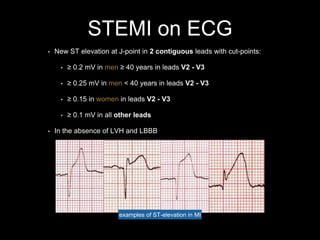
Stemi criteria
Download as PPTX, PDF7 likes7,192 views
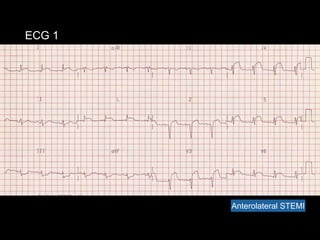
The document provides criteria for diagnosing ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) on electrocardiogram (ECG). It lists cut-off values for ST elevation in different leads used to identify STEMI based on the patient's age, sex and lead location. It cautions that baseline ECG abnormalities like left bundle branch block (LBBB) could obscure interpretation and provides examples of STEMI in different heart locations identified by affected leads on ECG.
1 of 11
Downloaded 146 times









Recommended
ECG CHALLENGE

ECG CHALLENGEPraveen Nagula This document provides descriptions of various ECG patterns and cardiac conditions:
- It describes limb lead reversal showing a sine wave pattern typical of hyperkalemia. Calcium gluconate and other treatments are recommended.
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm is defined as having a rate between 50-100 bpm and being a type of slow ventricular tachycardia that does not typically require treatment.
- Atrial flutter with a 4:1 conduction is described as typical or atypical, with atypical often occurring after surgeries. Atrial flutter can be cardioverted with the least amount of energy.
- Several other conditions are briefly defined such as complete heart block, dextro
WIDE QRS TACHYCARDIA

WIDE QRS TACHYCARDIAhttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/ 1) The document defines wide complex tachycardia as a rhythm with a QRS duration ≥120ms and heart rate >100 bpm.
2) The main causes listed are ventricular tachycardia (80% of cases) and supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy.
3) Key features that can help differentiate the underlying rhythm include QRS duration, axis, morphology, and the presence or absence of AV dissociation on electrocardiogram.
Myocardial infarction (MI) ecg localisation

Myocardial infarction (MI) ecg localisationMalleswara rao Dangeti This document discusses various non-coronary causes of ST-elevation on electrocardiograms (ECGs) including ventricular aneurysms, pericarditis, early repolarization patterns, left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle branch block, hypothermia, cardioversion, intraventricular hemorrhage, hyperkalemia, Brugada pattern, type 1C antiarrhythmic drugs, hypercalcemia, pulmonary embolism, hypothermia, myocarditis, and tumor invasion of the left ventricle. It then discusses left ventricular aneurysms, early repolarization, acute pericarditis, hyperkalemia, hypothermia, increased intracranial pressure, Brugada syndrome, Tak
Avrt and avnrt

Avrt and avnrtPDT DM CARDIOLOGY 1. AVNRT and AVRT are types of supraventricular tachycardia involving abnormal pathways for electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles.
2. AVNRT is caused by a reentry circuit within the AV node, while AVRT involves an accessory pathway bypassing the AV node.
3. There are different subtypes of AVNRT and AVRT depending on which pathways are involved in the antegrade and retrograde directions. Typical AVNRT involves a slow-fast pathway while typical AVRT involves orthodromic conduction over an accessory pathway.
Ventricular tachycardia

Ventricular tachycardiaApollo Hospitals Ventricular tachycardia is a fast heart rhythm originating from the ventricles with a rate over 100 bpm. It is classified based on duration (sustained vs non-sustained), morphology (monomorphic, polymorphic, sinusoidal), and symptoms. Causes include structural heart disease, electrolyte abnormalities, drugs, and prolonged QT interval. Diagnosis involves ECG criteria showing ventricular origin. Treatment depends on hemodynamic stability and may include antiarrhythmic drugs, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, catheter ablation, or surgery. Recurrent ventricular tachycardia is managed long term with devices, drugs, and treatment of underlying causes.
Ecg in acs

Ecg in acsLPS Institute of Cardiology Kanpur UP India The document discusses electrocardiograms (ECGs) in the context of acute coronary syndrome. It begins by describing the normal conduction system and the 12 standard ECG leads. It then explains how ECGs are recorded and the positioning of limb and precordial leads. The document discusses ST segments, T waves, and how to evaluate for ST elevations. It defines acute coronary syndrome and describes the classifications of ST-elevation MI, non-ST-elevation MI, and unstable angina based on ECG and cardiac enzyme findings. Specific ECG patterns for lateral, inferior, septal, and posterior wall MIs are also shown.
Brugada syndrome

