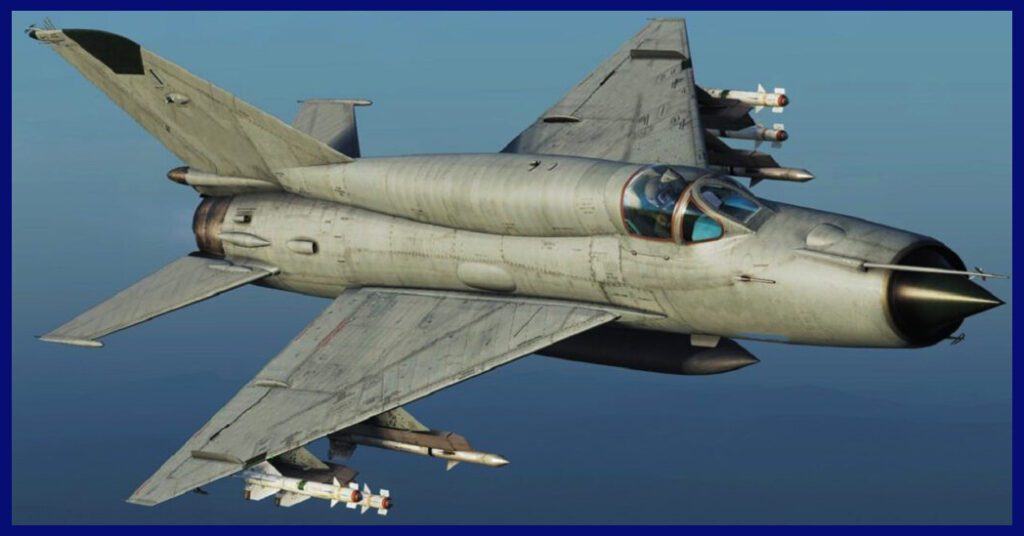
The evolution of aerial warfare has witnessed the emergence of exceptional weaponry, and among them stands the Vympel R-73 Archer – a short-range, highly capable Fox 2 category air-to-air missile, which has proven to be one of the world’s best missiles. It achieved this distinction by successfully downing a Pakistani F-16 in February 2019 with a single shot, without any miss. The modernization of Russian weapons is at its finest, as is customary.
Vympel R-73 Archer, in comparison to the most recent AIM-9 Sidewinder, was determined to be far more agile and capable in terms of seeker acquisition and tracking. This insightful comparison sparked the creation of more modern missiles like the ASRAAM, IRIS-T, and AIM-9X, aiming to enhance competitive capabilities.
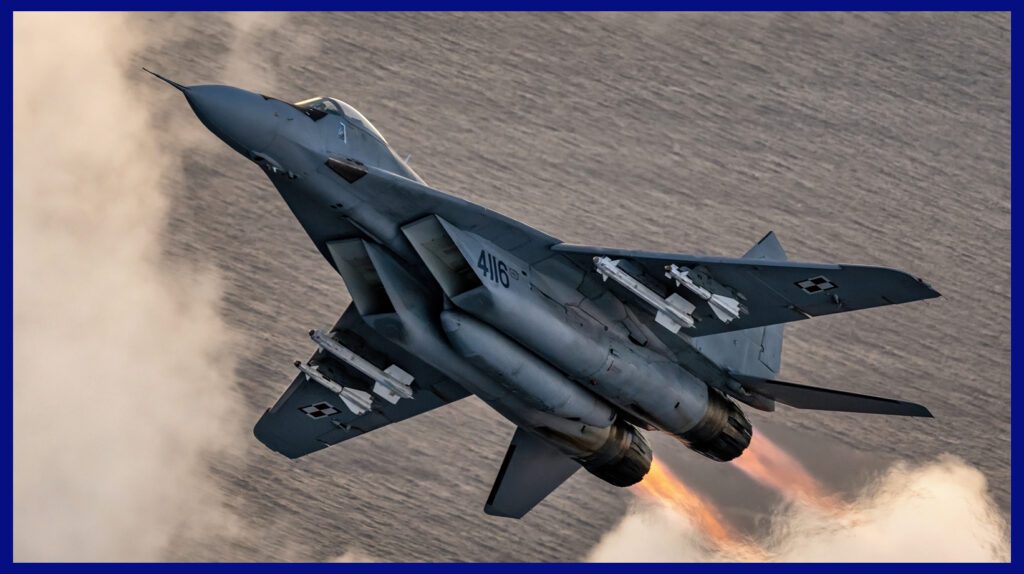


