A Harvard Business Review reports that 75% of new product ideas fail to reach the market. This is due to an inefficient R&D framework or poor strategic alignment.
R&D teams face constant pressure to work faster, improve processes, and deliver clear results. Despite significant investments, R&D progress can still be hindered by disconnected workflows, underused data, and missed collaboration opportunities. Challenges like managing resources, adopting new technologies, and coordinating across teams only add to the complexity.
A clear R&D framework can change this.
This study by GreyB explores the key elements of a practical R&D framework. These elements help organizations develop new products, manage risks, and track progress in a competitive environment.
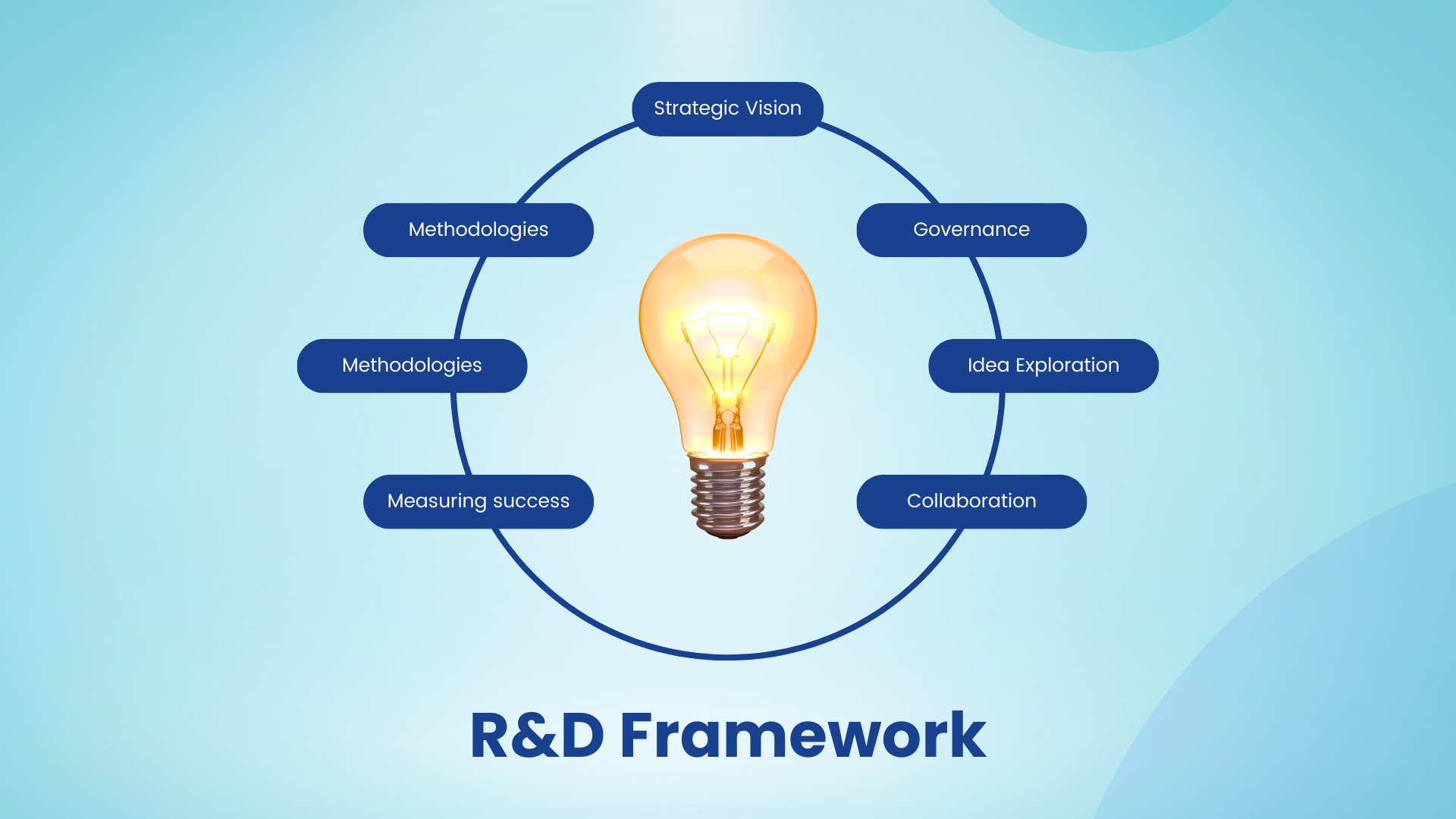
What is a Strong R&D Framework?
While an R&D strategy defines the overarching goals and priorities (the “why” and “what” of innovation), an R&D framework focuses on the “how” — how teams structure their efforts, evaluate ideas, and manage the execution of R&D projects.
An R&D framework provides a structured approach for planning, executing, and managing research and development projects. It outlines the processes, tools, and methodologies teams follow to transform ideas into tangible products or improvements.
Think of it as a blueprint for innovation—ensuring that ideas are developed in a repeatable, scalable, and efficient manner. Without a well-defined framework, even the most promising ideas can be lost to inefficiencies, misalignment with company goals, or poor resource management.
Key Elements of an Effective R&D Framework
1. Strategic Vision
Every successful R&D framework starts with a clearly defined strategic vision.
