Lesions of the Menisci
- 1. LESIONS OF THE MENISCI ROSSHINI JAGATHESWARAN 6/3/2014 1
- 2. Tears of the meniscus More likely to tear along its length 6/3/2014 2
- 3. Mechanism of Injury Rotational grinding force (knee flexed and twisted while taking weight – footballers) Common in medial meniscus Classification Vertical/Longitudinal Horizontal Radial 6/3/2014 3
- 4. Vertical/longitudinal tears Most common Anterior horn tear Posterior horn tear Bucket-handle tear 6/3/2014 4
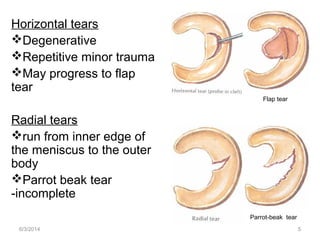
- 5. Horizontal tears Degenerative Repetitive minor trauma May progress to flap tear Radial tears run from inner edge of the meniscus to the outer body Parrot beak tear -incomplete Flap tear Parrot-beak tear 6/3/2014 5
- 6. Clinical Features Usually a young person Twisting injury Sports injury Symptoms Pain Avoids further activity Locking of the knee in partial flexion (DIAGNOSTIC) Swelling Recur periodically after trivial twists and strains 6/3/2014 6
- 7. Signs Joint may be held slightly flexed Effusion of the knee – patellar tap positive Wasting of quadriceps Tenderness localised to joint line Full flexion but limited extension McMurray’s test positive Apley’s grinding test positive Thessaly test positive 6/3/2014 8
- 8. Differences between hemarthrosis and effusion Hemarthrosis Effusion Swelling seen immediately after injury Swelling presents later after injury Cruciate or peripheral meniscal lesion in the absence of a fracture Tear of the inner meniscus or synovial irritation Patella tap positive 6/3/2014 9
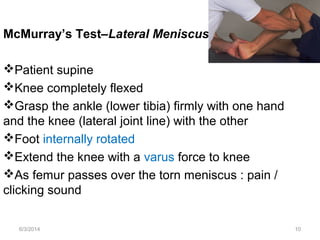
- 9. McMurray’s Test–Lateral Meniscus Patient supine Knee completely flexed Grasp the ankle (lower tibia) firmly with one hand and the knee (lateral joint line) with the other Foot internally rotated Extend the knee with a varus force to knee As femur passes over the torn meniscus : pain / clicking sound 6/3/2014 10
- 10. McMurray’s Test – Medial Meniscus Patient supine Knee completely flexed Grasp the ankle (lower tibia) firmly with one hand and the knee (medial joint line) with the other Foot externally rotated Extend the knee with a valgus force to knee As femur passes over the torn meniscus : pain / clicking sound 6/3/2014 11
- 11. Apley’s grinding test Patient prone Knee flexed to 90 degrees Knee rotated Compression force applied Pain indicates torn meniscus 6/3/2014 13
- 12. Thessaly Test Patient stands flat footed on one leg Examiner hold his/her hands Flex the affected knee to 20 degrees Ask patient to twist body side to side thrice Pain at medial or lateral joint lines, locking – meniscal tear 6/3/2014 14
- 13. Investigations Plain X-rays Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Arthroscopy 6/3/2014 15
- 16. Differential Diagnosis Loose bodies Recurrent dislocation of patella Fracture of tibial spine Partial tear of medial collateral ligament Torn anterior cruciate ligament 6/3/2014 19
- 17. Tears of the meniscus Treatment Dealing with the locked knee •Gentle passive flexion and rotation Conservative •After an cute episode, joint held straight in plaster backslab for 3-4 weeks •Crutches and quadriceps exercise •RICE protocol Operative •Indicated if joint cannot be unlocked and symptoms are recurrent 6/3/2014 20