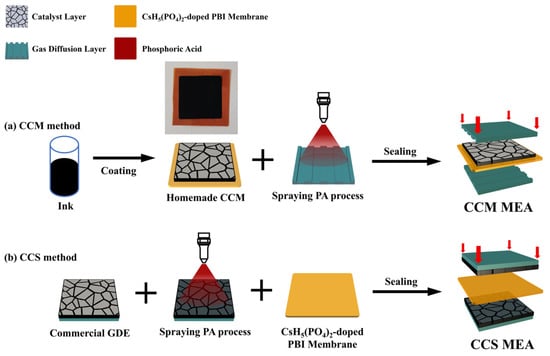
<p>The schematic experimental setup for the hydrolysis test.</p> Full article ">Figure 2
<p>(<b>a</b>) Calculated vertical phase diagrams of Al-10Bi-Fe (wt.%); (<b>b</b>–<b>d</b>) calculated phase fractions diagrams of Al-10Bi-(3, 7, 10) Fe (wt.%).</p> Full article ">Figure 3
<p>SEM images at various magnifications of as-atomized Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders: (<b>a</b>–<b>a<sub>2</sub></b>) Al-10Bi-3Fe (wt.%); (<b>b</b>–<b>b<sub>2</sub></b>) Al-10Bi-7Fe (wt.%); and (<b>c</b>–<b>c<sub>2</sub></b>) Al-10Bi-10Fe (wt.%).</p> Full article ">Figure 4
<p>EDS analysis of the cross-section of the Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders: (<b>a</b>) Al-10Bi-3Fe, with element distributions: (<b>a<sub>1</sub></b>) Al; (<b>a<sub>2</sub></b>) Bi; (<b>a<sub>3</sub></b>) Fe; (<b>b</b>) Al-10Bi-7Fe (wt.%), with element distributions: (<b>b<sub>1</sub></b>) Al; (<b>b<sub>2</sub></b>) Bi; (<b>b<sub>3</sub></b>) Fe; (<b>c</b>) Al-10Bi-10Fe (wt.%), with element distributions: (<b>c<sub>1</sub></b>) Al; (<b>c<sub>2</sub></b>) Bi; (<b>c<sub>3</sub></b>) Fe.</p> Full article ">Figure 5
<p>XRD patterns of the as-atomized Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders (<b>a</b>) separated XRD patterns; (<b>b</b>) stacked patterns focusing on the Al (111) peak.</p> Full article ">Figure 6
<p>Charts of the hydrolysis of Al-Bi-Fe variations using deionized water at different reaction temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 °C: (<b>a</b>) the hydrogen yield vs. time curve; (<b>b</b>) the conversion rate.</p> Full article ">Figure 7
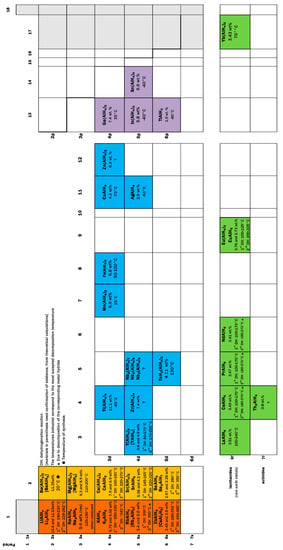
<p>Cost and hydrolysis performance for various active Al alloys: (1) red area indicates Ga, In, Sn doping alloys; (2) yellow area indicates Ga, In-free alloys; and (3) green area indicates Sn-free alloys. The data are drawn from references [<a href="#B23-materials-17-04973" class="html-bibr">23</a>,<a href="#B24-materials-17-04973" class="html-bibr">24</a>,<a href="#B26-materials-17-04973" class="html-bibr">26</a>,<a href="#B27-materials-17-04973" class="html-bibr">27</a>,<a href="#B29-materials-17-04973" class="html-bibr">29</a>,<a href="#B30-materials-17-04973" class="html-bibr">30</a>].</p> Full article ">Figure 8
<p>Plots of the hydrolysis of the Al-Bi-Fe variations using deionized water at different reaction temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 °C (<b>a</b>) hydrogen yield rates vs. time curves, (<b>b</b>) the Arrhenius plots.</p> Full article ">Figure 9
<p>SEM images of the hydrolysis products of Al-Bi-Fe variations using deionized water at different reaction temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 °C.</p> Full article ">Figure 10
<p>The morphological changes on the surface of Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders at different stages of the hydrolysis process, along with a schematic representation of the reaction mechanism.</p> Full article ">