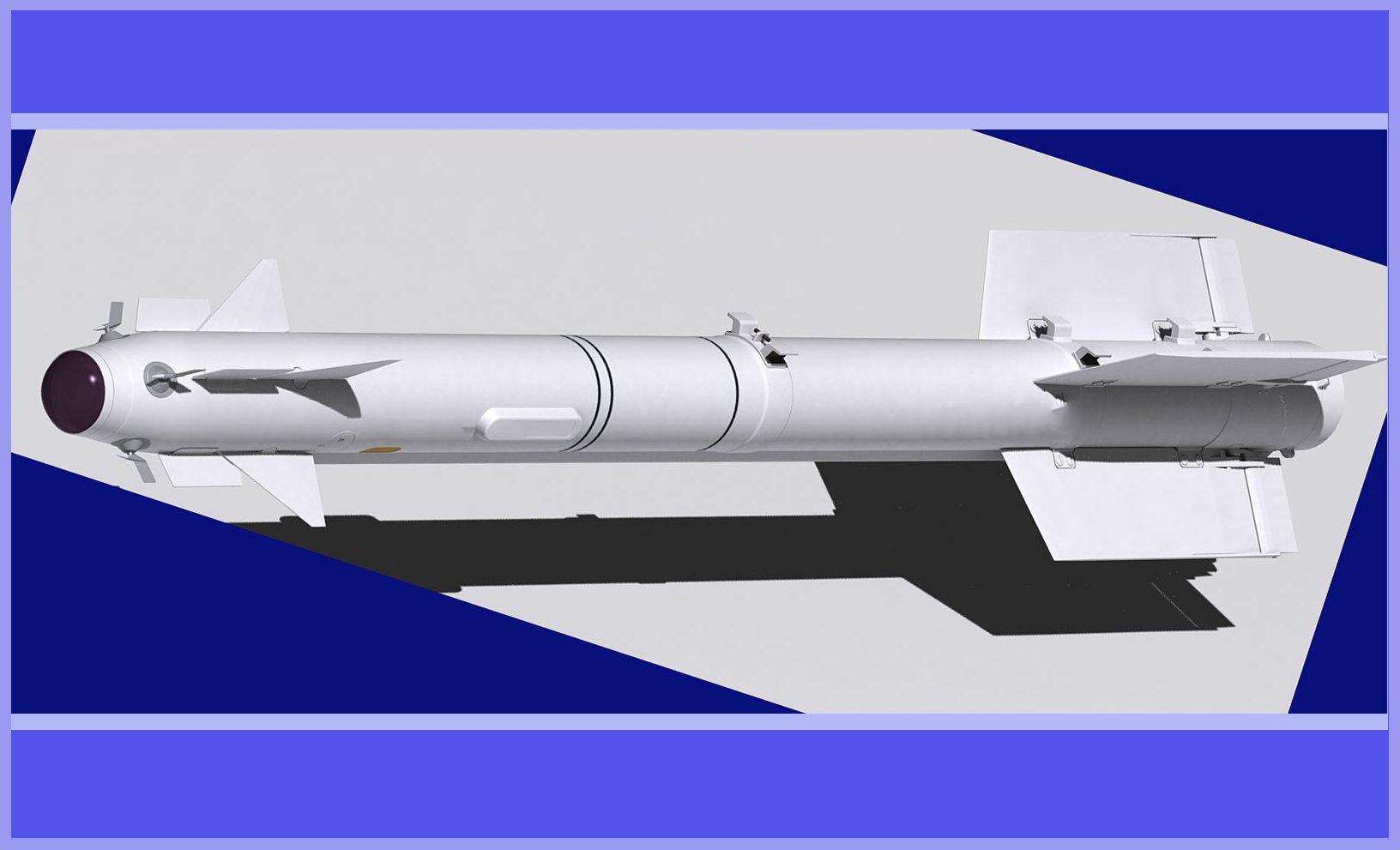
It is an advanced Fire-And-Forget (Fox 2) Missile system, meticulously designed to effectively take down both current and upcoming fighters, attack aircraft, bombers, helicopters, drones, and cruise missiles, encompassing even those executing intricate manoeuvres involving up to 12 g-forces. This cutting-edge system empowers the platform to seamlessly intercept a target from any conceivable angle, ensuring operational success regardless of prevailing weather conditions or the time of day, while remaining resilient against accidental and intentional jamming disruptions.
Advancements in the Development of the Vympel R-73 Missile
