2005 Kashmir earthquake: Difference between revisions
m replace links to deleted portals: Portal:Earthquakes → Portal:Earth sciences |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''2005 Kashmir earthquake''' occurred at {{tooltip|08:50:39 Pakistan Standard Time|03:50:39 GMT}} on 8 October in |
The '''2005 Kashmir earthquake''' occurred at {{tooltip|08:50:39 Pakistan Standard Time|03:50:39 GMT}} on 8 October in Pakistan-administered [[Azad Kashmir]]. It was [[epicenter|centered]] near the city of [[Muzaffarabad]], and also affected Pakistan's [[Khyber Pakhtunkhwa]] province and Indian-administered [[Jammu and Kashmir]]. It registered a [[moment magnitude scale|moment magnitude]] of 7.6 and had a maximum [[Mercalli intensity scale|Mercalli intensity]] of VIII (''Severe''). The earthquake also affected countries in the surrounding region where tremors were felt in [[Afghanistan]], [[Tajikistan]] and [[China|Chinese]] [[Xinjiang]]. The severity of the damage caused by the earthquake is attributed to severe upthrust. It is considered the deadliest earthquake to hit [[South Asia]] since the [[1935 Quetta earthquake]].<ref name="Dawn_Quetta_2005">{{cite web|url=http://www.dawn.com/2005/10/25/fea.htm|title=The great Quetta tragedy|publisher=[[Dawn (newspaper)|DAWN Newspaper]]|date=25 October 2008}}</ref> |
||
==Earthquake== |
==Earthquake== |
||
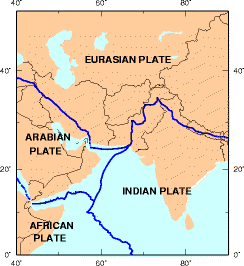
[[Kashmir]] lies in the area of collision of the [[Eurasian Plate|Eurasian]] and [[India Plate|Indian tectonic plates]]. The geological activity born out of this collision, also responsible for the birth of the Himalayan mountain range, is the cause of unstable [[seismicity]] in the region. The [[United States Geological Survey]] (USGS) measured its magnitude as a minimum of 7.6 on the [[moment magnitude scale]], with its epicentre about {{convert|19|km|mi|abbr=on}} northeast of Muzaffarabad, |
[[Kashmir]] lies in the area of collision of the [[Eurasian Plate|Eurasian]] and [[India Plate|Indian tectonic plates]]. The geological activity born out of this collision, also responsible for the birth of the Himalayan mountain range, is the cause of unstable [[seismicity]] in the region. The [[United States Geological Survey]] (USGS) measured its magnitude as a minimum of 7.6 on the [[moment magnitude scale]], with its epicentre about {{convert|19|km|mi|abbr=on}} northeast of Muzaffarabad, Azad Kashmir, and {{convert|100|km|mi|abbr=on}} north-northeast of the national capital [[Islamabad]]. |
||
===Damage=== |
===Damage=== |
||
[[File:earthquake Information for Pakistan.png|thumb|left|Map depicting regional tectonic plates]] |
[[File:earthquake Information for Pakistan.png|thumb|left|Map depicting regional tectonic plates]] |
||
Most of the devastation hit north Pakistan and Kashmir. In Kashmir, the three main districts were badly affected and Muzaffarabad, the state capital of |
Most of the devastation hit north Pakistan and [[Pakistan administered Kashmir]]. In Kashmir, the three main districts were badly affected and Muzaffarabad, the state capital of Pakistan-administered Kashmir, was hardest hit in terms of casualties and destruction. Hospitals, schools, and rescue services including police and armed forces were paralysed. There was virtually no infrastructure and communication was badly affected. More than 70% of all casualties were estimated to have occurred in Muzaffarabad. Bagh, the second-most-affected district, accounted for 15% of the total casualties. |
||
The Pakistani government's official death toll as of November 2005 stood at 87,350 although it is estimated that the death toll could reach over 100,000. Approximately 138,000 were injured and over 3.5 million rendered homeless. According to government figures, 19,000 children died in the earthquake, most of them in widespread collapses of school buildings. The earthquake affected more than 500,000 families. In addition, approximately 250,000 farm animals died due to collapse of stone barns, and more than 500,000 large animals required immediate shelter from the harsh winter. |
The Pakistani government's official death toll as of November 2005 stood at 87,350 although it is estimated that the death toll could reach over 100,000. Approximately 138,000 were injured and over 3.5 million rendered homeless. According to government figures, 19,000 children died in the earthquake, most of them in widespread collapses of school buildings. The earthquake affected more than 500,000 families. In addition, approximately 250,000 farm animals died due to collapse of stone barns, and more than 500,000 large animals required immediate shelter from the harsh winter. |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
