BPAD
- 1. BPAD- CURRENT EPISODE OF MANIA WITH PSYCHOTIC SYMPTOMS CASE PRESENTATION ON JOANN REBEKAH VARGHESE PHARM D
- 2. •Bipolar disorder (BD), also known as manic-depression, is a common, chronic and often severe cyclic mood disorder characterised by recurrent fluctuations in mood, energy and behaviour. •Bipolar Disorder is a lifelong illness with a variable course and requires both non pharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments for mood stabilisation . Bipolar disorder
- 3. •The exact aetiology of bipolar disorder is unknown. Bipolar disorder is thought to be a complex genetic disease that is environmentally influenced and caused by a wide range of neurobiologic abnormalities. •Stressful life events, alcohol or substance use, and changes in the sleep-wake cycle can elicit the expression of genetic or biologic vulnerabilities that cause dysregulation of neurotransmitters, neuroendocrine pathways, and second messenger systems. Etiology
- 4. •Many theories have been proposed regarding the pathophysiology of mood disorders. Family, twin, and adoption studies report an increased lifetime prevalence risk of having mood disorders among first-degree relatives of patients with bipolar disorder. •Genetic linkage studies suggest multiple gene loci can be involved in the heredity of mood disorders. • Environmental or psychosocial stressors, nutritional deficiencies, infections, immunologic reactions, sleep deprivation, and disruption of circadian rhythms can cause dysregulation in neurotransmitters, hormones, endocrine function, neuropeptides, cations, intracellular second messengers, and signal transduction pathways. Pathophysiology
- 5. SECONDARY CAUSES OF MANIA •Medical conditions that cause mania •Medications that cause mania •Somatic therapies that induce mania
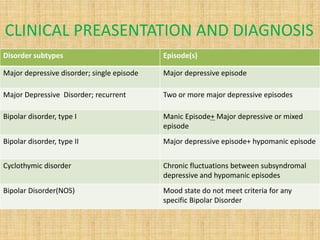
- 6. CLINICAL PREASENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS Disorder subtypes Episode(s) Major depressive disorder; single episode Major depressive episode Major Depressive Disorder; recurrent Two or more major depressive episodes Bipolar disorder, type I Manic Episode+ Major depressive or mixed episode Bipolar disorder, type II Major depressive episode+ hypomanic episode Cyclothymic disorder Chronic fluctuations between subsyndromal depressive and hypomanic episodes Bipolar Disorder(NOS) Mood state do not meet criteria for any specific Bipolar Disorder
- 7. DSM-IV-TR Criteria for a Manic Episode 1. A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting ≥1 week (or of any duration if hospitalization is necessary). 2. During the period of mood disturbance, at least three of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) and have been present to a significant degree: • Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity • Decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) • More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking. • Flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing distractibility (i.e., attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant external stimuli) • Increase in goal-directed activity (either social, at work, at school,
- 8. •Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a high potential for painful consequences (e.g., the person engages in unrestrained buying sprees, sexual indiscretions, or foolish business investing) 3. The symptoms do not meet the criteria for a mixed episode. 4. The mood disturbance is sufficiently severe to cause marked impairment in occupational functioning or in usual social activities or relationships with others, or to necessitate hospitalization to prevent harm to self or others, or there are psychotic features. 5. The symptoms are not caused by the direct physiologic effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication, or other treatment) or a general medical condition (e.g., hyperthyroidism).
- 9. PATIENT DEMOGRAPHIC DETAILS PATIENT NAME:XYZ AGE: 26 YEARS SEX:MALE IP NO: 25499 DEPARTMENT:PSYCHIATRY DOA: 3-8-2015 DOD: 9-8-2015
- 10. Reason for admission Decreased need for sleep since 2months, increased activity (work) since 2 months, talking about big plans and getting irritated since 15 days
- 11. Past medical history •H/o reduced sleep, big ambitions and plans, increased talkativeness and sexual interest. •H/o sadness, reduced talking to people, weeping episodes, fearfulness, lack of interest at work . •On medications: lithium and olanzapine since 3 years.