- Analyze market trends and competitor benchmarks through emerging technologies, market reports, patent landscapes, and industry forecasts. Identify growth areas such as AI-driven technologies or sustainable packaging.
- Leverage customer feedback and surveys to identify specific pain points or unmet needs, such as increasing the durability of products or developing allergen-free materials.
- Define measurable objectives that provide a clear direction for R&D efforts. For example, reducing the time from concept to prototype by 20% through streamlined workflows or ensuring that at least 30% of new developments align with emerging industry trends. Ensure these objectives support compliance requirements and sustainability priorities.
- Clarify objectives by addressing key business questions: What are the company’s long-term research priorities? Is the focus on developing new products, entering new markets, or optimizing existing processes?
The vision must be clearly defined and communicated across the organization.
Unilever has integrated sustainability into its R&D framework, ensuring that all new product developments support its long-term environmental goals. This approach enables the company to drive innovation while meeting growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and complying with evolving regulations.
2. Governance and Decision-Making Structure
To ensure an effective R&D framework, clearly define who makes key decisions, approves projects, and enforces processes. A well-structured governance model keeps teams aligned and projects on track.
A strong governance structure provides:
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Every team member should understand their role in the R&D process, whether generating ideas, conducting research, or making financial decisions.
- Agile Decision-Making: R&D teams must reach decisions quickly to stay ahead of the competition. A well-defined governance structure removes bottlenecks and minimizes bureaucracy, enabling faster progress.
It’s also crucial to establish who makes decisions and how they are made. Many organizations adopt a stage-gate approach, where critical decision points (gates) are built into the R&D process. This ensures ongoing evaluation, allowing projects to move forward.
3. Data-Backed Idea Exploration
Innovation starts with ideas, but without structure, it can become unfocused. A well-designed R&D framework includes data-backed decision-making to identify, evaluate, and prioritize ideas that align with market needs and technological advancements.
With research-backed intelligence, teams can uncover new opportunities or refine existing concepts—novel ingredients, formulations, or alternative materials. With a research platform like Slate, this process becomes more streamlined, ensuring every decision is guided by data and aligned with strategic innovation goals.
Take, for example, a cosmetic company exploring next-generation sunscreens. If they ask, “What new chemical formulations are used in sunscreens today?” Slate provides a precise, data-backed response—helping them navigate emerging trends and make informed R&D decisions.
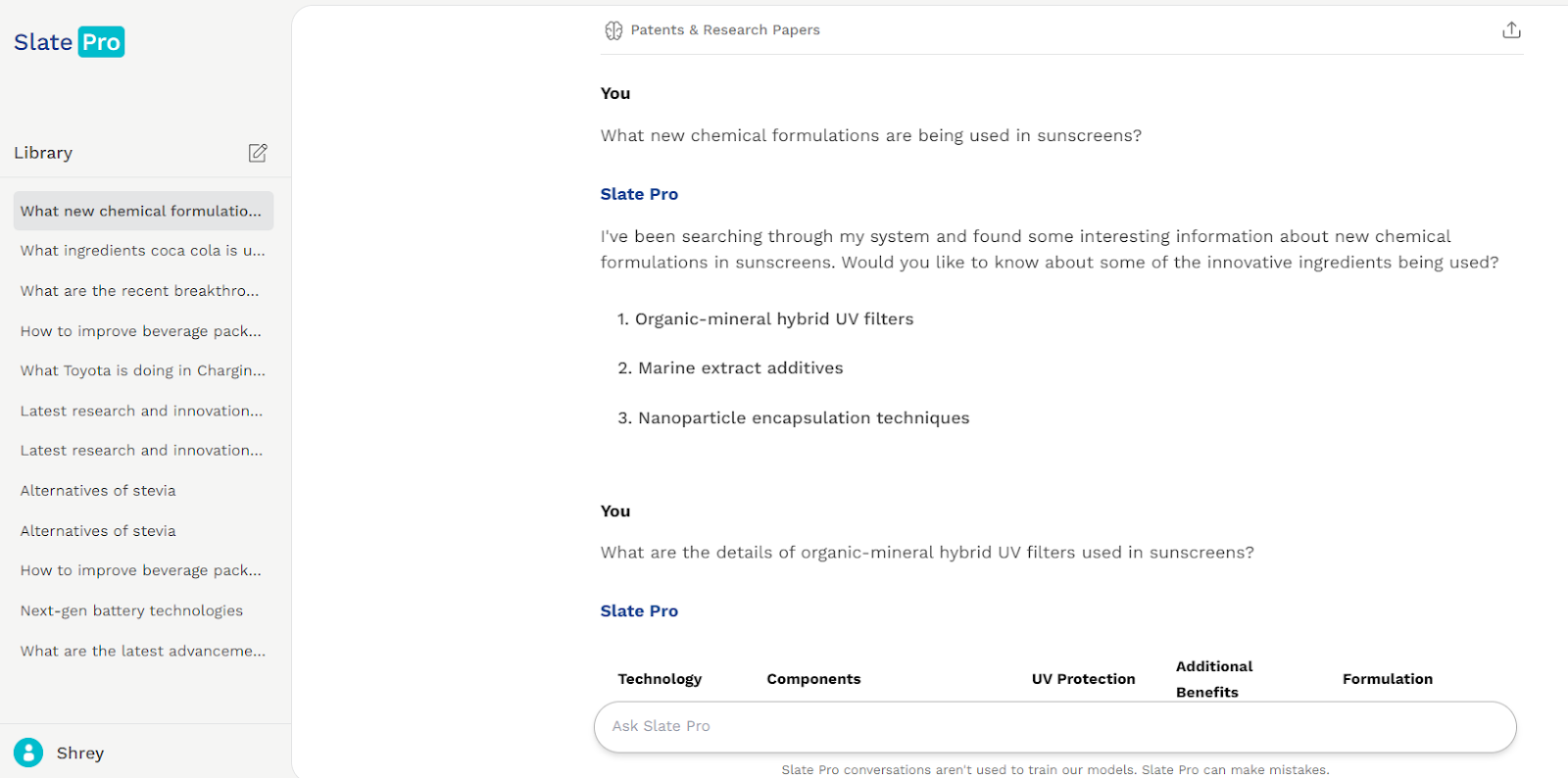
Slate categorizes your research to provide solutions relevant to your specific area.
