Axilla
- 1. Axilla & Axillary Dissection Mohammed Suleiman Al Jajeh 20133422 Phase IV NEAR EAST UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
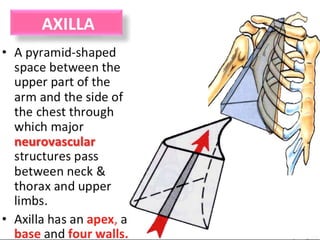
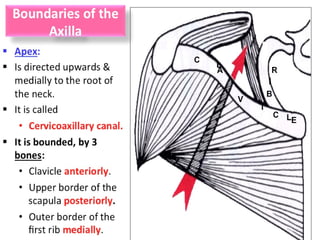
- 2. Objectives a. Define Axilla . b. Give its boundaries and contents . c. Axillary Dissection .
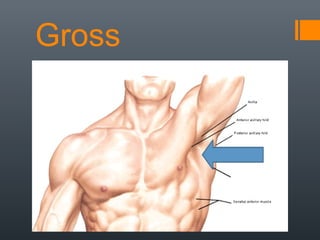
- 3. Gross
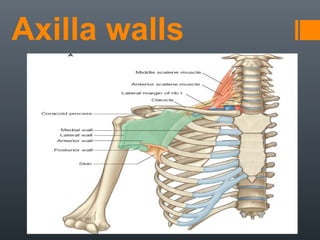
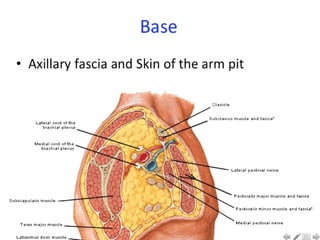
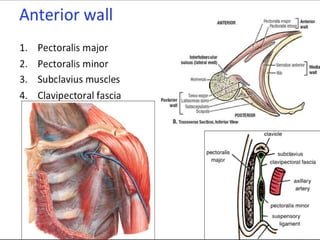
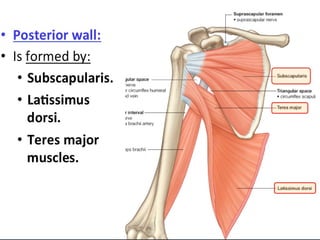
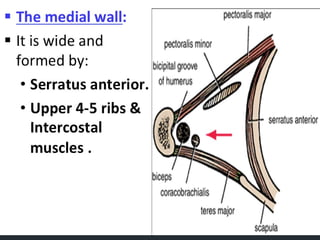
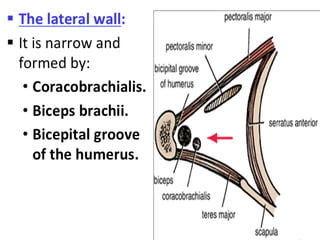
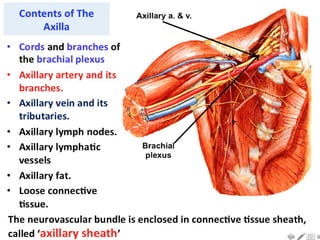
- 5. Axilla walls
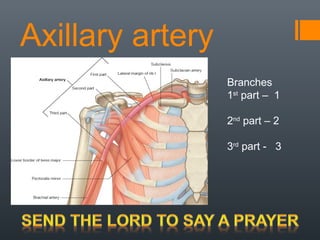
- 13. Axillary artery Branches 1st part – 1 2nd part – 2 3rd part - 3
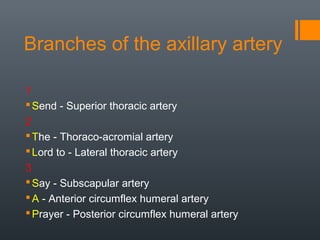
- 14. Branches of the axillary artery 1 Send - Superior thoracic artery 2 The - Thoraco-acromial artery Lord to - Lateral thoracic artery 3 Say - Subscapular artery A - Anterior circumflex humeral artery Prayer - Posterior circumflex humeral artery
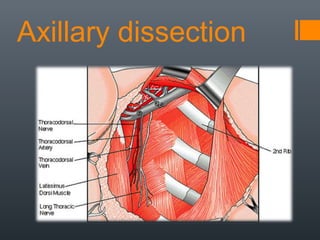
- 16. Background Axillary dissection is a surgical procedure that incises the axilla to identify, examine, or remove lymph nodes. Axillary dissection, either alone or with mastectomy usually calls for general anesthesia Cancer in the lymph nodes usually cannot be felt, so doctors need to remove the lymph nodes and examine them under a microscope to find out if they contain cancer
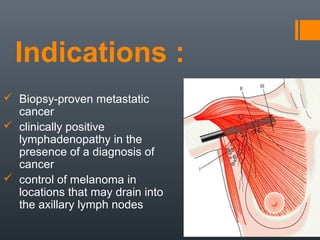
- 17. Indications : Biopsy-proven metastatic cancer clinically positive lymphadenopathy in the presence of a diagnosis of cancer control of melanoma in locations that may drain into the axillary lymph nodes
- 18. When Axillary lymph node dissection is Done ? A. During a radical mastectomy . B. With breast-conserving surgery . C. When a lymph node biopsy is not suitable .