Brugada syndromekazi alam nowaz Brugada Syndrome is characterized by ST elevation in leads V1-V3, structurally normal hearts, and a risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. It is caused by mutations in the SCN5A gene which codes for cardiac sodium channels. It is more prevalent in Southeast Asian populations and clinical manifestations often first occur in the third to fourth decade of life. Diagnosis requires a characteristic ECG pattern that can be enhanced by sodium channel blockers. An ICD is the first-line treatment for preventing sudden cardiac death from ventricular arrhythmias in symptomatic patients.
Lvh & rvh

Lvh & rvhNiyaz Mohammed This document discusses left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). It defines LVH as an increase in left ventricle mass due to increased wall thickness or cavity size. There are two types of LVH - systolic overload from conditions like hypertension which compromise the left ventricle during systole, and diastolic overload from things like valvular diseases which compromise it during diastole. The document outlines ECG criteria for diagnosing LVH including Sokolov-Lyon and Cornell voltage criteria. It also discusses RVH manifestations on ECG like right axis deviation, tall R waves in right precordial leads, and an S1S2S3 pattern.
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)Kerolus Shehata - Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is caused by conditions that damage the left bundle branch, such as hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathy, and ischemic heart disease.
- LBBB is diagnosed based on criteria including a QRS duration of over 120ms and abnormal ST segment and T wave patterns.
- The prognosis of LBBB depends on any underlying heart conditions, with LBBB increasing the risk of mortality. LBBB may resolve temporarily following a premature ventricular contraction due to resetting of the conduction system.
Tachyarrhythmias

TachyarrhythmiasSCGH ED CME This document discusses various tachyarrhythmias, including:
- Supraventricular tachycardias like atrial flutter, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, and AV reentrant tachycardia.
- Ventricular arrhythmias including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular flutter.
- Irregular rhythms such as atrial fibrillation.
It provides details on characteristics like rate, morphology, underlying causes, and treatment approaches for each type of tachycardia. Emphasis is placed on distinguishing ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy in clinical evaluation.
Systolic murmur

Systolic murmurSujay Iyer This document discusses systolic murmurs. It defines a systolic murmur as a prolonged vibration due to disturbed blood flow that manifests as turbulence, usually heard best at the site of turbulence. Systolic murmurs can be ejection or regurgitant in nature. Ejection murmurs occur with forward blood flow through the outflow tracts of the left or right ventricle. Regurgitant murmurs occur with retrograde blood flow from a high pressure to low pressure chamber. Common causes, characteristics, and features of different types of systolic murmurs are described in detail.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathyFuad Farooq A 17-year-old male basketball player collapsed during practice and suffered cardiac arrest. An autopsy later revealed he had hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a genetic heart condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick. HCM is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. The patient had previously noticed some shortness of breath with exertion but it did not limit his activity. He was found to have a heart murmur as a child but it was never investigated. HCM causes the left ventricle to become thickened and stiff, which can obstruct blood flow out of the heart and cause heart failure, chest pain, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.
Mitral valve prolapse

Mitral valve prolapseHasnein Mohamedali MD Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a common condition where the mitral valve leaflets bulge into the left atrium during systole. While often asymptomatic, it can increase the risk of arrhythmias, endocarditis, stroke, and mitral regurgitation. The classic findings are a mid-to-late systolic click and murmur. Treatment involves monitoring for complications and addressing symptoms like with beta-blockers. For severe mitral regurgitation, early surgical repair is recommended to prevent left ventricular dysfunction.
Right and left ventricular hypertrophy

Right and left ventricular hypertrophyRawalpindi Medical College Left ventricular hypertrophy is an increase in the mass of the left ventricle that can be caused by hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, aortic stenosis, or athletic training. It is defined on an ECG as increased voltages in certain leads. Risk factors include age, gender, high blood pressure, obesity, and genetic factors. If left untreated, LVH can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, heart attack, or sudden cardiac death. Right ventricular hypertrophy is the enlargement of the right ventricle and can be caused by pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart defects, or lung diseases. Both LVH and RVH are diagnosed using ECG criteria and can cause chest pain, palpitations
Ecg changes in mi