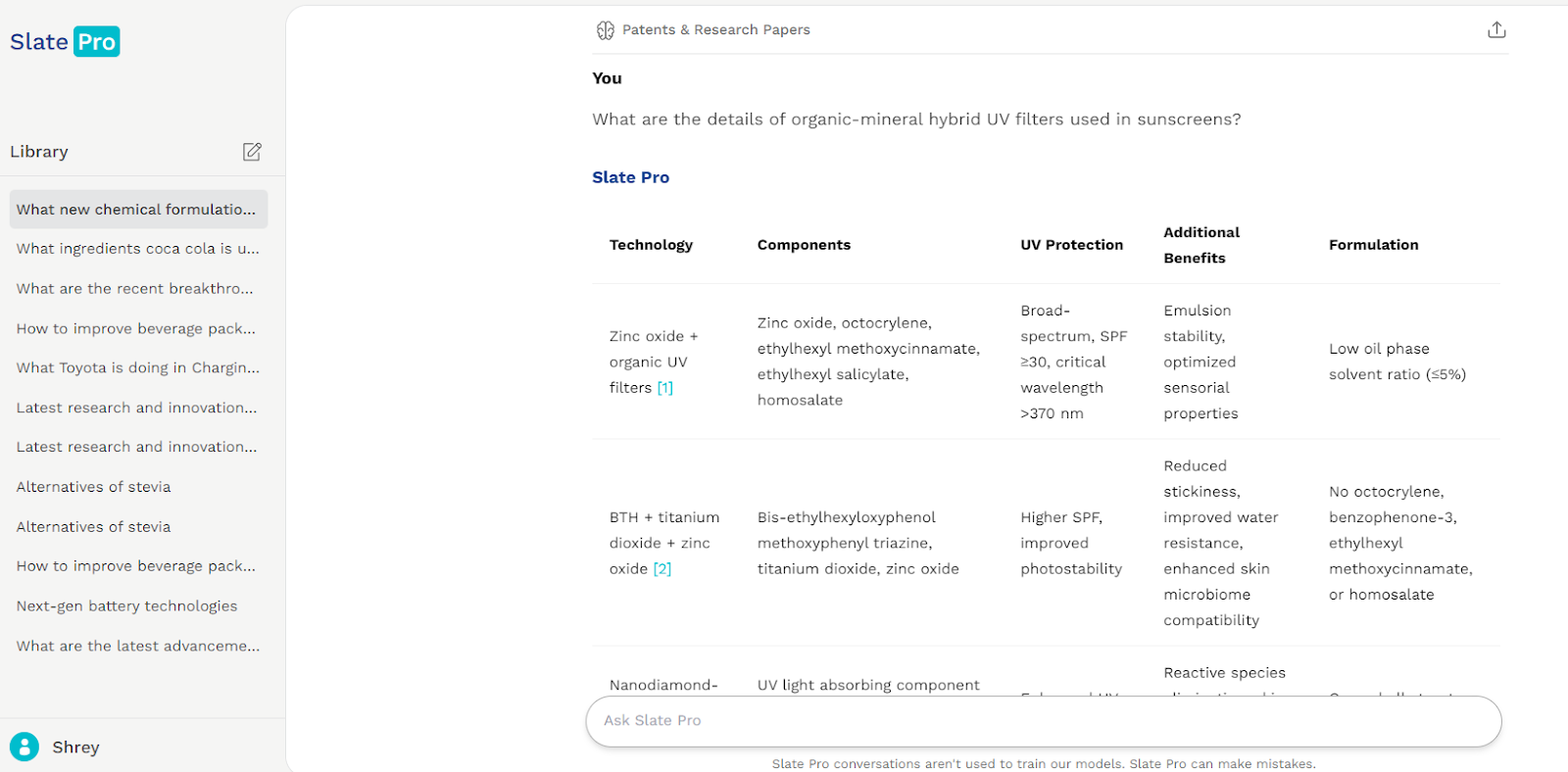
The above result lists various sunscreen formulations, citing the source to support the company’s research findings.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Encourage teams to share insights so everyone stays on the same page with project goals.