The R-73 was created to take the place of the older R-60 (AA-8 “Aphid”) armament for use by Soviet fighter aircraft at close range. The first missiles officially entered service in 1984 after work began in 1973 when it became operational.
Beginning in 1994, the R-73 was modified in manufacturing to the R-73M standard, which saw service in Russia in 1997. In addition to enhanced IRCCM ( Infrared Counter-Counter-Measures ), the R-73M has a longer range and a broader seeker angle ( to 60° off-boresight ). The R-74 and its export derivative RVV-MD are additional advancements. They are anticipated to supplement the R-73’s existing service variations.
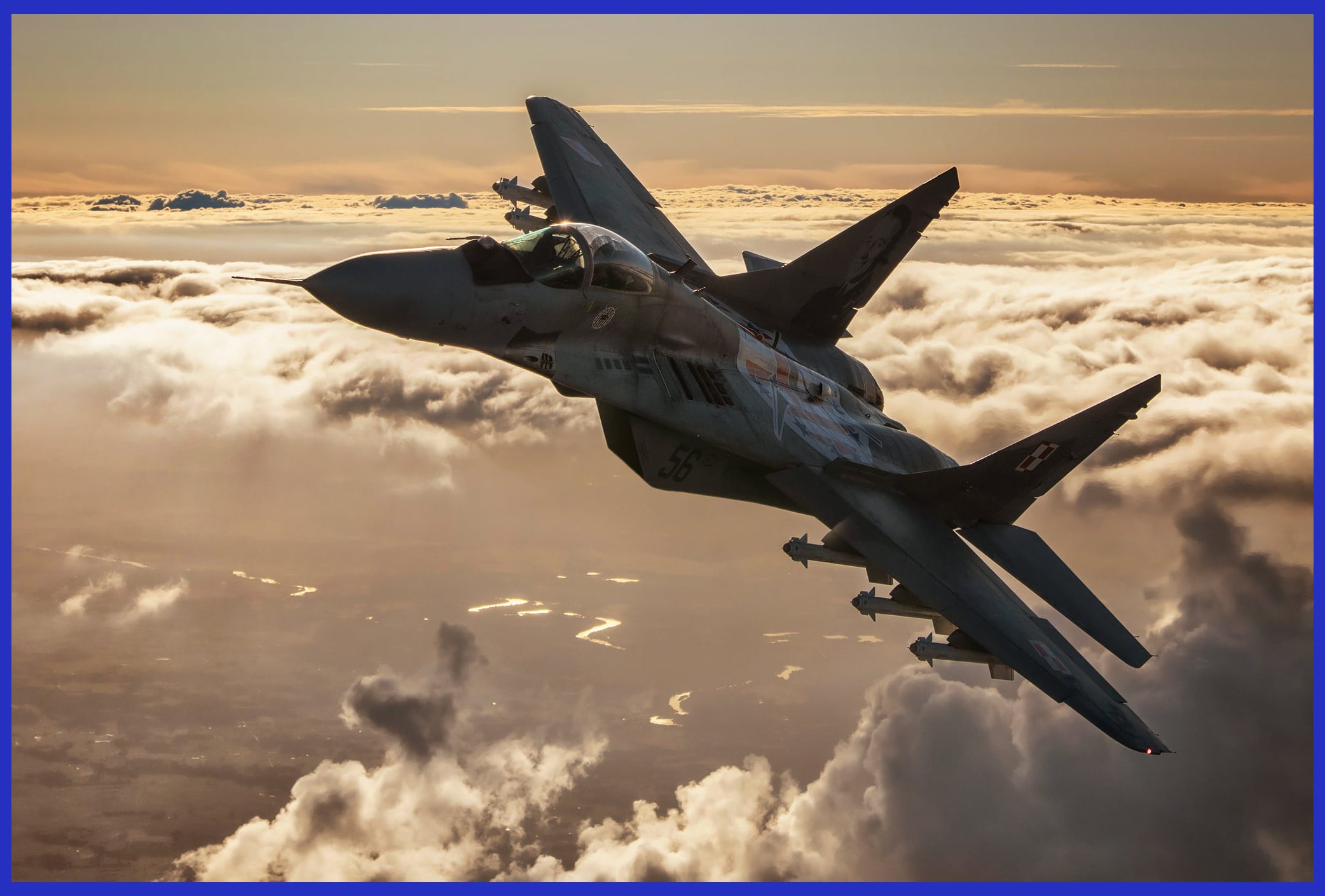