Ecg changes in miIndhu Reddy This document summarizes electrocardiogram (ECG) findings related to myocardial infarction (MI). It describes the ECG changes that occur in the hyperacute, evolved, and chronic phases of MI. These include ST segment elevation, T wave changes, Q wave development, and other abnormalities. It also discusses ECG patterns related to injury of specific coronary artery territories and criteria for diagnosing MI when a left bundle branch block is present.
hocm.pptx

hocm.pptxakifab93 HCM is a common genetic heart disease reported in populations globally
Inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern
The distribution of HCM is equal by sex, although women are diagnosed less commonly than men
The prevalence of unexplained asymptomatic hypertrophy in young adults has been reported to range from 1:200 to 1:500
Approach to bradyarrythmias1

Approach to bradyarrythmias1Bhargav Kiran This document discusses bradyarrhythmias and approach to treatment. It defines various types of sinus node dysfunction and AV conduction blocks including sick sinus syndrome, sinus pause, sinus arrest, tachy-brady syndrome, and different degrees of AV block. It describes evaluation of sinus node function including intrinsic heart rate, sinus node recovery time and SA conduction time. It discusses reversible and irreversible causes of bradyarrhythmias and guidelines for pacemaker implantation for sinus node and AV node dysfunction. Treatment options including medications and permanent pacing are outlined.
Sinus Node Dysfunction

Sinus Node DysfunctionRaghu Kishore Galla The sinus node is the dominant pacemaker of the heart located in the right atrium. Sinus node dysfunction can cause abnormal automaticity or conduction, resulting in bradycardic rhythms like sinus bradycardia, sinus pauses, or tachycardic rhythms like inappropriate sinus tachycardia. Evaluation involves surface ECG, exercise testing, drug challenge, and invasive electrophysiological study if needed to diagnose sinus node disorders.
ARVD (Arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) - updated task force cr...

ARVD (Arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) - updated task force cr...Imran Ahmed This document discusses arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). It begins by explaining the genetics of ARVC, noting that mutations can be either dominant or recessive. It then describes the natural history, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and criteria used to diagnose ARVC based on the revised Task Force Criteria. This includes major and minor criteria in categories such as imaging, electrocardiography findings, biopsy results, and family history. The document concludes by discussing management strategies for ARVC including ICD therapy, antiarrhythmic drugs, ablation, heart failure treatment, and transplantation.
Bundle branch blocks

Bundle branch blocksSonukurian RBBB is characterized by a QRS duration ≥0.12s with an RSR' pattern in V1 and a wide S wave in V6. Causes include myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, and pulmonary embolism. LBBB has a QS or rS pattern in V1 and a late intrinsicoid deflection in V6. It is associated with ischemic heart disease and cardiomyopathy. New onset LBBB alone is no longer considered a STEMI equivalent. The Sgarbossa criteria help identify MI in the presence of LBBB. Left anterior and posterior fascicular blocks involve specific QRS and axis changes and help localize conduction system disease. Trifascicular block represents complete heart block with bifascicular
Stemi

Stemikazi alam nowaz The document discusses guidelines for the treatment of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It defines STEMI as a type of acute coronary syndrome where a completely occlusive thrombus results in total cessation of blood flow seen as ST elevation on an electrocardiogram. Immediate treatment goals for STEMI patients include pain control, rapid identification for reperfusion therapy, and avoiding inappropriate discharge. Initial emergency room management involves aspirin, clopidogrel, nitrates, morphine, and supplemental oxygen. Reperfusion options include fibrinolysis or primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Complications of STEMI can be early issues like cardiogenic shock or late problems like heart failure.
AVNRT

AVNRThttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/ AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), or atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia, is a type of tachycardia (fast rhythm) of the heart. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), meaning that it originates from a location within the heart above the bundle of His. AV nodal reentrant tachycardia is the most common regular supraventricular tachycardia. It is more common in women than men (approximately 75% of cases occur in females). The main symptom is palpitations. Treatment may be with specific physical maneuvers, medication, or, rarely, synchronized cardioversion. Frequent attacks may require radiofrequency ablation, in which the abnormally conducting tissue in the heart is destroyed.
AVNRT occurs when a reentry circuit forms within or just next to the atrioventricular node. The circuit usually involves two anatomical pathways: the fast pathway and the slow pathway, which are both in the right atrium. The slow pathway (which is usually targeted for ablation) is located inferior and slightly posterior to the AV node, often following the anterior margin of the coronary sinus. The fast pathway is usually located just superior and posterior to the AV node. These pathways are formed from tissue that behaves very much like the AV node, and some authors regard them as part of the AV node.
The fast and slow pathways should not be confused with the accessory pathways that give rise to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW syndrome) or atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT). In AVNRT, the fast and slow pathways are located within the right atrium close to or within the AV node and exhibit electrophysiologic properties similar to AV nodal tissue. Accessory pathways that give rise to WPW syndrome and AVRT are located in the atrioventricular valvular rings. They provide a direct connection between the atria and ventricles, and have electrophysiologic properties similar to ventricular myocardium.
STEMI Equivalent 