- 19. How ALND is done ? a. ALND is done using general anesthesia in a hospital operating room. b. The surgeon makes an incision under the arm. The surgeon usually removes at least 10 lymph nodes . After the lymph nodes are removed, a small tube (drain) is placed in the incision which reduces the chance of swelling from fluid building up in the tissue. The drain is left in place for a few days or until there is little drainage.
- 20. Gross
- 21. Related factors I. Age at time of surgery II. Body habitus (IBW) III. Cardiac disease or diabetes IV. Smoking history V. Tumor size VI. Number of nodes (Sometimes more than 10 lymph nodes are removed)
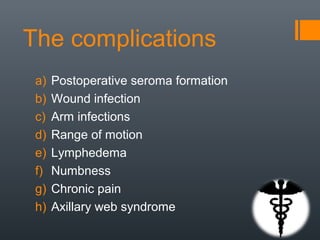
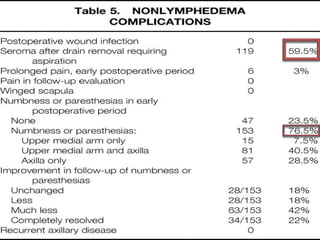
- 22. The complications a) Postoperative seroma formation b) Wound infection c) Arm infections d) Range of motion e) Lymphedema f) Numbness g) Chronic pain h) Axillary web syndrome
- 23. Seroma It’s the persistent drainage of axillary lymphatic fluid . Cause : a result from transection of lymphatic vessels, the use of electrocautery and local inflammatory response . incidence of seroma formation ranges from 35% to as high as 97% in breast cancer patients .
- 24. Lymphedema One of the most morbid complications Assessed by measuring both arms at the same site Incidence varies from 5% to 80% . Casues : 1. Due to injury to lymphatics and veins by surgery tumor 2. infiltration of lymphatics . It’s usually responsive to compression therapy Higher rates with increased BMI & Post Radiotherapy
- 25. Sensory -intercostobrachial nerve Conservation of the IBN, while anatomically preferable, is not functionally necessary during axillary dissection for breast cancer. if it is not possible to dissect the nerve free of tumor, then it can be sacrificed, which results in the loss of sensation in the upper, inner arm .
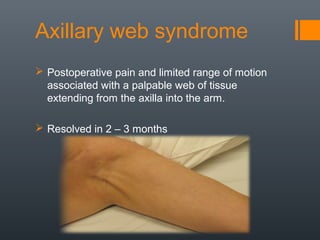
- 26. Axillary web syndrome Postoperative pain and limited range of motion associated with a palpable web of tissue extending from the axilla into the arm. Resolved in 2 – 3 months
- 28. Hint : * The most common complication after axillary dissection is Lymphedema . * We did not measure the arm circumference before surgery , because changes in the extended follow-up period are also dependent on weight loss and gain
- 29. Teşekkür ederim References : 1.GRAY’S ANATOMY 2.ANNALS OF SURGERY 3.MEDSCAPE.COM 4.Canadian Cancer Society