- 12. Family History Married since 7 years, has no children History of present illness Patient was apparently alright about 2 months back and was working at Gujarat. He started to sleep very little and work day and night. He has been very happy since 30 days and started to spend excess money and he is thinking that he is getting a job in an interview and is paid lakhs of rupees higher than his current payment. He also has dreams about Bagalkot to make it a big city. Habits Tobacco(+)
- 13. General physical examination Patient is conscious, cooperative and oriented to time, place and person . Afebrile . Pulse: 98bpm . BP: 132/80mmHg
- 14. Speech: Tone, Tempo, Volume, Increased spontaneity Mood: Happy Reactivity: Mobility: MENTAL STATE EXAMINATION
- 15. Systemic examination: CVS: S1,S2 Heard, no murmur RS: NVBS (+) , No added sounds CNS: No FND P/A: Soft, non tender
- 17. PROVISIONAL DIAGNOSIS BPAD- CURRENT EPISODE OF MANIA WITH PSYCHOTIC SYMPTOMS
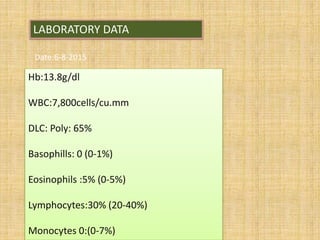
- 18. LABORATORY DATA Date:6-8-2015 Hb:13.8g/dl WBC:7,800cells/cu.mm DLC: Poly: 65% Basophills: 0 (0-1%) Eosinophils :5% (0-5%) Lymphocytes:30% (20-40%) Monocytes 0:(0-7%)
- 19. RBC: 4.38 millions/cu.mm ( 4.6-4.8 milloins/cu.mm) PLATELETS: 3,82,000(1,50,000- 4,50.000/cu.mm) RBS: 118mg/dl S. Lithium: 0.21mmol/l (0.60-1.20)
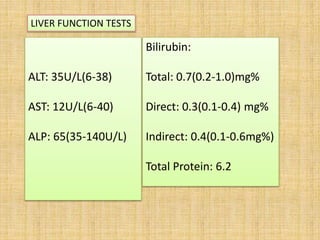
- 20. ALT: 35U/L(6-38) AST: 12U/L(6-40) ALP: 65(35-140U/L) Bilirubin: Total: 0.7(0.2-1.0)mg% Direct: 0.3(0.1-0.4) mg% Indirect: 0.4(0.1-0.6mg%) Total Protein: 6.2 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
- 21. Serum Electrolytes Sodium : 131mEq/L (135-147mEq/L) Potassium 3.5mEq/L (3.5-5.2mEq/L) Chlorides 106mEq/L (95-107mEq/L) Calcium 9.0mg/dl(8.8-10.2mg/dl) Magnesium: 1.9 mg/dl(1.8-2.9)
- 22. S. T3 107ng/dl (60-200) S.T4 : 10.8µgm/dl (4.0-12.0) TSH: 1.69 micro units/ml(0.25-4.30) THYROID FUNCTION TESTS
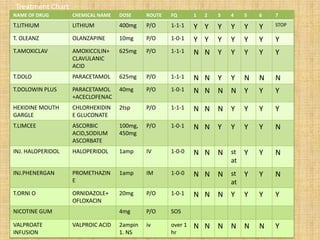
- 23. NAME OF DRUG CHEMICAL NAME DOSE ROUTE FQ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 T.LITHIUM LITHIUM 400mg P/O 1-1-1 Y Y Y Y Y Y STOP T. OLEANZ OLANZAPINE 10mg P/O 1-0-1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y T.AMOXICLAV AMOXICCILIN+ CLAVULANIC ACID 625mg P/O 1-1-1 N N Y Y Y Y Y T.DOLO PARACETAMOL 625mg P/O 1-1-1 N N Y Y N N N T.DOLOWIN PLUS PARACETAMOL +ACECLOFENAC 40mg P/O 1-0-1 N N N N Y Y Y HEXIDINE MOUTH GARGLE CHLORHEXIDIN E GLUCONATE 2tsp P/O 1-1-1 N N N Y Y Y Y T.LIMCEE ASCORBIC ACID,SODIUM ASCORBATE 100mg, 450mg P/O 1-0-1 N N Y Y Y Y N INJ. HALOPERIDOL HALOPERIDOL 1amp IV 1-0-0 N N N st at Y Y N INJ.PHENERGAN PROMETHAZIN E 1amp IM 1-0-0 N N N st at Y Y N T.ORNI O ORNIDAZOLE+ OFLOXACIN 20mg P/O 1-0-1 N N N Y Y Y Y NICOTINE GUM 4mg P/O SOS VALPROATE INFUSION VALPROIC ACID 2ampin 1. NS iv over 1 hr N N N N N N Y Treatment Chart
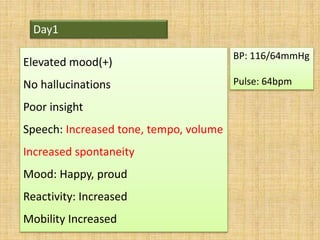
