Protect Your Investment: Are AGS Diamond Certificates a Smart Choice?
By Gary A.
Edited by Brian M.
Published Jun 2, 2021
Edited on Dec 18, 2024
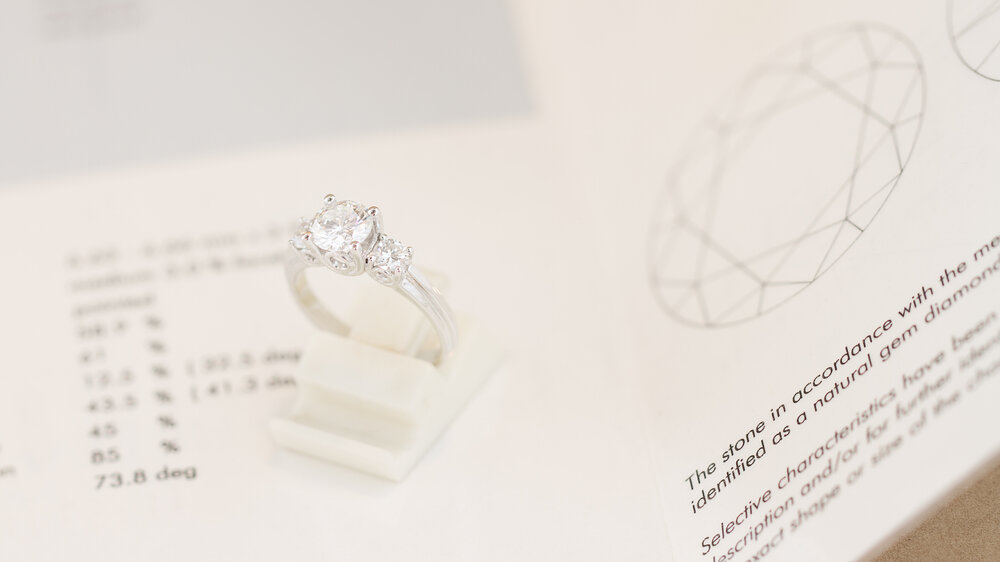
When it comes to ensuring quality and precision, an AGS Diamond Certificate gives you confidence in a gem that has been meticulously graded for its cut, color, clarity, and carat, making your choice even more meaningful.

Navigate This Guide:
- Understanding AGS Diamond Certification: 7 Quick Practical Tips for Buying an Engagement Ring
- Introduction
- A Brief History of the AGS Lab
- Deep Dive into AGS Diamond Certification
- Comparing AGS and GIA: A Critical Analysis
- Advantages & Disadvantages of an AGS Certification
- Our Expert Take
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions About AGS Diamond Certification
Before we dive deeper into the specifics, here are some practical tips to help guide your decision-making process:
Understanding AGS Diamond Certification: 7 Quick Practical Tips for Buying an Engagement Ring
When selecting a diamond engagement ring, understanding the nuances of diamond certification, particularly from the American Gem Society (AGS), is crucial. Here are practical tips to guide you through this process, ensuring you make an informed and confident decision.
- Tip 1: Verify the AGS Certification Online: Before finalizing your purchase, ensure the diamond comes with an AGS certification. You can verify the authenticity of the AGS report by using the AGS cert lookup service available on their official website. This verification confirms that the diamond matches the specifications listed in the report.
- Tip 2: Understand the AGS Grading Scale: Familiarize yourself with the AGS grading scale, which ranges from 0 to 10. A grade of 0 indicates the highest quality, particularly in terms of cut, color, and clarity. Knowing these grades will help you assess the diamond’s quality more accurately.
- Tip 3: Examine the AGS Cut Grade Closely: The cut of a diamond significantly impacts its brilliance and fire. AGS is renowned for its precise cut grading, especially the AGS 000 Triple Zero grade, which denotes top-tier cut quality. Pay special attention to the cut grade on the AGS report to ensure optimal light performance.
- Tip 4: Compare AGS Certification with Other Diamonds: When viewing diamonds, compare the AGS certified diamonds with others. This comparison helps you visually appreciate the differences in quality as indicated by the certification, especially in terms of brilliance and overall appearance.
