Pelvic injuries trauma 2012
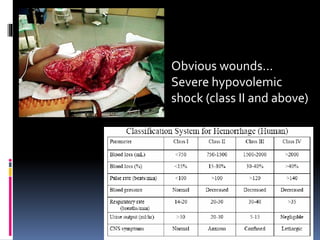
- 2. DEFINITION Injuries or fractures that involve the pelvis bone and structure Why important? Highest mortality in pelvic fractures Rates can reach 20% Amount of force causing unstable pelvic fractures also causes severe organ damage
- 3. When to suspect… High velocity MVA (eg…)
- 4. Obvious wounds… Severe hypovolemic shock (class II and above)
- 5. When to suspect… (subtle signs) Bruises around flank or pelvis
- 6. Haematuria
- 7. If suspect pelvic injury… Disrupts pelvic ring Not disrupting pelvic ring
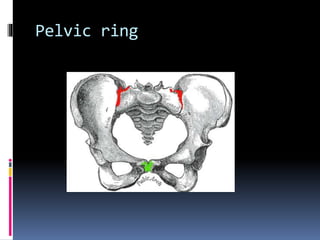
- 8. Pelvic ring
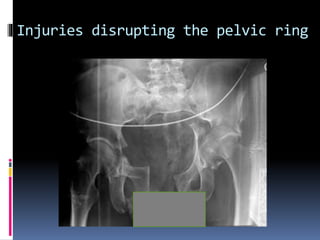
- 9. Injuries disrupting the pelvic ring
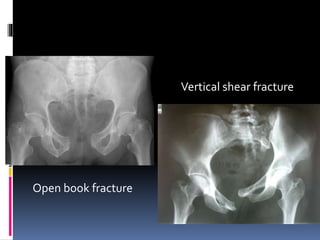
- 10. Open book fracture Vertical shear fracture
- 11. Injuries not disrupting pelvic ring Pubic rami fractures Iliac wing fractures
- 12. What is most important? HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK!
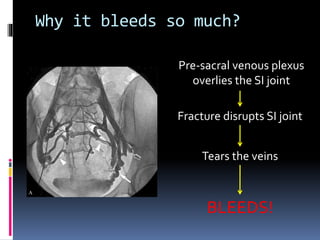
- 13. Why it bleeds so much? Pre-sacral venous plexus overlies the SI joint Fracture disrupts SI joint Tears the veins BLEEDS!
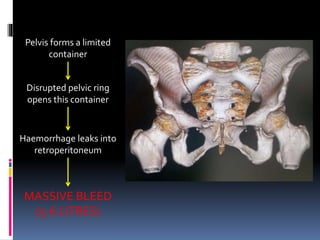
- 14. Pelvis forms a limited container Disrupted pelvic ring opens this container Haemorrhage leaks into retroperitoneum MASSIVE BLEED (5-6 LITRES)
- 15. What to do? A&E level Follow ATLS protocol (ABCDE) Most important to fluid resuscitate As massive bleeding suspected – blood must be transfused (volume expanders while waiting blood) Application of temporary pelvic stabilizer (binder / c-clamp)
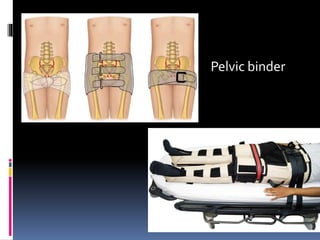
- 16. Pelvic binder
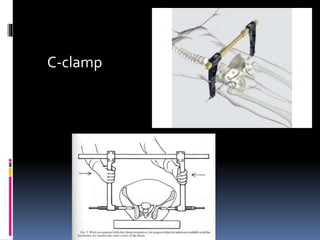
- 17. C-clamp
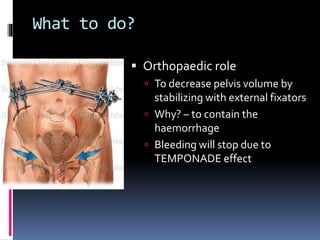
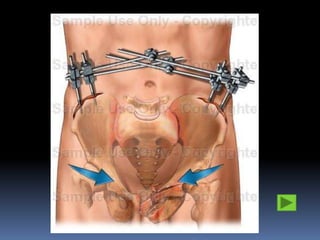
- 18. What to do? Orthopaedic role To decrease pelvis volume by stabilizing with external fixators Why? – to contain the haemorrhage Bleeding will stop due to TEMPONADE effect
- 19. How to do? Pin placement: 2cm posterior to ASIS along iliac crest Reduction: If open book – internal rotate the hip If vertical shear – traction through a supracondylar pin 1st Hold: At least 2 bars must be clamped together
- 20. Pelvic # classification (Tile’s) Type A – STABLE A1 – # not involving ring A2 – stable, minimally displaced ring #
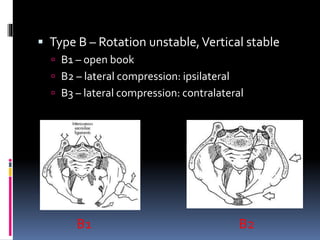
- 21. Type B – Rotation unstable, Vertical stable B1 – open book B2 – lateral compression: ipsilateral B3 – lateral compression: contralateral B1 B2
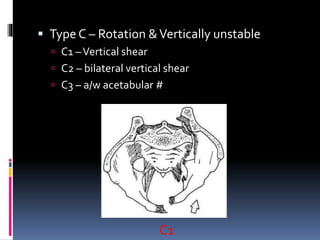
- 22. Type C – Rotation & Vertically unstable C1 –Vertical shear C2 – bilateral vertical shear C3 – a/w acetabular # C1
- 23. THANK YOU