STEMI Equivalent Rashid Abuelhassan This document provides an overview of various electrocardiogram (ECG) findings that can indicate acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or critical stenosis requiring intervention. It discusses ECG patterns seen in posterior MIs, left main coronary artery occlusions, De Winter's T waves, Wellen's syndrome, and Sgarbossa's criteria. Assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction is also reviewed, including fractional shortening, Simpson's method, and E-point septal separation. Limitations of certain methods in specific conditions are noted.
Eisenmenger syndrome

Eisenmenger syndromeKapil Vasanth This document provides an overview of Eisenmenger syndrome, including its definition, causes, classifications, modes of presentation, and treatment approaches. Some key points include:
- Eisenmenger syndrome is defined as irreversible pulmonary hypertension caused by uncorrected congenital shunts between the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
- It can be caused by defects such as ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, and patent ductus arteriosus. Its presentation and progression depends on factors like the size and location of the defect.
- Patients typically experience symptoms like dyspnea, cyanosis, hyperviscosity, and right heart failure. Complications can include hemoptysis, stroke, and cerebral abs
Long QT Syndrome

Long QT SyndromeStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine 1) A 70-year-old woman presented with fever for 20-25 days and was found to have bradycardia and a prolonged QT interval, consistent with acquired prolonged QT syndrome.
2) She later developed ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest. Electrical cardioversion was required to restore sinus rhythm.
3) A temporary pacemaker was inserted and she was monitored in the intensive care unit. Her QT interval gradually normalized over the next few days with treatment.
EISENMENGER SYNDROME- PAUL WOOD

EISENMENGER SYNDROME- PAUL WOODDr. Murtaza Kamal MD,DNB,DrNB Ped Cardiology This document discusses Eisenmenger syndrome, a condition where pulmonary hypertension develops due to increased blood flow through defects between the systemic and pulmonary circulations. It provides details on causes, clinical features, pathology findings, and treatments. Key points include:
- Eisenmenger syndrome is caused by defects like VSDs, ASDs, and PDA that allow high blood flow to the lungs and cause pulmonary hypertension over time.
- Common causes of death include hemoptysis from pulmonary artery ruptures, heart failure, and complications from attempted defect repair surgery.
- Pathological findings show thickened pulmonary arteries that resemble the fetal pattern and contribute to high pulmonary vascular resistance.
- Medical treatments are generally ineffective once int
Aortic stenosis for post graduates

Aortic stenosis for post graduatesPROFESSOR DR. MD. TOUFIQUR RAHMAN A 63-year-old man presented with syncope, shortness of breath, and other symptoms for 2 years. Examination found dyspnea, tachycardia, low blood pressure, a systolic thrill, and left ventricular hypertrophy. Imaging showed severe aortic stenosis. The patient underwent transcatheter aortic valve implantation and is now doing well.
Brady arryhthmias

Brady arryhthmiasPraveen Nagula Bradyarrhythmias are caused by problems with impulse formation in the sinus node or impulse conduction through the AV node. Sinus node dysfunction can cause sinus bradycardia, sinus pause/arrest, or chronotropic incompetence. Atrioventricular block is classified as first, second, or third degree and may be caused by conditions like CAD, drugs, or infiltrative diseases. Second degree AV block is further classified as Mobitz type I or II based on PR interval characteristics. Third degree AV block causes complete dissociation between atrial and ventricular rhythms.
Stemi equivalents

Stemi equivalentsMohamed Hamoda 1) STEMI equivalents refer to patients with acutely occluded coronary arteries who do not present with classical ECG changes but have worse outcomes. Common equivalents include de Winter ST/T waves, Wellens' syndromes, ST elevation in aVR, new LBBB, isolated posterior MIs, and upright T waves in V1.
2) Wellens' syndromes present with progressive T wave inversions in leads V2-V3 and little cardiac marker elevation, indicating critical proximal LAD stenosis.
3) ST elevation in aVR with widespread ST depression indicates high-risk left main or three-vessel coronary disease requiring emergent angiography.
Stemi equivalents