- Tip 5: Assess the Diamond’s Proportions and Symmetry: AGS reports provide detailed information on the diamond’s proportions and symmetry, which are critical for its aesthetic appeal. Ensure that these measurements align with the ideal standards for the diamond shape you’ve chosen.
- Tip 6: Look for AGS 000 Triple Zero Diamonds: If you’re aiming for the highest quality, consider AGS 000 Triple Zero diamonds. These diamonds have achieved the top grade in cut, color, and clarity according to AGS standards, ensuring exceptional beauty and value.”
- Tip 7: Check for Laser Inscription for Verification: Many AGS certified diamonds have a laser inscription on the girdle, matching the report number. This feature provides an additional layer of verification and ensures the diamond authintication.
Now that you’ve got these practical tips, use Jeweler AI below to find the perfect engagement ring that suits your style and budget:
Introduction
The differences that exist between every diamond in the world today are so profound that creating a reliable and trustworthy system for grading them – and, by extension, assigning value to them – is incredibly difficult. While certain bodies like HDL, EGL and IGI have formulated their own approaches, only one or two have managed to earn the near-unanimous recognition and trust of the global diamond community.
The GIA is, of course, one of them – and we talk at length about their value for shoppers in this article – but the AGS is widely considered to be a close second.
The AGS (American Gem Society) is one of the pioneers in the diamond industry and known for creating the gemstone grading system, using a scale of 0-10, for the classification of diamond characteristics. It is one of the world’s most respected gemstone laboratories, and gems with an AGS certification have the quality of the diamond ensured.
The Prestige of AGS in the Diamond World
An AGS certification means that a diamond has undergone some pretty rigorous checks to determine its quality – without which, we cannot accurately judge its value.
A non-profit body dedicated to ensuring a strong playing field for shoppers – many of whom are total newcomers to the process of picking out a strong diamond – it is recognized in many parts of the world as one of the most reliable, consistent and exacting organizations out there.
In other words, a diamond that is AGS certified is one that has been checked and graded independently, with a view to simplifying the diamond-buying process for newcomers and experts alike.
A Brief History of the AGS Lab
The American Gem Society was founded in 1943 by a small group of retail jewelers who had the interests of buyers in mind, and a keen interest in protecting them against fraud in the diamond industry. Even now, they are bound to uphold the highest standard of ethics and integrity in the diamond industry, where ensuring a high level of dependability for first-time shoppers is essential.
In 1966, AGS was the first organization to establish its own gemological laboratory to create a diamond cut grading system that consumers could read and understand. They accurately and consistently graded diamonds using their Four Cs grading system, providing consumers with a greater amount of education and clarity in choosing a diamond.
Deep Dive into AGS Diamond Certification
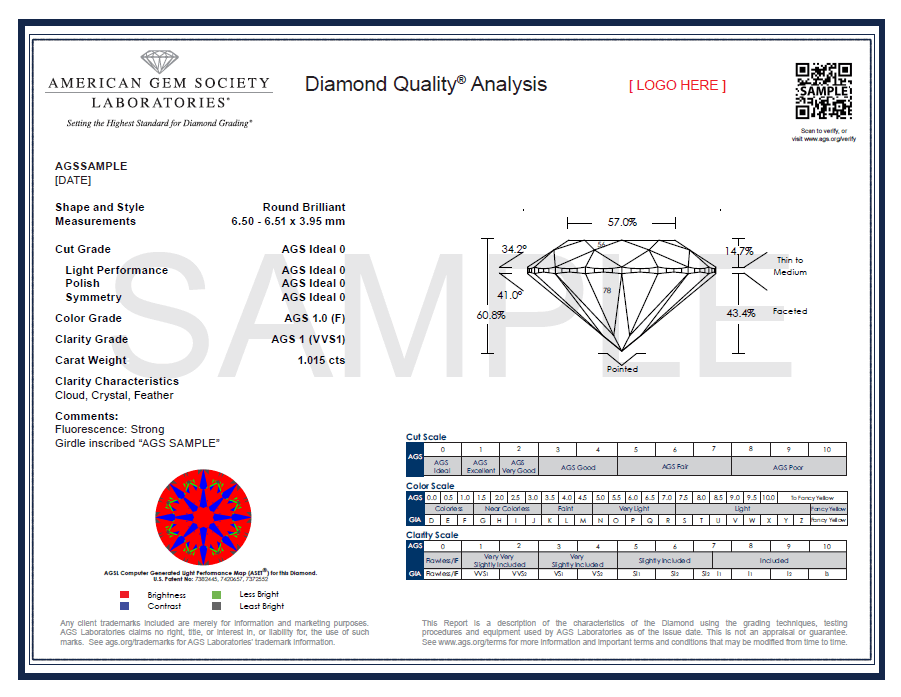
AGS’s diamond grading is categorized by 4 Cs: carat, followed by color, clarity, and cut, all of which are graded on the 0-10 scale. Each diamond is analyzed and graded by at least two gemologists, based on these four qualities.