- Hold regular cross-department meetings to keep objectives clear and ensure teams are aligned.
- Use a central knowledge management system (e.g., Slate) to store research documents, patents, shared updates, technical literature, and findings.
Successful R&D involves multiple departments, including marketing, product development, manufacturing, and customer service. A well-structured R&D framework helps teams work together smoothly and ensures that innovation efforts are connected across the company.
Companies like L’Oréal and Unilever use central knowledge management systems to connect global teams. This ensures that R&D efforts stay aligned across regions and product categories.
A Griffith University study of 100 R&D heads found that cross-functional collaboration in product development leads to greater success in commercialization. Open communication channels help team members understand their role in the framework and the value they bring to the R&D process.
5. Risk Management and Mitigation
Risk is a natural part of R&D, but a well-structured framework helps identify, assess, and mitigate potential challenges. Recognizing risks early, whether technical, financial, or regulatory, allows teams to create contingency plans before they become major obstacles.
Some effective risk management strategies include:
- Phased Funding: Instead of committing the entire R&D budget to a single project, release funding in stages based on progress and key milestones.
- Pilot Testing: Before moving to full-scale development, conduct pilot tests or build prototypes to evaluate feasibility and market acceptance.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for different possibilities by developing “what-if” scenarios. This helps teams anticipate challenges and create strategies to address them.
These strategies ensure that risks are managed effectively without derailing projects or resulting in major losses.
6. R&D Framework Methodologies
Different R&D frameworks help manage projects through various stages, from concept to commercialization. Three standard methods are:
Stage-Gate Process: The Stage-Gate process breaks the development cycle into distinct stages, with decision points (gates) in between. At each gate, projects are evaluated using predefined criteria. Based on the review, teams decide whether to move forward, make adjustments, or stop the project altogether.
Agile R&D: Agile R&D focuses on flexibility, iterative development, and teamwork across departments. Teams work in short sprints to build prototypes, test ideas, and refine them based on feedback. This approach is especially used in fast-changing industries where market demands and technology evolve rapidly.
Lean R&D: Lean R&D focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value. It streamlines R&D processes by cutting unnecessary steps and focusing on delivering customer value.
These methodologies ensure that projects are carefully managed, risks are mitigated, and timelines are adhered to.
Explore other innovation frameworks that shape R&D processes.
7. Measure the Success of an R&D Framework
One of the biggest challenges in R&D is measuring success. Unlike other business functions, R&D outcomes can be challenging to quantify, particularly in the early stages of a project. To build a strong framework, companies need clear metrics that track how well research activities are structured, executed, and aligned with business goals.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for evaluating the success of an R&D framework include:
- Time to Market (TTM): Track how quickly a project moves from research to commercialization. Companies can compare current timelines with past projects or industry benchmarks to spot delays and make improvements.
- Return on Innovation (ROI): Evaluate the financial return on R&D investments. Companies can track profits from R&D-driven products to see if resources are used effectively. This helps prioritize projects with the highest impact and align with strategic goals.
- Project Success Rate: Track how many R&D projects move through key stages and reach commercialization or its strategic goal. Companies can calculate this by comparing the number of completed projects to those stopped early or abandoned mid-way.
- Collaboration Efficiency: Assesses how well different teams share knowledge and align on projects. One way to measure this is by tracking how often departments collaborate on projects and how quickly they resolve issues. Team feedback can also highlight areas that need improvement.
- Knowledge Utilization: Measure how often teams use internal research, patents, or past project learnings in new developments.
- Risk Mitigation Effectiveness: Track how well the framework helps identify and manage risks early in the R&D process. Companies can measure this by comparing the number of risks flagged in the early stages to unexpected failures later in development. Fewer late-stage failures mean better risk management.
Challenges in Implementing an R&D Framework (and How to Solve Them)
Even with a well-structured framework, companies can face several challenges. Here’s one of the most common hurdles and how to address it:
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
R&D leaders often struggle to balance projects that deliver quick results with those that drive long-term innovation. Managing resources and expectations is key to maintaining this balance.
One solution is a dual-track strategy, where companies manage a mix of short-term projects that meet immediate business needs and long-term research focused on breakthrough innovations.
For example, Apple invests heavily in future technologies like AR/VR and autonomous systems while continuously improving its existing products like iPhones and MacBooks. Separate teams work on these projects to ensure that short-term product enhancements don’t slow down the company’s long-term innovation efforts.
Portfolio Management
Not every R&D idea will reach the market, so managing the project pipeline effectively is essential. R&D teams must balance high-risk, high-reward innovations with smaller, incremental improvements that meet current business needs. Allocating resources wisely ensures that the most promising projects receive the attention they deserve.
To make informed decisions, companies often use stage-gate or milestone-based evaluations. These methods help determine which projects should move forward and which should be discontinued. A structured approach like this keeps the R&D pipeline aligned with business goals while minimizing wasted resources.
Resource Constraints
R&D projects require significant investment in both talent and technology. However, limited resources can make it challenging for organizations to pursue ambitious innovation goals.
A PwC study of board-level executives from 1,757 companies across 25+ countries and 30 sectors found that companies can overcome resource challenges by building strategic partnerships.
Collaborating with startups, universities, research institutions, and even competitors helps organizations access new talent, technology, and expertise without bearing the full cost alone.