===Aftershocks=== |
===Aftershocks=== |
||
There were many secondary earthquakes in the region, mainly to the northwest of the original epicentre. A series of strong aftershocks occurred near [[Muzaffarabad]].<ref>[http://archive.financialexpress.com/news/pak-in-panic-as-quake-rocks-kashmir/153050 "Pak in panic as quake rocks Kashmir"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208171252/http://archive.financialexpress.com/news/pak-in-panic-as-quake-rocks-kashmir/153050 |date=8 December 2015 }} Reuters, ''The Financial Express'', 19 October 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.</ref> As of 27 October 2005<ref>[http://www.reliefweb.int/rw/RWB.NSF/db900SID/KKEE-6HWRYR?OpenDocument "Pakistan: A summary report on Muzaffarabad earthquake"] ''ReliefWeb'', 7 November 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.</ref> there had been more than |
There were many secondary earthquakes in the region, mainly to the northwest of the original epicentre. A series of strong aftershocks occurred near [[Muzaffarabad]].<ref>[http://archive.financialexpress.com/news/pak-in-panic-as-quake-rocks-kashmir/153050 "Pak in panic as quake rocks Kashmir"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208171252/http://archive.financialexpress.com/news/pak-in-panic-as-quake-rocks-kashmir/153050 |date=8 December 2015 }} Reuters, ''The Financial Express'', 19 October 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.</ref> As of 27 October 2005<ref>[http://www.reliefweb.int/rw/RWB.NSF/db900SID/KKEE-6HWRYR?OpenDocument "Pakistan: A summary report on Muzaffarabad earthquake"] ''ReliefWeb'', 7 November 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.</ref> there had been more than 978 aftershocks with a magnitude of 4.0 and above that continued to occur daily. Since then, measurements from satellites have shown that mountain parts directly above the [[epicenter]] have risen by a few meters, giving ample proof that the rising of the Himalayas is still going on, and that this earthquake was a consequence of that.<ref>BBC series: ''Earth: The Power of the Planet.'', part 1. ''Volcano''</ref> |
||
==Response== |
==Response== |
||
Revision as of 03:38, 19 October 2019
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2015) |
| UTC time | 2005-10-08 03:50:40 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 7703077 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 2005-10-08 |
| Local time | 08:50 Pakistan Standard Time |
| Magnitude | 7.6 Mw [1] |
| Depth | 15 km (9.3 mi) [1] |
| Epicenter | 34°27′N 73°39′E / 34.45°N 73.65°E [1] |
| Type | Oblique-slip |
| Areas affected | Pakistan, India, Afghanistan |
| Max. intensity | VIII (Severe) [2] |
| Landslides | Yes [3] |
| Aftershocks | 5.9 Mw 8 Oct at 03:57 [4] 5.8 Mw 8 Oct at 03:58 [5] 6.4 Mw 8 Oct at 10:46 [6] |
| Casualties | 86,000–87,351 dead [7] 69,000–75,266 injured [7] 2.8 million displaced [7] |
The 2005 Kashmir earthquake occurred at 08:50:39 Pakistan Standard Time on 8 October in Pakistan-administered Azad Kashmir. It was centered near the city of Muzaffarabad, and also affected Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province and Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir. It registered a moment magnitude of 7.6 and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The earthquake also affected countries in the surrounding region where tremors were felt in Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Chinese Xinjiang. The severity of the damage caused by the earthquake is attributed to severe upthrust. It is considered the deadliest earthquake to hit South Asia since the 1935 Quetta earthquake.[8]
Earthquake
Kashmir lies in the area of collision of the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. The geological activity born out of this collision, also responsible for the birth of the Himalayan mountain range, is the cause of unstable seismicity in the region. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) measured its magnitude as a minimum of 7.6 on the moment magnitude scale, with its epicentre about 19 km (12 mi) northeast of Muzaffarabad, Azad Kashmir, and 100 km (62 mi) north-northeast of the national capital Islamabad.