The R-73 missile features an infrared homing system that operates based on heat-seeking technology. This advanced missile incorporates a highly sensitive cryogenically cooled seeker, enhancing its performance. Notably, the missile boasts a significant “off-boresight” capability, enabling the seeker to detect targets positioned as much as 40 degrees away from the missile’s centerline. A remarkable feature of the R-73 is its compatibility with a helmet-mounted sight (HMS), which empowers pilots to designate targets by simply directing their gaze towards them.
The missile possesses a minimum engagement range of approximately 300 meters, while its maximum aerodynamic reach extends to nearly 40 km. This weaponry finds utilization across multiple aircraft models including the MiG-29, MiG-31, Su-27/33, Su-34, and Su-35. Additionally, it has also been equipped with upgraded variants of the MiG-21, MiG-23, Sukhoi Su-24, and Su-25 aircraft.


Later Generation Variations of the Vympel R-73 Missile
The family of later-generation Vympel R-73 missile variations encompasses a range of advanced models, each contributing unique capabilities to its arsenal. These variations include the R-73E, R-73M, R-74, RVV-MD, R-74M, R-74M2, and the SAMAR (Surface-to-Air Missile System), collectively expanding the missile’s effectiveness and versatility.
The K-74M, an upgraded version of the R-74, is designed for use on the MiG-35, MiG-29K/M/M2, Su-27SM, Su-30MK, and Su-35S and has fully digital and reprogrammable systems. The fifth-generation Sukhoi Su-57 aircraft is slated for a further upgrade called the K-74M2. This missile has a smaller cross-section to fit into weapon bays and will unquestionably perform similarly to the AIM-9X and ASRAAM. According to the most recent information, the K-MD will replace the K-74M2 in the future.
Out of all air-to-air versions, SAMAR is a Surface-to-Air Missile for Assured Retaliation, a short-range air defence system ( SAM system ) that has been developed by Indian Air Force ( IAF ), Base Repair Depot ( BRD ). In partnership with Simran Flowtech Industries and Yamazaki Denki.


The SAMAR Air Defense system, which has been approved for induction, consists of refurbished Russian-supplied Vympel R-73E infrared-guided air-to-air missiles (AAMs) that have been reprogrammed to be employed as Surface to Air short range Air Defence systems. A unique & distinctive idea to utilise the huge stock of missiles for air defence.
The SAMAR Air Defense system, which was displayed recently at Aero India 2023, has successfully completed all firing trials and can engage low-flying aerial targets from UAVs, helicopters, and fighter jets at a distance of 12 km.
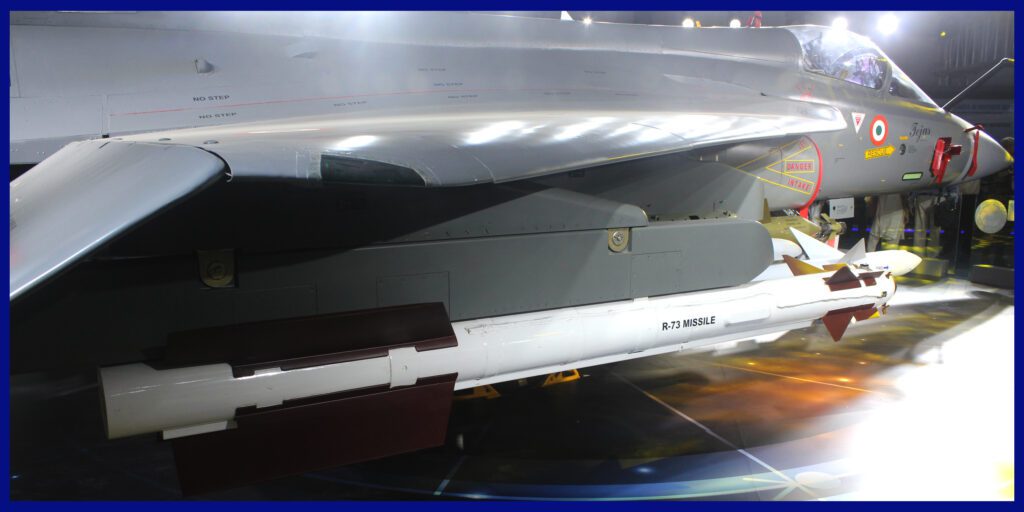
The Indian Air Force (IAF) currently possesses thousands of Vympel R-73E missiles in its inventory. These missiles are well-suited for potential deployment in a new role as a short-range air defence system. However, it’s worth noting that these missiles have now reached the end of their operational lifespan for use on fighter jets and cannot be employed safely in that capacity.