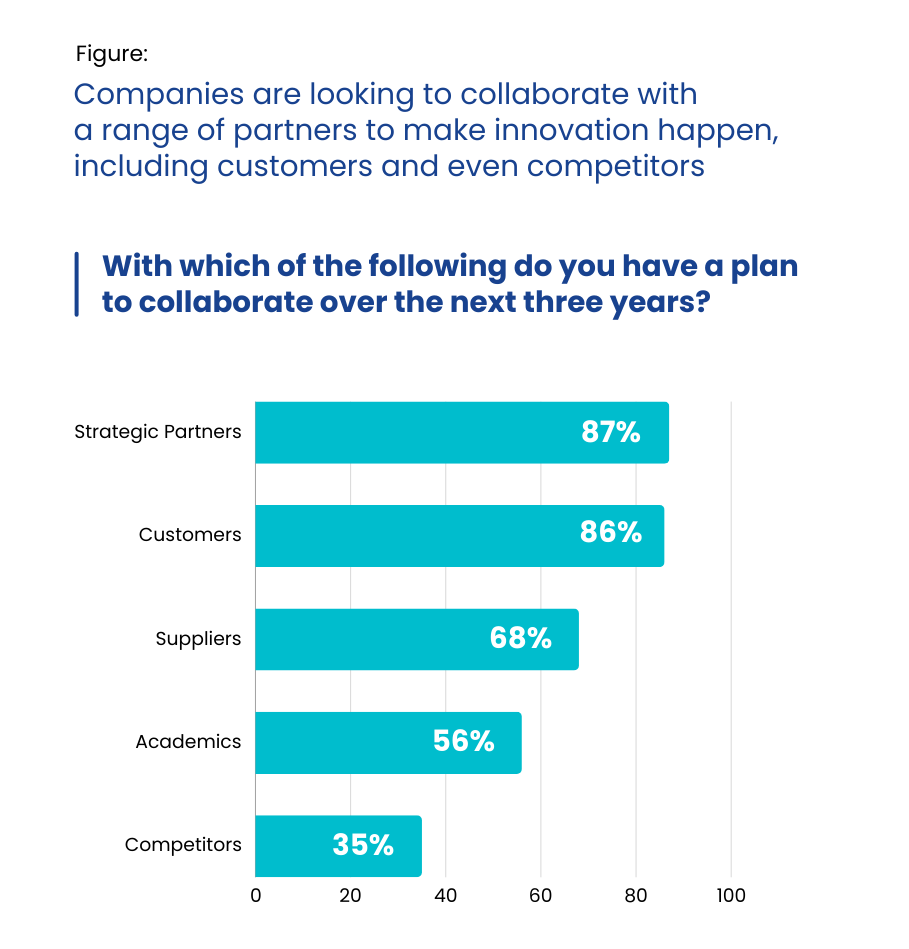
These collaborations allow organizations to leverage external expertise and technology, reducing the strain on internal resources.
Risk of Failure
Failure is an inherent aspect of innovation. R&D teams must cultivate a culture that views failure as an opportunity to learn rather than a setback.
3M’s “15% rule” is a notable example of this approach, allowing employees to spend 15% of their time working on personal projects. Despite initial failures, many successful innovations like “Post-it Notes” and “Scotch Tape” have emerged from this model of fostering creativity and experimentation.
Which R&D framework fits your organization?
The structure of your R&D team plays a critical role in how effectively your organization can execute innovation efforts. There are two core R&D structures within an organization: centralized and decentralized.
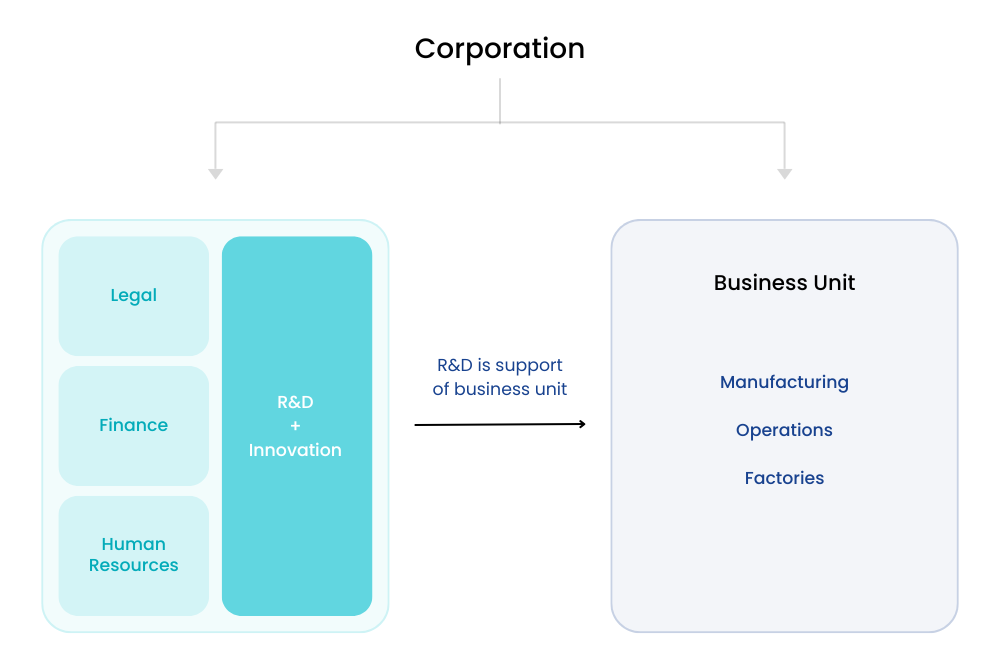
Centralized R&D
A single department or group in the organization manages all R&D activities. This ensures consistency and alignment across projects, as all research is directed from the top down. This model is common in industries like pharmaceuticals and aerospace, where long-term and large-scale projects are the norm.
