Tor Presentation
- 1. TOR An Onion Routing
- 2. Introduction Onion Routing(Tor) is a toolset for a wide range of organizations and people that want to improve their safety and security on the Internet. Tor can help you anonymize web browsing and publishing, instant messaging and other applications. . It also enables software developers to create new communication tools with built-in privacy features. and individuals to share information over public networks without compromising their privacy.
- 3. Objective of Onion Routing (Tor) The purpose of Onion Routing is to protect the anonymity of a user who wants to communicate over a network. It will hide the destinations of all communications initiated by the user. Any outside observers will not be able to tell whom the user is communicating with and for how long. To achieve this goal, the concept of Onion Routing has been introduced. Onion Routing aims to defend against traffic analysis , a form of network surveillance that threatens personal anonymity and privacy, confidential business activities and relationships, and state security.
- 4. For example, if you're travelling abroad and you connect to your employer's computers to check or send mail, you can inadvertently reveal your national origin and professional affiliation to anyone observing the network, even if the connection is encrypted.
- 5. Need For Onion Routing Using Onion Routing(Tor) protects you against a common form of Internet surveillance known as “traffic analysis”. Traffic analysis can be used to infer who is talking to whom over a public network. Knowing the source and destination of your Internet data, allows others to track your behavior and interests.
- 6. Internet data packets have two parts: a data payload and a header used for routing. The data payload is whatever is being sent, whether that's an email message, a web page, or an audio file. Even if you encrypt the data payload of your communications, traffic analysis still reveals a great deal about what you're doing and, possibly, what you're saying. That's because it focuses on the header, which discloses source, destination, size, timing, and so on.
- 7. A basic problem for the privacy minded is that the recipient of your communications can see that you sent it, by looking at headers. So can authorized intermediaries like Internet service providers, and sometimes unauthorized intermediaries as well. A very simple form of traffic analysis might involve sitting somewhere between sender and recipient on the network, looking at headers.
- 8. Use Of Onion Routing Here comes the need of services like Onion Routing.Onion Routing is a flexible communications infrastructure that is resistant to both eavesdropping and traffic analysis. Onion Routing prevents the transport medium from knowing who is communicating with whom -- the network knows only that communication is taking place. In addition, the content of the communication is hidden from eavesdroppers up to the point where the traffic leaves the OR network.
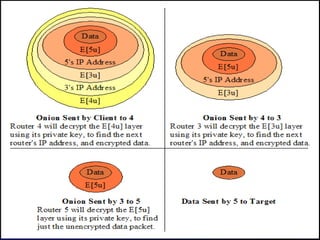
- 9. How Onion Routing Works Onion Routing instead of making a connection directly to a destination machine, builds an anonymous connection(route) through several other Onion Routers to the destination. Each Onion Router can only identify adjacent Onion Routers along the route. Before sending data over an anonymous connection, Onion Router first makes an Onion.An onion is a special data structure where the actual data to be travelled on the network is placed at its center and different encrypted layers are sorrounded by it.
- 10. This onion thus follows a specific route through the network.Each encrypted layer only contains the address of the next Onion Router in the route.Hence each Onion Router peels off the layer from the Onion in order to know the address of the next adjacent Onion Router to which the Onion is to be sent. So no router will ever know the full path that is travelled by the onion. Once the onion reaches its destination it will have been reduced to the original data packet. Since no outside observer will be able to follow an onion while it is traveling through an anonymous network, the communication is completely anonymous.
- 12. Data passed along the anonymous connection appears different at each Onion Router,in this way data can not be tracked in a route at any point.When the connection is broken, all information about the connection is cleared at each Onion Router. Onion Routing differs from other anonymity services in many ways:Communication is real-time and bidirectional; there is no centralized trusted component,because there is a network of routers.
- 13. If some how an outsider manages to enter the network of Onion Routers, he will only be able to see the last Onion Router and the next Onion Router to which Onion is to be sent. The absolute source and destination of the onion are still hidden. In this way Onion Routing protects its communications against traffic analysis attacks and makes it very hard for network observers (such as crackers, companies, and governments) to reliably see who is talking to whom and for what purpose.
- 14. Advance Implementation Of Onion Routing TOR is currently the most advanced implementation of Onion Routing in use today. Tor is currently deployed on the Internet.Tor design is actually based on the Onion Routing design & its concepts.
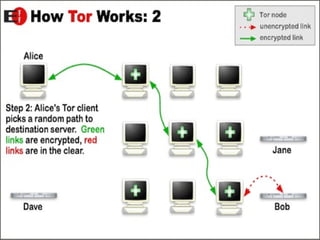
- 15. How Tor Works Tor uses the same method as of Onion Routing.It handles the problems like traffic analysis, by distributing your data over several places on the Internet, so no single point can link you to your destination. Instead of taking a direct route from source to destination, data packets on the Tor network take a random pathway through several servers that cover your tracks so no observer at any single point can tell where the data came from or where it's going.
- 16. To create a private network with Tor, the Tor software builds a circuit of encrypted connections through servers on the network. Each server along the way knows only which server gave it data and which server it is giving data to. No individual server ever knows the complete path that a data packet has taken. Once a circuit has been established, many kinds of data can be exchanged and several different sorts of software applications can be deployed over the Tor network.
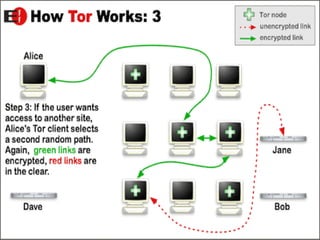
- 19. For efficiency, the Tor software uses the same circuit for connections that happen within the same minute or so. Later requests can be given to form a new circuit, to keep people from linking your earlier actions to the new ones.
- 21. Tor also makes it possible for users to hide their locations while offering various kinds of services. It allows Tor users to set up a website where people publish material without worrying about censorship. Nobody would be able to determine who was offering the site, and nobody who offered the site would know who was posting to it.
- 22. Tor VS Onion Routing Tor has proved to be far better than Onion Routing. There are main improvements of Tor over initial Onion Routing design. Currently Tor is a very good implementation of Onion Routing, ready to be used to protect anonymity and privacy of online communications. e.g., In the original Onion Routing, only the last router in a route can act as the destination point. Tor changes the concept slightly, allowing any router along the route to be an exit point. This means that an attacker observing the end of a circuit will have a harder time figuring out where the traffic goes.
- 23. In original Onion routing,a network of onion routers was automatically selected,while using the Tor software you can easily form a network of routers of your own choice by selecting them from the list of up-to-date routers on the network. The original Onion Routing design only protected the identity of an initiator of a connection. The responder was presumed to be with a well-known IP address. Thus the responder can be easily mapped to a person.
- 24. Users Of Tor Individuals use Tor to keep websites from tracking them and their family members, or to connect to news sites, instant messaging services. Tor's “Hidden Service” let users publish web sites and other services without needing to reveal the location of the site. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) use Tor to allow their workers to connect to their home website while they're in a foreign country, without notifying everybody nearby that they're working with that organization.
- 25. Uses A branch of the U.S. Navy uses Tor for open source intelligence gathering, and one of its teams used Tor while deployed in the Middle East recently. Law enforcement uses Tor for visiting or surveilling web sites without leaving government IP addresses in their web logs. To download Tor Software, visit http://tor.eff.org/