The Internet is the worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that use the Internet protocol suite, TCP/IP to link devices globally. It is safe to refer to it as a network of networks. Since 1995 the Internet has tremendously impacted culture and commerce. In Uganda and many other developing countries, Internet appreciation has been slower compared to developed nations. However, more people appreciated the Internet upon the rise of social media and blogs in developing countries. Right now we are in the age of the World Wide Web, a space where digital content is served to users of the Internet. The web is what most beginning Internet users care about. However, getting to know the basic terms of the Internet and World Wide Web is a huge boost. Without further ado, lets dive into the list of top Internet and World Wide Web terms.
The list of top Internet terms and World Wide Web terms for dummies.
Browser.
First on the list of top Internet terms and World Wide Web terms for dummies is the Browser. Internet users access the Web through Web browsers. Computer and mobile devices come bundled with browsers out of the box. However, you can download other browsers from the internet and install them on devices.
Browsers let you see web pages, graphic content, almost everything online. Most browsers are free software packages. Some of the most popular browsers include Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, Opera, among others.

The major role of all browsers it to convert HTML and XML code to something a human can read, understand and maybe appreciate.
Web Page.
I remember when the Buzz Magazine rocked our high school lives, good ol’ days. There was this particular page that had questions (20 or 25? Can’t remember, but trust me, I loved it). Think of the World Wide Web as the whole book and a Web Page as any page in that book. This is the second on the list of top Internet terms and World Wide Web terms for dummies
A web page is what you see in your browser when you are on the Internet. It may contain text, diagrams, images, ads, links or a combination of those. In most cases you hover around the web page by scrolling with the mouse or finger for touch screen devices.

There was no real interaction with my beloved Buzz Magazines back in school, just reading a bunch of articles and opening the next page. However, you can interact with certain parts of the web page by clicking or tapping. This can be clicking on certain links (text snippets that have a distinct colour from the other text) to lead you to other web pages. Every website is made up of a web page or a collection of web pages.
URL.
Coming third on the list of top Internet and World Wide Web terms is the URL. This abbreviation stand for Uniform Resource Locator. URLs are the web browser unique addresses of internet pages and files. Each web page, website or any file on the Web has a unique URL that you can use to locate it.


Think of it as your home address that you give to friends so they can visit. URLs are now so common, they are literally everywhere. On business cards, posters and banners, on new products, television commercials, in articles on blog content, everywhere.
They mostly take this format;
http://www.anywebsite.com/page
URL shortening services like bit.ly and goo.gl can be used to make long and complicated URLs a bit of mask. However, they all follow the set out rules of URL naming.
Parts of the URL.
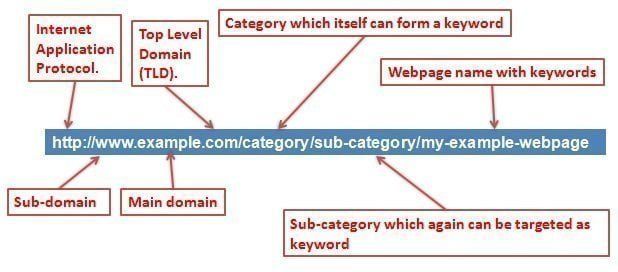