- 24. Day1 Elevated mood(+) No hallucinations Poor insight Speech: Increased tone, tempo, volume Increased spontaneity Mood: Happy, proud Reactivity: Increased Mobility Increased BP: 116/64mmHg Pulse: 64bpm
- 25. Day 1 Medication: T. Lithium T. Olanzapine
- 26. Day 2 NFC Improvement: 20% App: Good B/B: Regular Judgement: Impaired TREATMENT: APC BP: 130/90mmHg Pulse: 100bpm
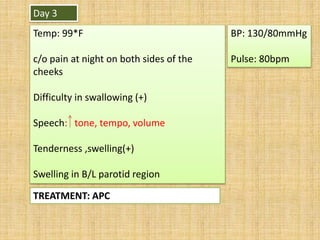
- 27. Day 3 Temp: 99*F c/o pain at night on both sides of the cheeks Difficulty in swallowing (+) Speech: tone, tempo, volume Tenderness ,swelling(+) Swelling in B/L parotid region TREATMENT: APC BP: 130/80mmHg Pulse: 80bpm
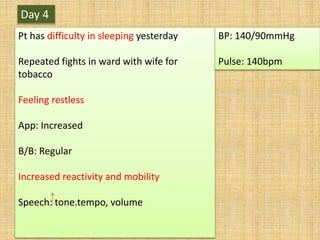
- 28. Day 4 Pt has difficulty in sleeping yesterday Repeated fights in ward with wife for tobacco Feeling restless App: Increased B/B: Regular Increased reactivity and mobility Speech: tone.tempo, volume BP: 140/90mmHg Pulse: 140bpm
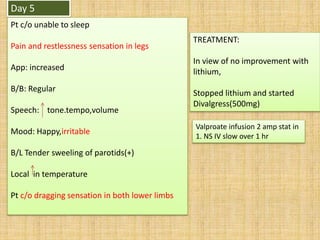
- 29. Day 5 Pt c/o unable to sleep Pain and restlessness sensation in legs App: increased B/B: Regular Speech: tone.tempo,volume Mood: Happy,irritable B/L Tender sweeling of parotids(+) Local in temperature Pt c/o dragging sensation in both lower limbs TREATMENT: In view of no improvement with lithium, Stopped lithium and started Divalgress(500mg) Valproate infusion 2 amp stat in 1. NS IV slow over 1 hr
- 30. Day 6 NFC Pt c/o pain in both Lower limbs and throat Afebrile TREATMENT: APC BP: 140/90mmHg Pulse 95bpm
- 31. Day 7 NFC Improvement: 50% Speech: tone, tempo , volume(n) Mood: happy Mobility: Increased Irritability reduced TREATMENT: APC BP: 140/90 mmHg Pulse 88bpm
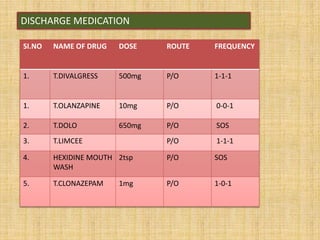
- 32. DISCHARGE MEDICATION SI.NO NAME OF DRUG DOSE ROUTE FREQUENCY 1. T.DIVALGRESS 500mg P/O 1-1-1 1. T.OLANZAPINE 10mg P/O 0-0-1 2. T.DOLO 650mg P/O SOS 3. T.LIMCEE P/O 1-1-1 4. HEXIDINE MOUTH WASH 2tsp P/O SOS 5. T.CLONAZEPAM 1mg P/O 1-0-1
- 33. PHARMACEUTICAL CARE PLAN SUBJECTIVE EVIDENCES •Decreased need for sleep since 2months •increased activity (work) since 2 months •talking about big plans and getting irritated since 15 days
- 34. ASSESSMENT BASED ON THE SUBJECTIVE EVIDENCES THE PATIENT WAS DIAGNOSED TO HAVE BPAD WITH CURRENT EPISODE OF MANIA WITH PSYCHOTIC SYMPTOMS
- 35. MONITORING PARAMETERS DISEASE SPECIFIC •Mood episodes •Suicidal ideation
- 36. •Medication adherence •Adverse effects •Thyroid function tests •S. Electrolytes •Renal function tests DRUGS SPECIFIC
- 37. Treatment Goals •Control of acute symptoms •Symptom remission •Return to normal level of functioning •Prevention of relapses •Reduction of suicide
- 38. TREATMENT OPTIONS GENERAL GUIDELINES •Assess for secondary causes of mania or mixed states (eg: alcohol or drug use) •Discontinue antidepressants •Taper of stimulants and caffeine if possible •Treat substance abuse •Encourage good nutrition, exercise, adequate sleep,stress reduction an psychosocial therapy.