Damage
Most of the devastation hit north Pakistan and Pakistan administered Kashmir. In Kashmir, the three main districts were badly affected and Muzaffarabad, the state capital of Pakistan-administered Kashmir, was hardest hit in terms of casualties and destruction. Hospitals, schools, and rescue services including police and armed forces were paralysed. There was virtually no infrastructure and communication was badly affected. More than 70% of all casualties were estimated to have occurred in Muzaffarabad. Bagh, the second-most-affected district, accounted for 15% of the total casualties.
The Pakistani government's official death toll as of November 2005 stood at 87,350 although it is estimated that the death toll could reach over 100,000. Approximately 138,000 were injured and over 3.5 million rendered homeless. According to government figures, 19,000 children died in the earthquake, most of them in widespread collapses of school buildings. The earthquake affected more than 500,000 families. In addition, approximately 250,000 farm animals died due to collapse of stone barns, and more than 500,000 large animals required immediate shelter from the harsh winter.
As Saturday is a normal school day in the region, most students were at schools when the earthquake struck. Many were buried under collapsed school buildings. Many people were also trapped in their homes and, because it was the month of Ramadan, most people were taking a nap after their pre-dawn meal and did not have time to escape. Reports indicate that entire towns and villages were completely wiped out in northern Pakistan, with other surrounding areas also suffering severe damage.

- "...a second, massive wave of death will happen if we do not step up our efforts now", Kofi Annan said on 20 October with reference to the thousand remote villages in which people are in need of medical attention, food, clean water and shelter and the 120,000 survivors that have not yet been reached."[9]
According to Pakistan's Interior Minister Aftab Ahmad Sherpao, Prime Minister Shaukat Aziz "made the appeal to survivors" on 26 October to come down to valleys and cities for relief,[10] because bad weather, mountainous terrain, landslides and blocked roads are making it difficult for relief workers to reach each house and the winter snows are imminent."
In Islamabad, the Margalla Towers, an apartment complex in sector F-10, collapsed and killed many of the residents. Four deaths were reported in Afghanistan, including a young girl who died in Jalalabad, after a wall collapsed on her. The quake was felt in Kabul, but the effects were minimal there.
Aftershocks
There were many secondary earthquakes in the region, mainly to the northwest of the original epicentre. A series of strong aftershocks occurred near Muzaffarabad.[11] As of 27 October 2005[12] there had been more than 978 aftershocks with a magnitude of 4.0 and above that continued to occur daily. Since then, measurements from satellites have shown that mountain parts directly above the epicenter have risen by a few meters, giving ample proof that the rising of the Himalayas is still going on, and that this earthquake was a consequence of that.[13]
Response

The national and international humanitarian response to the crisis was extensive. In the initial phases of response, the Pakistan Medical corps, Corps of Engineers, Army aviation and a large number of infantry units played important roles. Lt. Gen Afzal, Maj. Gen. Imtiaz, and Maj. Gen Javid were the leaders of their formations. Maj.Gen Farrukh Seir was in charge of foreign relief co-ordination. The relief work in Jammu and Kashmir was led by IAS officers of the state administration, Bashir Runyal and Jaipal Singh. In early 2006, the Government of Pakistan organized a donors' conference to raise money for reconstruction and development of the area. A total of $6.2 billion was pledged and a large amount of the money was delivered in terms of services of international NGOs with high pay scales. The rest of the money pledged, which was given to the Government of Pakistan for reconstruction and development, was used by a reconstruction authority called Earthquake Reconstruction and Rehabilitation Authority, which was made by then military regime to accommodate retired high military officials and while keeping the command of the reconstruction and rehabilitation authority directly under the military. The basic infrastructure, including tertiary care, health, education, road networks, water supply, waste management and other basic needs, was still underdeveloped and had not reached pre-earthquake status in the region. In 2008, Direct Relief had provided more than $14 million in assistance to local partners set to rebuild the healthcare infrastructure.[14]
