Red Lesions #1.pptx
- 1. Dr. Hidayah Elyas Lecture 1 :- Red Diseases of Oral Cavity Napata Collage Dentistry program Oral Medicine Semester (9)
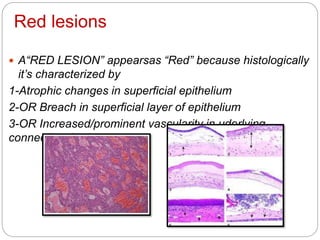
- 2. Red lesions A“RED LESION” appearsas “Red” because histologically it’s characterized by 1-Atrophic changes in superficial epithelium 2-OR Breach in superficial layer of epithelium 3-OR Increased/prominent vascularity in uderlying connective tissue
- 3. Causes Of Oral Red Lesions 1. Oral ulcers 2. Mucosal inflammation 3. Reactive lesions 4. Atrophy 5. Purpura 6. Vascular anomalies 7. Neoplasms
- 4. Mucosal Inflammation Viral infections Fungal infections Radiation induced mucositis Chemotherapy induced mucositis Immunological reactions
- 5. Denture stomatitis (Chronic Atrophic Candidiasis) Inflammation (manifesting as erythema) of mucosa beneath denture. Usually maxillary. Management:- Cure any underlying systemic problem Chances of getting infection are increased if denture worn for 24 hours a day. Dentures should be left out of mouth at night, cleaned & disinfected by placing in antiseptic denture cleanser (Milton’s Solution).
- 6. Denture stomatitis (Chronic Atrophic Candidiasis) A discoloring agent e.g; Rayner’s Blue Solution to see whether you are cleaning denture thoroughly Mucosal infection is eradicated by 1-Brushing palate 2-Using antifungals for 4 weeks. Effective agents include Nystatin or Miconazole oral gel administered concurrently with Chlorhexidine mouthwash
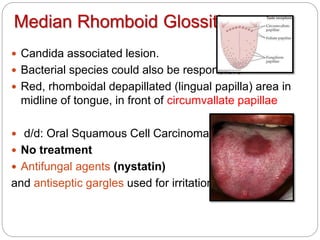
- 7. Median Rhomboid Glossitis Candida associated lesion. Bacterial species could also be responsible Red, rhomboidal depapillated (lingual papilla) area in midline of tongue, in front of circumvallate papillae d/d: Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma No treatment Antifungal agents (nystatin) and antiseptic gargles used for irritation
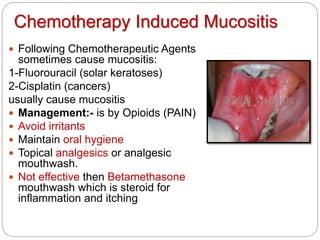
- 8. Chemotherapy Induced Mucositis Following Chemotherapeutic Agents sometimes cause mucositis: 1-Fluorouracil (solar keratoses) 2-Cisplatin (cancers) usually cause mucositis Management:- is by Opioids (PAIN) Avoid irritants Maintain oral hygiene Topical analgesics or analgesic mouthwash. Not effective then Betamethasone mouthwash which is steroid for inflammation and itching
- 9. Radiation mucositis Occurs usually within 3 Weeks of irradiation by Radiation Therapy of Head & Neck Tumors. Clinically presents as “Mild Erythema” to “Deep Mucosal Ulceration”. In advance stage Ulcers are covered by Pseudomembrane. Management is by opoids (morphine & hydromorphone), Avoid irritants (smoking, spicy food & alcohol) Maintain good oral hygeine Topical analgesics (lidocaine) Amifostine 200mg /day Prevents xerostomia healing of the mucosa usually starts to take place within 3 weeks of end of radiotherapy
- 10. Mucositis due to Immunological Reaction Following are some Autoimmune Conditions which can induce Mucositis: 1. Plasma cell gingivostomatitis 2. Granulomatous disorders (wegener’s granulomatosis) 3. Amyloidosis 4. Graft versus host disease (GVHD)
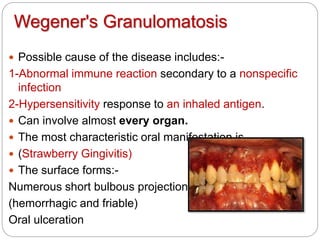
- 11. Wegener's Granulomatosis Possible cause of the disease includes:- 1-Abnormal immune reaction secondary to a nonspecific infection 2-Hypersensitivity response to an inhaled antigen. Can involve almost every organ. The most characteristic oral manifestation is (Strawberry Gingivitis) The surface forms:- Numerous short bulbous projections (hemorrhagic and friable) Oral ulceration
- 12. Wegener's Granulomatosis Investigation:-Cytoplasmic localization (c-ANCA) is useful The drugs of choice are :- 1. Cyclophosphamide with Glucocorticoids 2. (suppress immune reaction) 3. Cytoplasmic antineutrophil 4. Cytoplasmic antibodies
- 13. NOTE Cyclophosmamide Is an alkylating agent used for treatment of:- 1-Cancer 2-Auto-immune Diseases But it has Life Threatening Adverse Effects such as:- 1-Acute Myeloid Leukemia, 2-Bladder Cancer 3-Permanent Infertility if given in high doses
- 14. Lichenoid Reaction in GVHD(Graft versus host disease) Graft causing damaged immune response against the recipient Allogenic bone marrow transplant. Mucosal lesions more common in chronic GVHD.. Lichenoid Reactions (widespread as comp to Lichen Planus).. Painful Erythema, Mucosal Ulceration, Oral Purpura. May be associated with infections such as Candidiasis & HSV Infection or with Xerostomia Treatment Oral Hygiene Measures, Analgesics, Immunosuppressant's such as CICLOSPORIN , Non-astringent Mouthwash, Nystatin Mouthwash incase of fungal infections, Saliva Supplements and Pilocarpine (Recovery after 1 year post transplant)
- 15. Lupus Erythematosus Auto-immune More common in women (20-40 yrs). Triggered by sun exposure, drugs hormones and chemicals Amongst others, two types: DLE and SLE ORAL LESIONS comprise of White Striae with a Radiating Pattern, and these may terminate toward the center of the lesions, which has Erythematous appearance Palatal Lesion can be purely Erythematous DLE has Butterfly like rashes on cheek and nose termed Malar rash SLE diagnosis requires four or more of the American College of Rheumatology criterias Management of Intraoral Lesions via Topical steroids with Anti-Fungal Therapy
- 16. Pemphigus Vulgaris Rare etiology: Penicillamine, which is a chelating agent that removes certain materials from the blood ▪ ACE inhibitors, which are a type of blood pressure medication ▪ Systemic treatment includes: ▪ An anti-inflammatory drug called dapsone. ▪ Corticosteroids. ▪ Medicines containing gold. ▪ Medicines that suppress the immune system (such as cyclosporine)
- 17. Thank you