The Vympel R-73: A History of Operations
- A MiG-29UB from the Cuban Air Force shot down two Cessna 337s on February 24, 1996.
- In the course of the Eritrean-Ethiopian War, which took place between May 1998 and June 2000, R-73 missiles were actively employed in combat by Ethiopian Su-27s and Eritrean MiG-29s. Notably, the primary air-to-air missiles utilized during this conflict were the IR-homing R-60 and the R-73, responsible for the majority of aerial victories, with just two exceptions.
- On March 18, 2008, a Russian Air Force MiG-29 Fulcrum successfully intercepted a Georgian Hermes 450 UAV flying over Abkhazia. The MiG-29 effectively neutralized the UAV by launching an R-73 missile.
- During the critical 2019 airstrikes in Jammu and Kashmir, an Indian Air Force MiG-21 Bison demonstrated exceptional prowess by successfully engaging and ultimately bringing down a Pakistani F-16, a formidable 4th-generation fighter. In the face of substantial electronic countermeasures (ECM) employed by the opposition, the MiG-21’s cutting-edge helmet-mounted sight (HMS) empowered the pilot to execute a precise, one-shot takedown of the highly manoeuvrable F-16 Fighting Falcon.
- Colonel Igor Bedzay, the deputy commander of the Ukrainian Navy, perished on May 7, 2022, when a Russian Su-35 shot down his Mi-14. The Su-35 reportedly resorted to releasing an R-73 after missing its first shots with its 30 mm cannon, which ended up destroying the helicopter.


The Vympel R-73 Missile Specifications
- Weight: 105 kg ( 231 lb )
- Length: 9ft 7 in ( 2.93 m )
- Diameter: 6.5 in ( 165 mm )
- Warhead: 7.4 kg ( 16 lb )
- Detonation: InfraRed proximity fuse
- Engine: Solid propellant rocket
- Range: Min 300 m to Max 40 km
- Speed: Mach 2.5
- Guidance: Infrared homing and semi-active radar homing
- Launch Platform: All Russian Fighter aircraft. Including Indian-made HAL Tejas as well.


Moreover, don’t miss the golden opportunity to own an exquisite and awe-inspiring scale model of the MiG-21PMF fighter jet equipped with the Vympel R-73 Missile, conveniently available exclusively on AirModels. These remarkable and iconic military fighter jets boast an impeccable track record and are now available for purchase with worldwide delivery. Click here now to secure your piece before the limited stock is depleted.

In conclusion, the development and evolution of air-to-air missiles (AAMs) have played a pivotal role in shaping modern aerial warfare. These sophisticated weapons have evolved from early rudimentary designs to highly advanced and versatile systems, enabling fighter aircraft to engage and neutralize enemy threats with precision and effectiveness.
Over the years, AAMs have become integral components of air forces worldwide, contributing significantly to air superiority and national defence strategies. Their constant advancement in guidance systems, manoeuvrability, range, and lethality have made them formidable tools in the hands of fighter pilots.
Moreover, AAMs have been critical in maintaining the balance of power in conflicts and deterrence efforts, both at regional and global levels. Their ability to adapt to changing threat landscapes and technological advancements underscores their enduring importance on the modern battlefield.
As the development of AAMs continues, we can expect further innovations to enhance their capabilities, including improved sensors, stealth technologies, and networked integration into broader air defence systems. The future of air-to-air missiles promises to be a compelling chapter in the ongoing evolution of military technology, shaping the way nations protect their skies and assert their aerial dominance.


Important Announcement for Our Valued Readers!
After an article is published, it is possible that updates or changes may have occurred beyond the time of publication. Therefore, it is important to be aware that certain information in the article might be outdated. To ensure the most accurate analysis, it is highly recommended to verify the content with the latest sources available.
However, we are dedicated to delivering outstanding articles on military products and global updates. Maintaining quality and smooth operation requires resources. Your support sustains our efforts in providing insightful content. By purchasing high-quality products through our affiliated links, you help us keep our platform alive and acquire top-notch items. Your unwavering support is invaluable and inspires us to strive further.
We welcome your suggestions and requests for more information, as we value feedback from our readers. If there’s specific defence material or equipment not covered on our site, please share your request in the comments. We’ll strive to research and provide the required information. We sincerely thank you for your unwavering interest in our website, and we eagerly anticipate hearing from you! Enjoy your reading experience!
3 thoughts on “Vympel R-73 Archer”