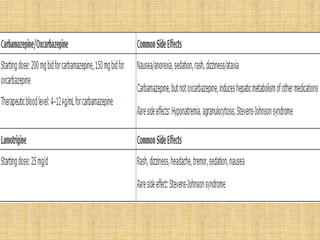
- 39. Pharmacological treatment of mania First, two or three drug combinations(lithium, valproate or SGA) plus a BZD ( loraepam or clonazepam) and/ or anti psychotic for short term adjunctive treatment of agitation or insomnia; lorazepam is recommended for catatonia Alternative: carbamazepine Second, if response is inadequate, consider a three drug combination: •Lithium plus an anticonvulsant plus an antipsychotuc •Anticonvulsant plus an anticonvulsant plus an antipsychotic Third, if response is inadequate, consider ECT for mania with psychosis or catatonia or add clozapine for treatment refractory illness
- 40. OTHER TREATMENTS... ELECTROCONVLSIVE THERAPY is a short term treatment for severe mania or depressive episodes , particularly when symptoms involve serious suicidal or psychotic symptoms or when medicines seem to be ineffective.
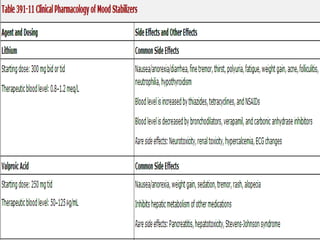
- 43. LITHIUM ADVERSE EFFECTS •GI Distress(nausea,vomiting,dyspepsia and diarrhoea), fine hand tremor, nephrogenic Diabetes insipidus, increased TSH levels, AV block, bradycardia. LITHIUM TOXICITY •>1.5mEq/L in blood. •Elderly pts have symptoms at their therapeutic level: GI Distress, tremor, dizziness, slurred speech, drowsiness, coma seizures, kidney damage.
- 44. GOALS ACHEVED •Improvement – 50% •Symptoms reduced
- 45. PHARMACIST INTERVENTION DRUG- DRUG INTERACTION HALOPERIDOL – LITHIUM Concurrent use of Lithium and Haloperidol may result in weakness, dyskinesias, Increased Extra pyramidal symptoms and brain damage.
- 46. PATIENT COUNSELLING ABOUT DISEASE Bipolar disorder is a relapsing mood disturbance with periods of both depressed and elevated mood, known as hypomania, or mania when severe. ABOUT DRUGS •Patient counseling that focuses on the medication's ability to prevent future episodes, especially the unwanted depressive episodes, and the negative financial, legal, and social consequences of manic episodes, is more effective than trying to convince a patient that a mood stabilizer will treat their euphoria, excessive optimism, and decreased need for sleep.
- 47. T. DIVALGRESS:Weight gain reported in patients with low or normal body mass index. Monitor platelets and liver function during first 3–6 months if evidence of increased bruising or bleeding. T. OLANZAPINE: Monitor for increased appetite with weight gain (primarily in patients with initial low or normal body mass index); monitor closely if rapid or significant weight gain occurs during early therapy; cases of hyperlipidemia and diabetes reported. T.CLONAZEPAM: BZDs cause minimal adverse effects compared with antipsychotics. They can cause CNS depression, sedation, dependence.
- 48. •Assess for secondary causes of mania or mixed states (eg: alcohol or drug use) •Taper of stimulants and caffeine if possible •Encourage good nutrition, exercise, adequate sleep.stress reduction and psychosocial therapy. LIFE STYLE MODIFICATIONS
- 49. THANK YOU