Stemi equivalentsMohamed Hamoda 1) STEMI equivalents refer to patients with acutely occluded coronary arteries who do not present with classical ECG changes but have worse outcomes. Common equivalents include de Winter ST/T waves, Wellens' syndromes, ST elevation in aVR, new LBBB, isolated posterior MIs, and upright T waves in V1.
2) Wellens' syndromes present with progressive T wave inversions in leads V2-V3 and little cardiac marker elevation, indicating critical proximal LAD stenosis.
3) ST elevation in aVR with widespread ST depression indicates high-risk left main or three-vessel coronary disease requiring emergent angiography.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)Kerolus Shehata - Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is caused by conditions that damage the left bundle branch, such as hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathy, and ischemic heart disease.
- LBBB is diagnosed based on criteria including a QRS duration of over 120ms and abnormal ST segment and T wave patterns.
- The prognosis of LBBB depends on any underlying heart conditions, with LBBB increasing the risk of mortality. LBBB may resolve temporarily following a premature ventricular contraction due to resetting of the conduction system.
Tachyarrhythmias

TachyarrhythmiasSCGH ED CME This document discusses various tachyarrhythmias, including:
- Supraventricular tachycardias like atrial flutter, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, and AV reentrant tachycardia.
- Ventricular arrhythmias including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular flutter.
- Irregular rhythms such as atrial fibrillation.
It provides details on characteristics like rate, morphology, underlying causes, and treatment approaches for each type of tachycardia. Emphasis is placed on distinguishing ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy in clinical evaluation.
Systolic murmur

Systolic murmurSujay Iyer This document discusses systolic murmurs. It defines a systolic murmur as a prolonged vibration due to disturbed blood flow that manifests as turbulence, usually heard best at the site of turbulence. Systolic murmurs can be ejection or regurgitant in nature. Ejection murmurs occur with forward blood flow through the outflow tracts of the left or right ventricle. Regurgitant murmurs occur with retrograde blood flow from a high pressure to low pressure chamber. Common causes, characteristics, and features of different types of systolic murmurs are described in detail.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathyFuad Farooq A 17-year-old male basketball player collapsed during practice and suffered cardiac arrest. An autopsy later revealed he had hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a genetic heart condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick. HCM is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. The patient had previously noticed some shortness of breath with exertion but it did not limit his activity. He was found to have a heart murmur as a child but it was never investigated. HCM causes the left ventricle to become thickened and stiff, which can obstruct blood flow out of the heart and cause heart failure, chest pain, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.
Mitral valve prolapse

Mitral valve prolapseHasnein Mohamedali MD Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a common condition where the mitral valve leaflets bulge into the left atrium during systole. While often asymptomatic, it can increase the risk of arrhythmias, endocarditis, stroke, and mitral regurgitation. The classic findings are a mid-to-late systolic click and murmur. Treatment involves monitoring for complications and addressing symptoms like with beta-blockers. For severe mitral regurgitation, early surgical repair is recommended to prevent left ventricular dysfunction.
Right and left ventricular hypertrophy

Right and left ventricular hypertrophyRawalpindi Medical College Left ventricular hypertrophy is an increase in the mass of the left ventricle that can be caused by hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, aortic stenosis, or athletic training. It is defined on an ECG as increased voltages in certain leads. Risk factors include age, gender, high blood pressure, obesity, and genetic factors. If left untreated, LVH can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, heart attack, or sudden cardiac death. Right ventricular hypertrophy is the enlargement of the right ventricle and can be caused by pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart defects, or lung diseases. Both LVH and RVH are diagnosed using ECG criteria and can cause chest pain, palpitations
Ecg changes in mi

Ecg changes in miIndhu Reddy This document summarizes electrocardiogram (ECG) findings related to myocardial infarction (MI). It describes the ECG changes that occur in the hyperacute, evolved, and chronic phases of MI. These include ST segment elevation, T wave changes, Q wave development, and other abnormalities. It also discusses ECG patterns related to injury of specific coronary artery territories and criteria for diagnosing MI when a left bundle branch block is present.
hocm.pptx

hocm.pptxakifab93 HCM is a common genetic heart disease reported in populations globally
Inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern
The distribution of HCM is equal by sex, although women are diagnosed less commonly than men
The prevalence of unexplained asymptomatic hypertrophy in young adults has been reported to range from 1:200 to 1:500
Approach to bradyarrythmias1