http://techjaja.com/home
The protocol: Anything that appears before :// is the protocol. In the above link, the protocol is “https“. Https and http are the most common protocols on the Internet. However, there are other protocols.
The main domain: This is what appears between www. and .com. The domain name in our example is “techjaja“. A domain can end in .com, .net, .org, .co.ug, among others.
HTTP and HTTPS.
At the beginning of this year, we shared news that your favorite Technology blog Techjaja had switched to HTTPS. HTTPS means “Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure”. Websites that have https protocol are more secure to visit than, well, websites that have http. HTTP means “Hyper Text Transfer Protocol”. Just that, no secure!
Https adds a protective layer to your entered passwords and other personal information.
IP Address.
Every device that connects to the internet uses an Internet protocol address (IP) for identification purposes. Think of the IP as your fingerprint on the web, although the IP is assigned automatically in most cases. However that not stuff a beginner wants to get into right now.
This is an example of an IP address: 192.4.398.21 or 41DA:F3:0:2F6D:5AA:FF:EDF4:7C3A
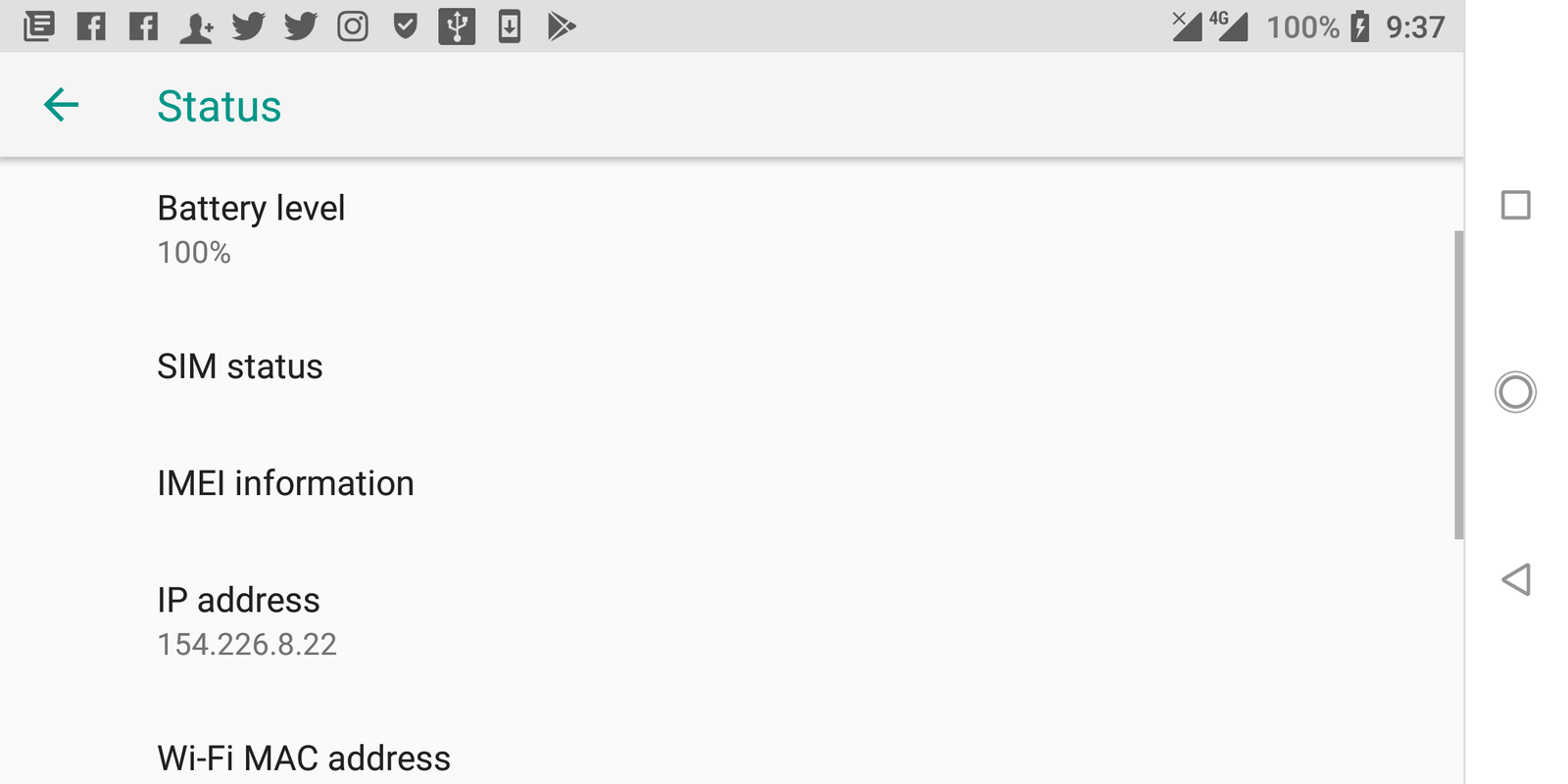

An IP address is basically for tracking purposes, just like the fingerprint would be traced back to you. Some IP addresses are permanently assigned or may change from time to time. however, an IP address is always unique.
Encryption and Authentication.
Encryption is basically mathematical scrambling of data so that it id hidden from unauthorized persons. It uses complex formulae to turn private data into incomprehensible hogwash that only a trusted reader can unscramble.
Many Ugandans are innocently using the power of encryption to dodge social media tax using VPN networks. And oh, WhatsApp messages are end-to-end encrypted too so that only the receiver reads them.
Authentication and encryption have a lot in common. Authentication is the complex way that computer systems verify that you are who you say you are. You therefore need proper authentication so that you gain access to encrypted data.
Cloud Computing
The cloud is a virtual space where you can use software you would rather rent than own. With web browsers, users access the cloud on the internet and log in to their online rented copies of their cloud-based software.

The use of cloud computing is increasing tremendously to match people’s need to access files from multiple devices. With the cloud, you can save music, photos, and other things and then access them from a range of internet enabled devices.
Cloud computing can involve cloud storage services like Dropbox, Drive, Sky Drive among others. Also a service such as Google Docs is an example of cloud computing. This one makes collaboration among individuals on the same files (docs) in the cloud possible.
Malware
Malware refers to malicious software designed by hackers.

It includes:
- Viruses
- Trojans
- Keyloggers
- Zombie programs
Malware does the following:
- Stealing private information.
- Taking remote control of your computer/device.
- Vandalize your device and alter its functionality.
Malware programs are all over the internet and a device needs a Firewall to protect it. Also important is the basic knowledge of how to prevent these malicious programs from getting to your devices.