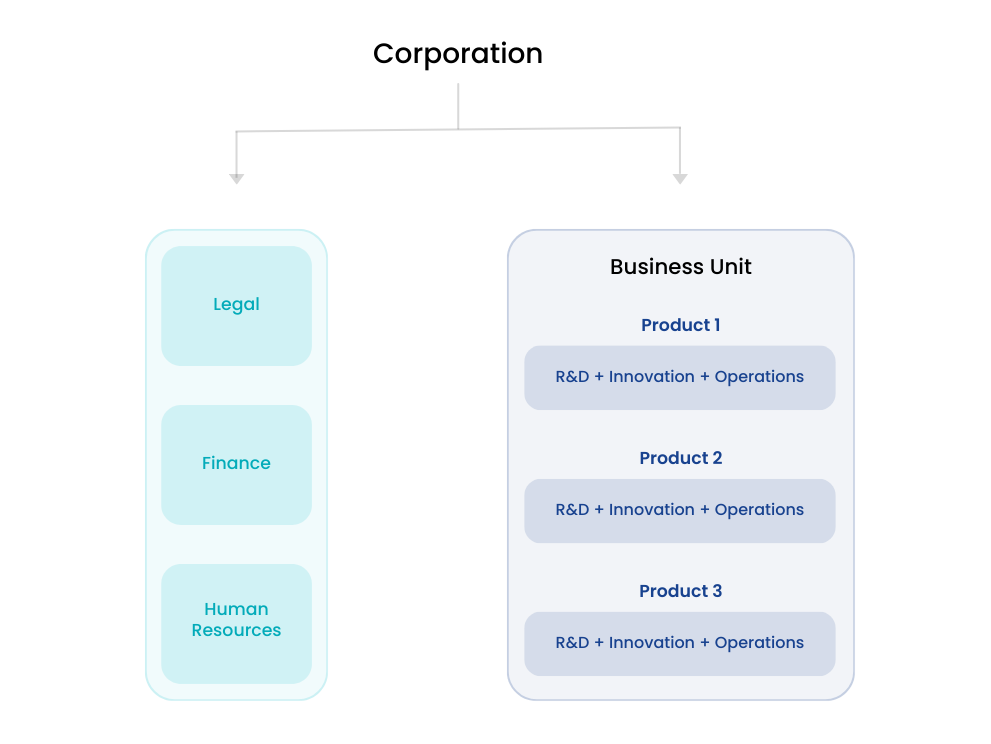
Decentralized R&D
R&D activities are distributed across different business units or teams. Each unit has its R&D team working on projects specific to that division. This approach is often seen in large multinational corporations. Different regions or product lines, like the consumer goods industry, require tailored innovation efforts.
Slate: A Centralized Platform for an effective R&D Framework
One of the biggest challenges in R&D is dealing with scattered, disconnected information. Research teams often spend hours (nearly 9 hours per week) just searching for data across multiple sources—patents, research papers, product details, and without a clear way to connect the dots.
60% of company executives say that time constraints and a lack of understanding of how to find information prevent employees from finding the data they need.
Slate by GreyB solves this problem by bringing all research activities, documents, and competitive insights into a single, organized platform.
Instead of navigating through disconnected sources, R&D teams can:
1. Ensure research efforts are interconnected – Rather than working in isolation, teams can connect patents, product labels, and research papers to see how insights from different sources support or challenge findings.
Slate’s integrated view enhances decision-making and speeds up the R&D process by highlighting key connections between different data points.