Approach to bradyarrythmias1Bhargav Kiran This document discusses bradyarrhythmias and approach to treatment. It defines various types of sinus node dysfunction and AV conduction blocks including sick sinus syndrome, sinus pause, sinus arrest, tachy-brady syndrome, and different degrees of AV block. It describes evaluation of sinus node function including intrinsic heart rate, sinus node recovery time and SA conduction time. It discusses reversible and irreversible causes of bradyarrhythmias and guidelines for pacemaker implantation for sinus node and AV node dysfunction. Treatment options including medications and permanent pacing are outlined.
Sinus Node Dysfunction

Sinus Node DysfunctionRaghu Kishore Galla The sinus node is the dominant pacemaker of the heart located in the right atrium. Sinus node dysfunction can cause abnormal automaticity or conduction, resulting in bradycardic rhythms like sinus bradycardia, sinus pauses, or tachycardic rhythms like inappropriate sinus tachycardia. Evaluation involves surface ECG, exercise testing, drug challenge, and invasive electrophysiological study if needed to diagnose sinus node disorders.
ARVD (Arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) - updated task force cr...

ARVD (Arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) - updated task force cr...Imran Ahmed This document discusses arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). It begins by explaining the genetics of ARVC, noting that mutations can be either dominant or recessive. It then describes the natural history, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and criteria used to diagnose ARVC based on the revised Task Force Criteria. This includes major and minor criteria in categories such as imaging, electrocardiography findings, biopsy results, and family history. The document concludes by discussing management strategies for ARVC including ICD therapy, antiarrhythmic drugs, ablation, heart failure treatment, and transplantation.
Bundle branch blocks

Bundle branch blocksSonukurian RBBB is characterized by a QRS duration ≥0.12s with an RSR' pattern in V1 and a wide S wave in V6. Causes include myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, and pulmonary embolism. LBBB has a QS or rS pattern in V1 and a late intrinsicoid deflection in V6. It is associated with ischemic heart disease and cardiomyopathy. New onset LBBB alone is no longer considered a STEMI equivalent. The Sgarbossa criteria help identify MI in the presence of LBBB. Left anterior and posterior fascicular blocks involve specific QRS and axis changes and help localize conduction system disease. Trifascicular block represents complete heart block with bifascicular
Stemi

Stemikazi alam nowaz The document discusses guidelines for the treatment of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It defines STEMI as a type of acute coronary syndrome where a completely occlusive thrombus results in total cessation of blood flow seen as ST elevation on an electrocardiogram. Immediate treatment goals for STEMI patients include pain control, rapid identification for reperfusion therapy, and avoiding inappropriate discharge. Initial emergency room management involves aspirin, clopidogrel, nitrates, morphine, and supplemental oxygen. Reperfusion options include fibrinolysis or primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Complications of STEMI can be early issues like cardiogenic shock or late problems like heart failure.
AVNRT

AVNRThttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/ AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), or atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia, is a type of tachycardia (fast rhythm) of the heart. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), meaning that it originates from a location within the heart above the bundle of His. AV nodal reentrant tachycardia is the most common regular supraventricular tachycardia. It is more common in women than men (approximately 75% of cases occur in females). The main symptom is palpitations. Treatment may be with specific physical maneuvers, medication, or, rarely, synchronized cardioversion. Frequent attacks may require radiofrequency ablation, in which the abnormally conducting tissue in the heart is destroyed.
AVNRT occurs when a reentry circuit forms within or just next to the atrioventricular node. The circuit usually involves two anatomical pathways: the fast pathway and the slow pathway, which are both in the right atrium. The slow pathway (which is usually targeted for ablation) is located inferior and slightly posterior to the AV node, often following the anterior margin of the coronary sinus. The fast pathway is usually located just superior and posterior to the AV node. These pathways are formed from tissue that behaves very much like the AV node, and some authors regard them as part of the AV node.
The fast and slow pathways should not be confused with the accessory pathways that give rise to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW syndrome) or atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT). In AVNRT, the fast and slow pathways are located within the right atrium close to or within the AV node and exhibit electrophysiologic properties similar to AV nodal tissue. Accessory pathways that give rise to WPW syndrome and AVRT are located in the atrioventricular valvular rings. They provide a direct connection between the atria and ventricles, and have electrophysiologic properties similar to ventricular myocardium.
STEMI Equivalent 