Carat
Grading a diamond’s carat is based on its weight, not its size. AGS measures the carat weight to the third decimal place using a digital carat scale, with the actual size of the diamond in millimeters (mm).
For example, a one-carat diamond is equal to 200 milligrams (0.2 grams). Two, 1-carat diamonds can be completely different sizes since they are measured in weight, not in size. Even two diamonds of the same carat weight and shape can differ significantly in their size, as proportion is considered under the Cut grade, rather than Carat.
Color
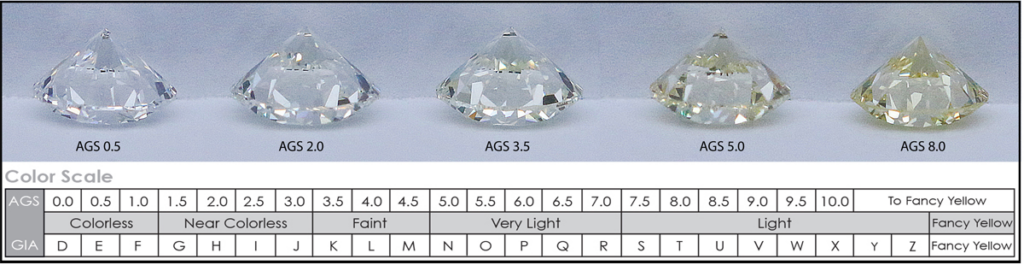
Color grade is determined by how white or colorless a diamond is. AGS grades diamonds on a color scale from 0-10, with 0 being the most colorless and 10 containing a yellow or brown color tint. The scale moved in increments of 0.5, with the first three grades (0, 0.5 and 1) representing the Colorless grades, and the following four grades (1.5-3.0) representing the Near Colorless grades.
You can see from the scale below how AGS grades the color of diamonds on the 0-10 scale, compared to the GIA letter scale. The color grade given by AGS helps identify the quality of the diamond’s color.
The case is the same for AGS diamonds as it is for GIA diamonds: the color scale is only relevant for clear diamonds. Fancy color diamonds are graded differently.
Clarity
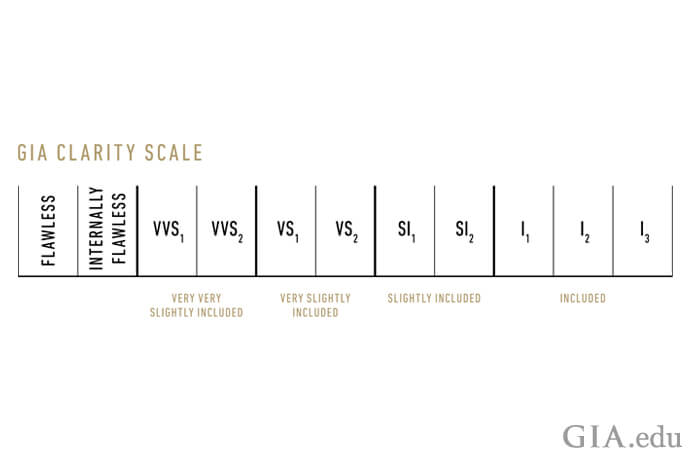
AGS grades clarity on how clean a diamond is from inclusions and blemishes and is determined by examining the diamond with a binocular microscope under specialized lighting.
