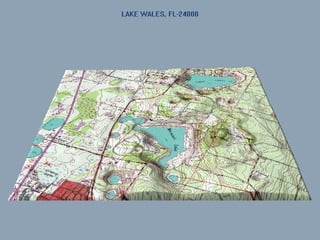
Karst Topography
- 2. Karst Topography A form of landform denudation based almost exclusively on carbonation (chemical weathering) Chemical weathering of joints and fractures can create huge subsurface cavities Requirements for formation [Note connection to hydrologic cycle] Water Limestone must be at least 80% calcium carbonate (CaCO3) Limestone must have a complex network of joints for water to pass through A zone of aeration (allows for water to flow) Vegetation cover providing different acids
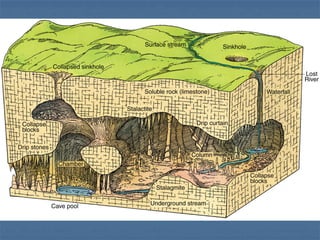
- 4. Features of Karst landscapes Sinkholes Caves and Caverns Poor surface drainage Disappearing surface streams Underground rivers
- 5. Sinkholes Depressions in the landscape Formed by water draining through a joint Doline: A sinkhole that intersects the water table, forming a small lake Collapse Sinkhole: sinkhole breaks through roof of Devil’s Sinkhole underlying cavern
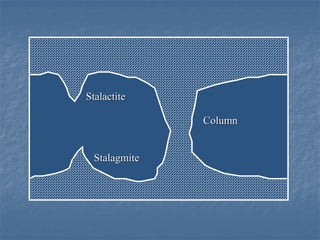
- 14. Caves and Caverns Caverns typically form near the water table, such that fluctuations in the level of the water table alternately inundate and drain them Phreatic zone Lowering of the water table (or uplift) later keeps them drained Dripstone: stalactites, stalagmites, columns
- 16. Stalactite Column Stalagmite

![Karst Topography
A form of landform denudation based almost
exclusively on carbonation (chemical
weathering)
Chemical weathering of joints and fractures can create
huge subsurface cavities
Requirements for formation [Note connection
to hydrologic cycle]
Water
Limestone must be at least 80% calcium carbonate
(CaCO3)
Limestone must have a complex network of joints for
water to pass through
A zone of aeration (allows for water to flow)
Vegetation cover providing different acids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/karsttopography-091115010604-phpapp01/85/Karst-Topography-2-320.jpg)