STEMI Equivalent Rashid Abuelhassan This document provides an overview of various electrocardiogram (ECG) findings that can indicate acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or critical stenosis requiring intervention. It discusses ECG patterns seen in posterior MIs, left main coronary artery occlusions, De Winter's T waves, Wellen's syndrome, and Sgarbossa's criteria. Assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction is also reviewed, including fractional shortening, Simpson's method, and E-point septal separation. Limitations of certain methods in specific conditions are noted.
Eisenmenger syndrome

Eisenmenger syndromeKapil Vasanth This document provides an overview of Eisenmenger syndrome, including its definition, causes, classifications, modes of presentation, and treatment approaches. Some key points include:
- Eisenmenger syndrome is defined as irreversible pulmonary hypertension caused by uncorrected congenital shunts between the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
- It can be caused by defects such as ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, and patent ductus arteriosus. Its presentation and progression depends on factors like the size and location of the defect.
- Patients typically experience symptoms like dyspnea, cyanosis, hyperviscosity, and right heart failure. Complications can include hemoptysis, stroke, and cerebral abs
Long QT Syndrome

Long QT SyndromeStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine 1) A 70-year-old woman presented with fever for 20-25 days and was found to have bradycardia and a prolonged QT interval, consistent with acquired prolonged QT syndrome.
2) She later developed ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest. Electrical cardioversion was required to restore sinus rhythm.
3) A temporary pacemaker was inserted and she was monitored in the intensive care unit. Her QT interval gradually normalized over the next few days with treatment.
EISENMENGER SYNDROME- PAUL WOOD

EISENMENGER SYNDROME- PAUL WOODDr. Murtaza Kamal MD,DNB,DrNB Ped Cardiology This document discusses Eisenmenger syndrome, a condition where pulmonary hypertension develops due to increased blood flow through defects between the systemic and pulmonary circulations. It provides details on causes, clinical features, pathology findings, and treatments. Key points include:
- Eisenmenger syndrome is caused by defects like VSDs, ASDs, and PDA that allow high blood flow to the lungs and cause pulmonary hypertension over time.
- Common causes of death include hemoptysis from pulmonary artery ruptures, heart failure, and complications from attempted defect repair surgery.
- Pathological findings show thickened pulmonary arteries that resemble the fetal pattern and contribute to high pulmonary vascular resistance.
- Medical treatments are generally ineffective once int
Aortic stenosis for post graduates

Aortic stenosis for post graduatesPROFESSOR DR. MD. TOUFIQUR RAHMAN A 63-year-old man presented with syncope, shortness of breath, and other symptoms for 2 years. Examination found dyspnea, tachycardia, low blood pressure, a systolic thrill, and left ventricular hypertrophy. Imaging showed severe aortic stenosis. The patient underwent transcatheter aortic valve implantation and is now doing well.
Brady arryhthmias

Brady arryhthmiasPraveen Nagula Bradyarrhythmias are caused by problems with impulse formation in the sinus node or impulse conduction through the AV node. Sinus node dysfunction can cause sinus bradycardia, sinus pause/arrest, or chronotropic incompetence. Atrioventricular block is classified as first, second, or third degree and may be caused by conditions like CAD, drugs, or infiltrative diseases. Second degree AV block is further classified as Mobitz type I or II based on PR interval characteristics. Third degree AV block causes complete dissociation between atrial and ventricular rhythms.
Viewers also liked (19)
Stemi equivalents

Stemi equivalentsMohamed Hamoda 1) STEMI equivalents refer to patients with acutely occluded coronary arteries who do not present with classical ECG changes but have worse outcomes. Common equivalents include de Winter ST/T waves, Wellens' syndromes, ST elevation in aVR, new LBBB, isolated posterior MIs, and upright T waves in V1.
2) Wellens' syndromes present with progressive T wave inversions in leads V2-V3 and little cardiac marker elevation, indicating critical proximal LAD stenosis.
3) ST elevation in aVR with widespread ST depression indicates high-risk left main or three-vessel coronary disease requiring emergent angiography.
Stemi equivalents

Stemi equivalentsMohamed Hamoda 1) STEMI equivalents refer to patients with acutely occluded coronary arteries who do not present with classical ECG changes but have worse outcomes. Common equivalents include de Winter ST/T waves, Wellens' syndromes, ST elevation in aVR, new LBBB, isolated posterior MIs, and upright T waves in V1.
2) Wellens' syndromes present with progressive T wave inversions in leads V2-V3 and little cardiac marker elevation, indicating critical proximal LAD stenosis.
3) ST elevation in aVR with widespread ST depression indicates high-risk left main or three-vessel coronary disease requiring emergent angiography.
STEMI and Acute Coronary Syndromes