Well over US$ 5.4 billion (400 billion Pakistani rupees)[15] in aid arrived from all around the world. Most of it coming from the United States which is calculated up to 70% of the total aid. US Marine and Army helicopters stationed in neighbouring Afghanistan quickly flew aid into the devastated region along with five CH-47 Chinook helicopters from the Royal Air Force that were deployed from the United Kingdom. Five crossing points were opened on the Line of Control (LOC), between India and Pakistan, to facilitate the flow of humanitarian and medical aid to the affected region, and aid teams from different parts of Pakistan and around the world came to the region to assist in relief.[16][17][18]
See also
- October 2015 Hindu Kush earthquake
- List of earthquakes in 2005
- List of earthquakes in Pakistan
- List of earthquakes in India
References
- ^ a b c ISC (2014), ISC-GEM Global Instrumental Earthquake Catalogue (1900–2009), Version 1.05, International Seismological Centre
- ^ USGS. "M7.6 - Pakistan". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ Bulmer, M.; Farquhar, T.; Roshan, M.; Akhtar, S. S.; Wahla, S. K. (2007), "Landslide hazards after the 2005 Kashmir earthquake", EOS, 88 (5): 53–68, Bibcode:2007EOSTr..88...53B, doi:10.1029/2007eo050001
- ^ USGS. "M5.9 - Pakistan". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ USGS. "M5.8 - Pakistan". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ USGS. "M6.4 - Pakistan". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ a b c USGS (4 September 2009), PAGER-CAT Earthquake Catalog (Earthquake ID 20051008035040), Version 2008_06.1, United States Geological Survey
- ^ "The great Quetta tragedy". DAWN Newspaper. 25 October 2008.
- ^ "Thousands at risk of starving in earthquake aid shortfall" The Times, 21 October 2005. Retrieved 24 February 2006.
- ^ Qayum, Khalid (26 October 2005), Pakistan Asks Quake Survivors to Leave Mountains Before Winter, Bloomberg News
- ^ "Pak in panic as quake rocks Kashmir" Archived 8 December 2015 at the Wayback Machine Reuters, The Financial Express, 19 October 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.
- ^ "Pakistan: A summary report on Muzaffarabad earthquake" ReliefWeb, 7 November 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.
- ^ BBC series: Earth: The Power of the Planet., part 1. Volcano
- ^ Hutain, Jenny (9 October 2008). "Direct Relief Aid Tops $14 Million on Pakistan Earthquake on 3yr Anniversary". Direct Relief. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- ^ Amr S. Elnashai (6 November 2006). "The Pakistan Earthquake of October 2005: A Reminder of Human-Science Interaction in Natural Disasters Risk Management". The Illinois International Review. Archived from the original on 17 May 2009. Retrieved 16 March 2009.
- ^ "Pakistan Asks Quake Survivors to Leave Mountains Before Winter" (Bloomberg News), 26 October 2005. Retrieved 24 February 2006.
- ^ "New figures put quake toll at more than 79,000" AP, MSNBC.com, 19 October 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.
- ^ "South Asia Earthquake: Fact Sheet #25 (FY 2006)" ReliefWeb, 17 November 2005. Retrieved 23 February 2006.
Further reading
- Pathier, E.; Fielding, E. J.; Wright, T. J.; Walker, R.; Parsons, B. E.; Hensley, S. (2006), "Displacement field and slip distribution of the 2005 Kashmir earthquake from SAR imagery" (PDF), Geophysical Research Letters, 33 (L20310): L20310, Bibcode:2006GeoRL..3320310P, doi:10.1029/2006GL027193
External links
- Television series 'Earthquake Diaries' on the rescue efforts
- The Earthquake and the U.S. Response – Institute for Policy Studies
- When The Earth Moved Kashmir – NASA Earth Observatory
- The Kashmir Earthquake of October 8, 2005: Impacts in Pakistan – Earthquake Engineering Research Institute
- The Earthquake of 8 October 2005 in northern Pakistan – George Pararas-Carayannis
- Remembering Oct 8, 2005: The day the earth shook – DAWN
- The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.
- ReliefWeb's main page for this event.
