2,1 | The “nature color” combination. It provides the most water penetrating. |

Four most common false-color band combinations are:
- Near infrared (red), green (blue), red (green). This is a traditional and popular band combination useful in seeing changes in plant health.
- Shortwave infrared (red), near infrared (green), and green (blue), often used to show foods or newly burned land.
- Blue (red), two different shortwave infrared bands (green and blue). We use this to differentiate between snow, ice, and clouds.
- Thermal infrared, usually shown in tones of gray to illustrate temperature.
Color Signatures on Standard False Color Composite of Surface Features
1. Healthy Vegetation and Cultivated Areas:
| Features | Color In Standard FCC |
|---|---|
| Evergreen | Red to magenta |
| Deciduous | Brown to red |
| Scrubs | Light brown with red patches |
| Cropped land | Pink to Bright red |
| Fallow land | Light blue to white |
| Wetland vegetation | Blue to grey |
2. Water body:
| Features | Color In Standard FCC |
|---|---|
| Clear water | Dark blue to black |
| Turbidity water body | Light blue |
3. Built up Area:
| Features | Color In Standard FCC |
|---|---|
| High density | Dark blue to bluish green |
| Low density | Light blue |
4. Waste lands/Rock outcrops:
| Features | Color In Standard FCC |
|---|---|
| Rock outcrops | Light brown |
| Sandy deserts/River sand/ | Light blue to white |
| Salt affected Deep ravines | Dark green |
| Shallow ravines | Light green |
| Water logged/Wet lands | Modeled black |
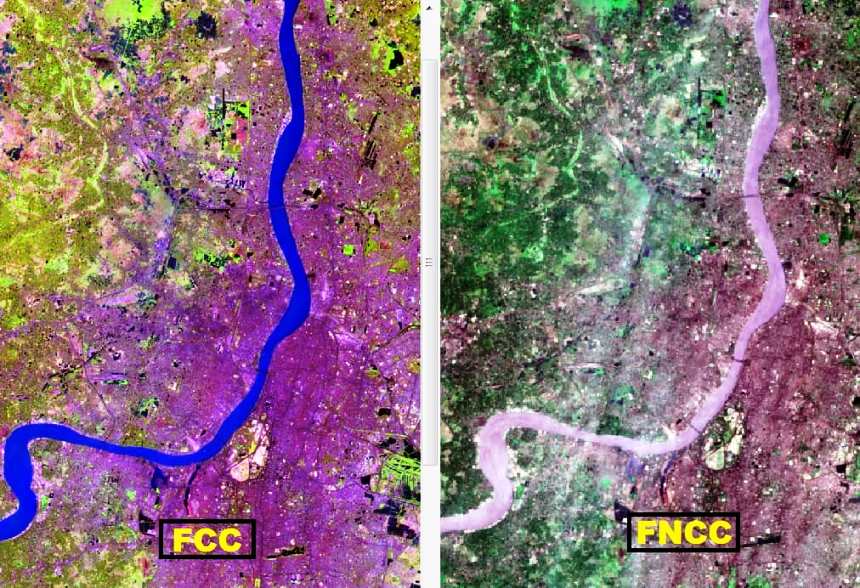
False Natural Color Composite (FNCC)
Some Sensors (SPOT, LISS-III, LISS-IV) do not capture the blue band, because of higher scattering problem. That means it’s not possible to generate true color composites.
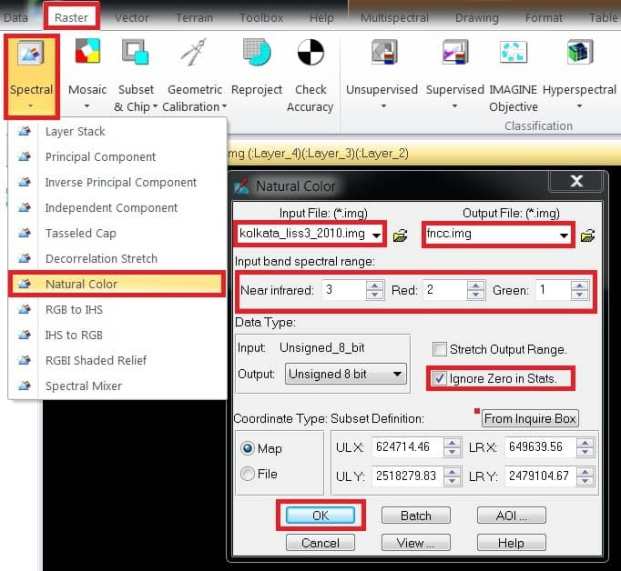
Perform FNCC
- Select Raster tab Resolution group choose Spectral click Natural Color.
- The Natural Color dialog opens, select your Input data file (e.g.- kolkata_2010_liss3).
- Choose your Output destination, and enter file name.
- Define the band spectral range, Near infrared-3, Red-2, Green-1.
- Check on the Ignore Zero in Stats checkbox.
- Finally click OK button to start this process.




Nice