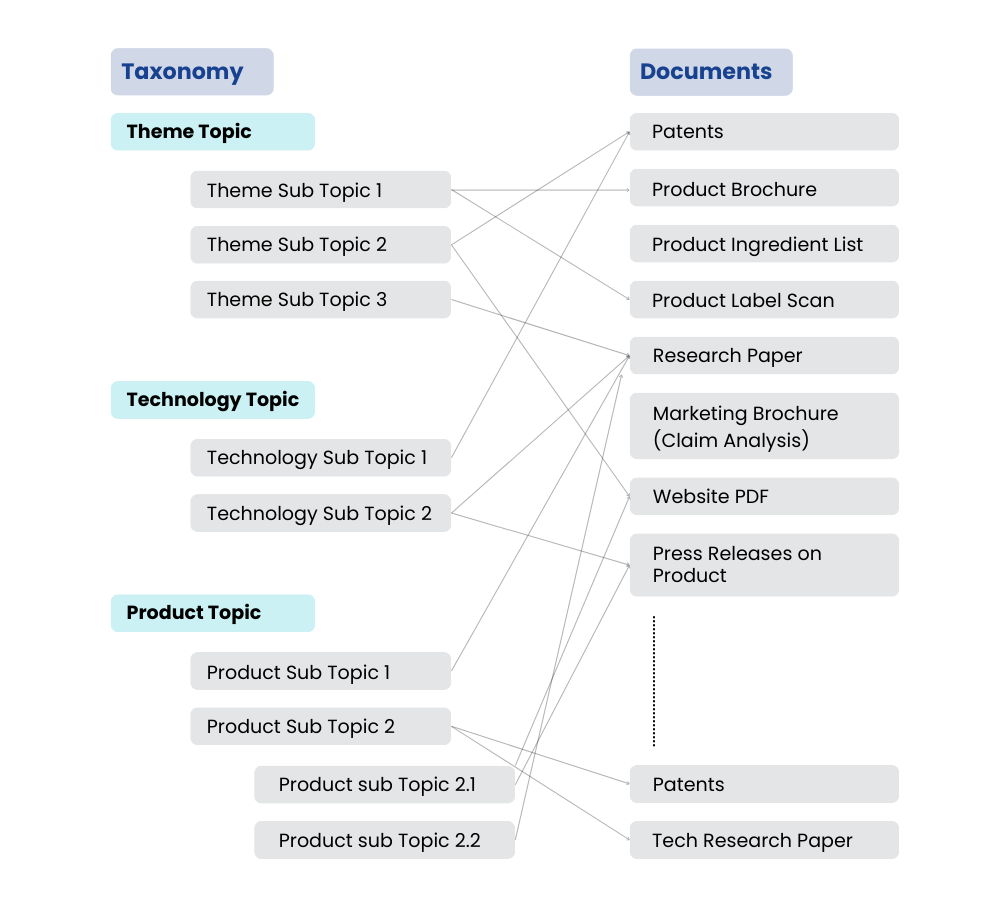
- Establish a structured approach to data management – A well-defined system categorizes research materials by technology, product type, geography, ingredients, and applications, making it easy to locate relevant information.
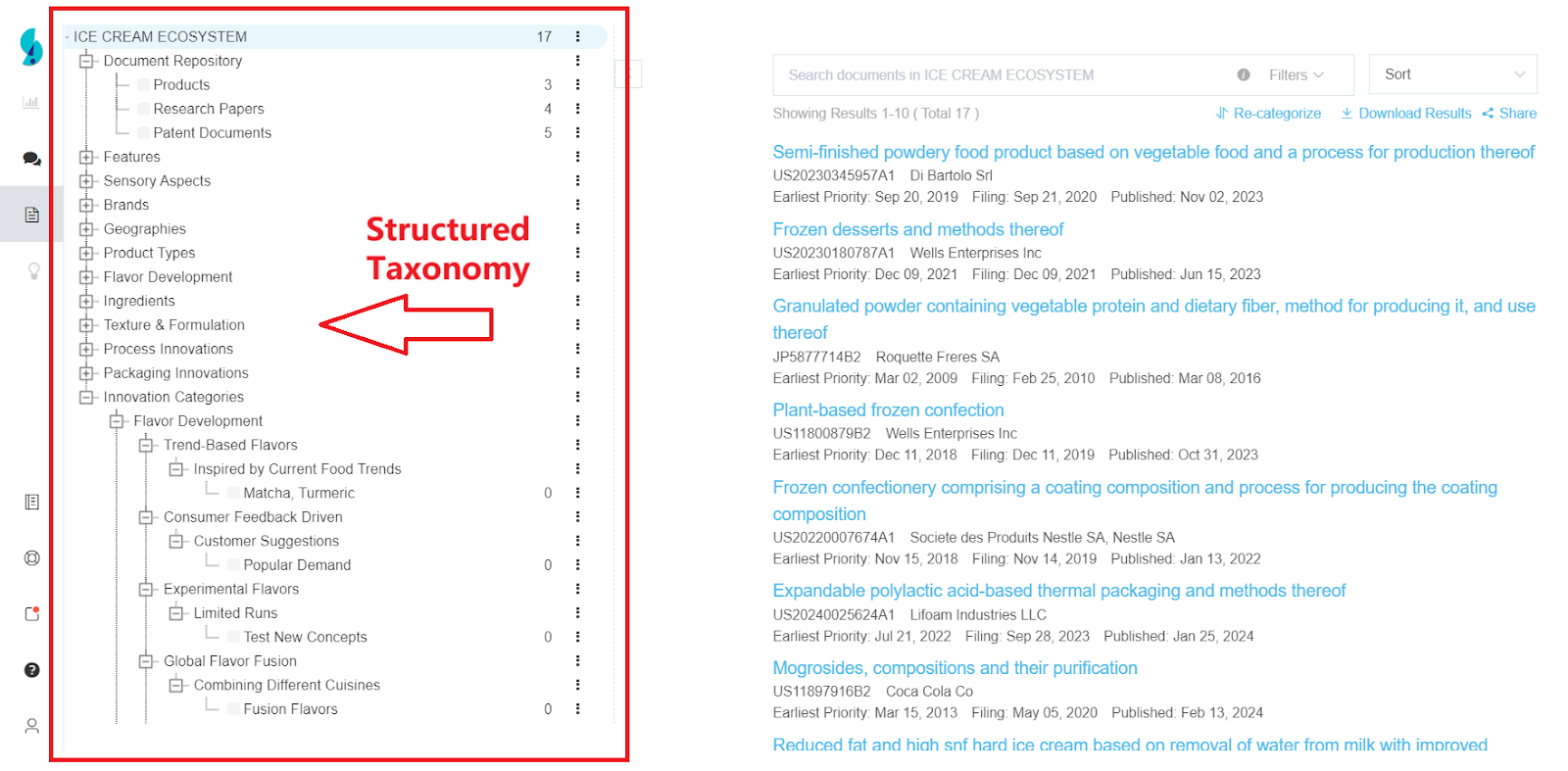
- Improve collaboration and knowledge-sharing – With built-in commenting and annotation tools, teams can highlight key findings, discuss real-time insights, and ensure research decisions align across departments.