Unraveling AGS Cut Grades and Their Impact
A diamond’s cut grade given by AGS is a bit different than other grades, as it’s given both a number and a word grading. Using a computerized device with revolutionary hardware and software to create a three-dimensional model of the diamond, AGS rates values for light performance including brightness, dispersion (fire), leakage, and contrast.
The diamond is then analyzed for its proportions, such as girdle, culet, weight ratio, durability, and tilt. A diamond’s finish is determined based on polish and symmetry.
A grade of Ideal and Excellent grades, depending on Shape, demonstrates proportions and angles cut for maximum fire and brilliance.
Comparing AGS and GIA: A Critical Analysis
While it depends on who you ask, we consider the AGS to be the next best thing to the GIA.
Investing in an AGS diamond is not accompanied by the same level of risk that we would attach to a diamond that has been graded by, say, the HRD or EGL. Why? Because, like the GIA, the AGS is committed to providing buyers with a dependable and impartial overview of the diamond that is as close to objective as possible – and therefore as consistent as possible.
Nevertheless, the GIA still remains the most accurate and reputable body for diamond grading – and, as a result, the most widely used. The original mastermind behind the Four Cs, this gemological institution ensures an incredibly high standard is met for their diamonds around the world, without any bias towards the vendor.
The GIA’s standards tend to be slightly stricter, which is why some vendors will turn to the AGS for certification after already receiving certification from the GIA. In some non-Round shapes, the AGS may grade color slightly higher, meaning that shoppers will pay considerably more.
The difference in quality and dependability between the AGS and GIA, however, is pretty slim, and buyers aren’t putting their money on the line when they opt for an AGS diamond.

Advantages & Disadvantages of an AGS Certification
Advantages
The AGS is a highly respected certification and having a diamond certified via its expert graders has many benefits. First, the certification offers a reliable grading for the diamond. It also ensures that your diamond has been analyzed by one of the best in the diamond business and that you’re receiving the diamond quality that is stated on the certificate. It provides peace of mind about the authenticity of your diamond as well as the high-security measures taken to grade the diamond.
Disadvantages
No grading body is considered to be as stringent as the GIA, and that high level of rigidity offers a pretty significant benefit to buyers: it means that diamonds that sit on the borderline between two colors or two clarity grades will generally be graded down, rather than up, meaning that you will never end up overpaying on lower quality.
Our Expert Take
While the AGS is regarded as the next best in terms of consistency and impartiality, the GIA remains unrivalled in its ability to ensure that buyers are never paying more for a diamond that sits on the cusp of two grades with totally different values.
You can click here to take a look at our wide range of diamonds, all of which are accompanied by a full GIA diamond report – and the high level of assurance their method offers buyers.
7 Frequently Asked Questions About AGS Diamond Certification
- Q: What is AGS Diamond Certification?
- A: AGS (American Gem Society) Diamond Certification is a credential provided by the AGS Laboratories, indicating that a diamond has been independently assessed and verified for quality based on the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) and other factors.
- Q: How does AGS grading compare to GIA?
- A: AGS and GIA are both highly reputable, but AGS is particularly known for its precise cut grading system. While GIA is a bit stricter in color and clarity grading, AGS provides a more detailed analysis of a diamond’s cut quality.
- Q: Can AGS certify lab-grown diamonds?
- A: Yes, AGS certifies lab-grown diamonds using the same rigorous standards as for natural diamonds.
- Q: Why is the AGS cut grade important?
- A: The AGS cut grade is vital because it directly impacts a diamond’s brilliance and sparkle. AGS 000 Triple Zero Diamonds represent the highest cut grade, indicating exceptional light performance.
- Q: How can I verify an AGS Diamond Certification?
- A: You can verify AGS diamond certification through the AGS cert lookup tool on their official website. This confirms the authenticity of the certificate and the diamond’s details.
- Q: Does AGS grade diamond color and clarity differently from GIA?
- A: While both AGS and GIA use similar scales, AGS may grade slightly higher in color for some non-round shapes. However, the differences are generally minimal.
- Q: What makes AGS certification trustworthy?
- A: AGS’s commitment to ethical standards, rigorous grading processes, and its reputation in the industry make its certifications highly trustworthy.
Unlock the brilliance with Jeweler AI – your guide to AGS-certified diamond perfection!
FOLLOW-UP GUIDE SERIES