- Create a process for evaluating and prioritizing projects. Slate enables systematic tracking of industry trends, competitor advancements, and internal research findings to help teams decide which R&D projects align with business goals and deserve priority.
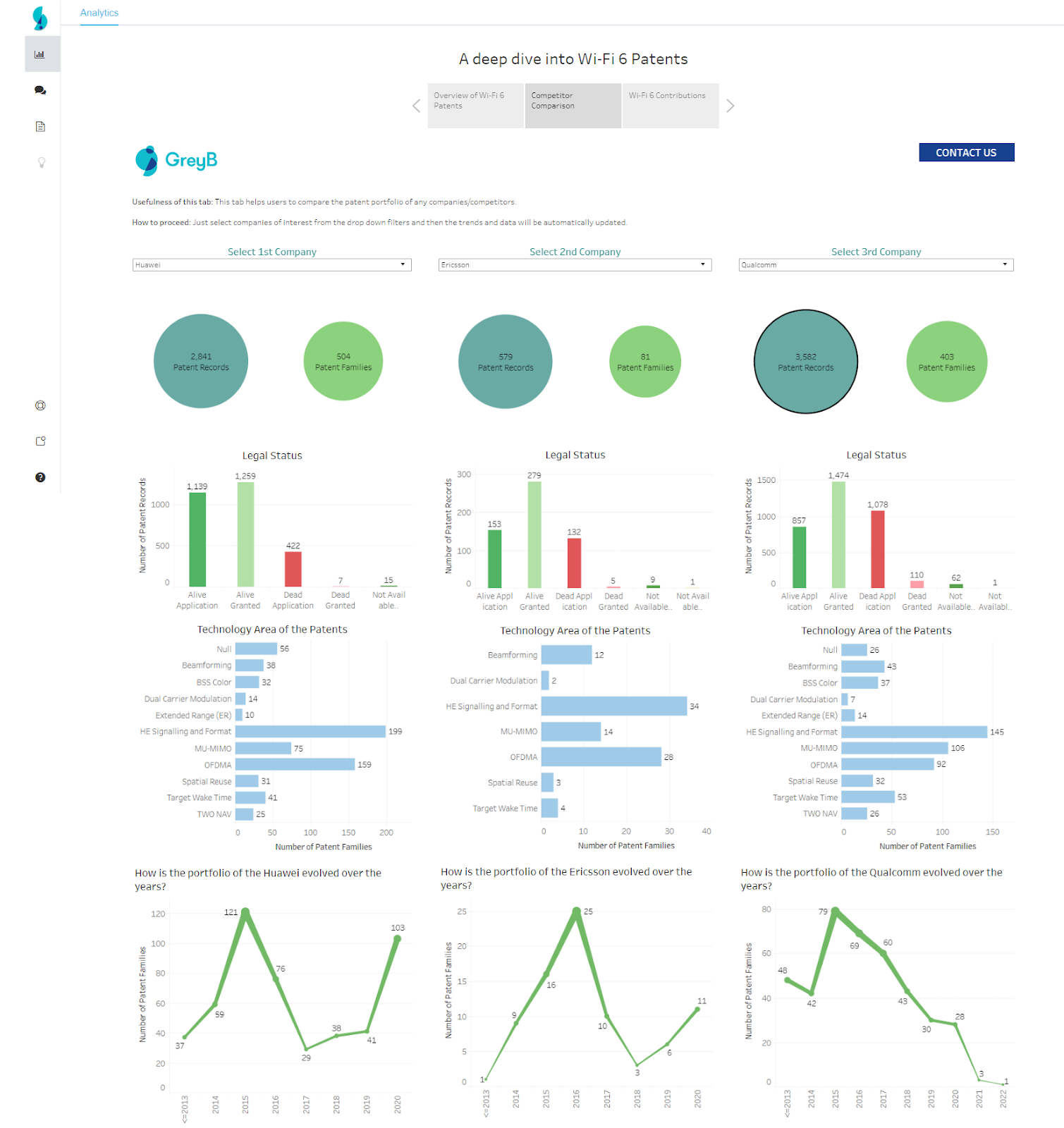
A strong R&D framework keeps research structured, decisions clear, and innovation moving forward. See how Slate helps you connect insights, streamline workflows, and bring better products to market—faster.
Get the Demo
Fill the form to book a demo
Authored by: Shrey Gupta, Product Marketer