STEMI and Acute Coronary SyndromesRommie Duckworth This highly energetic lecture presents the pathophysiology of S-T elevation myocardial infarction in an easy to understand style to help you best identify, triage and treat patients presenting with acute coronary syndromes. Using the latest research behind the AHA Guidelines changes, AHA National Faculty Rom Duckworth will help you better coordinate with you partners along the continuum of cardiac care. Emphasis is placed on risk factors, recognizing truly sick patients and coordinating care with hospital personnel.
Learning Objectives: Students will learn:
-The pathophysiology of S-T elevation myocardial infarction.
-The difference between STEMI, NSTEMI and unstable angina.
-Differing treatment methods and priorities for different cardiac syndromes.
-The function and importance of 12 lead ECG and prehospital diagnostic testing.
-The roles and responsibilities of EMS providers as the key element in “door-to-balloon” and “door-to-needle” time for STEMI patients.
www.romduck.com
www.RescueDigest.com
American Heart AVOID study: Air Versus Oxygen In ST-elevation myocardial Infa...

American Heart AVOID study: Air Versus Oxygen In ST-elevation myocardial Infa...Emergency Live We’ve been waiting for the AVOID study, since we mentioned it a few years ago in another post on the harm of excessive oxygen. AVOID (Air Versus Oxygen in Myocardial Infarction). Now, it’s out. As expected, it shows that unnecessary oxygen supplement worsens outcome. The surprise is just how big a difference it makes! In this study, too much oxygen increased recurrent MI fivefold!
Avoiding hyperoxemia isn’t new. Normoxemia has been a trend, but lacked hard evidence in form of an RCT, and the reflex-O2-mask in ED has been hard to fight. Right now, the full AVOID article has yet to be released, but the results have just been presented at AHA’s congress in Chicago last week. And AHA has posted a video interview with Dr. Stub, one of the investigators of the AVOID trial, on the results, as well as posted his presentation slides here. This research performed an investigator initiated multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare supplemental oxygen therapy with no oxygen therapy in normoxic patients with STEMI to determine its effect on myocardial infarct size.
ORIGINAL SOURCE: http://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_469664.pdf
King Bay ECG/STEMI

King Bay ECG/STEMIUFJaxEMS This document provides a summary of basics of electrocardiography (EKG/ECG) interpretation for emergency medicine. It begins with an overview of cardiac anatomy and the electrical conduction system. It then discusses components of the EKG including waves, intervals, rates, and rhythms. Common arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular tachycardia are summarized. Interpretation of EKG findings including rates, rhythms, intervals, and morphologies are covered. The document concludes with a focus on ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) including location, treatment protocols, and example EKGs.
Recognition & management of bradycardia pediatrics AG

Recognition & management of bradycardia pediatrics AGAkshay Golwalkar This document provides an overview of bradycardia in children, including definitions, types, recognition, ECG characteristics, and management. It describes bradycardia as an abnormally slow heart rate for a child's age that can rapidly lead to cardiopulmonary compromise. The document outlines initial steps to stabilize a child with bradycardia, including checking for hypotension, decreased consciousness, shock, or respiratory distress. It also provides guidelines for determining the heart rate from an ECG and classifying different types of bradycardic rhythms like sinus bradycardia or heart block. Reversible causes of bradycardia are listed as well as an algorithm for treating symptomatic bradycardia with medications.
Ecg 101 with answers

Ecg 101 with answerschricres This document provides an overview of ECG interpretation. It discusses key elements like rhythm, axis, intervals, complexes and segments. Specific conditions are highlighted like inferior posterior STEMI and RV infarct. The importance of systematic analysis is emphasized. Pattern recognition, trends over serial ECGs and correlating findings with the clinical scenario are important skills. Confirming posterior STEMI with lateral precordial lead placement is advised. Overall it is a comprehensive guide to the fundamentals of ECG interpretation and applications in patient care.
ACLS algorithms 

ACLS algorithms Kerolus Shehata The document provides guidelines for treating cardiac arrest due to asystole or pulseless electrical activity (PEA). It outlines the pulseless arrest algorithm which involves checking the rhythm, performing CPR at 100 compressions per minute, establishing IV/IO access, administering epinephrine every 3-5 minutes, and treating potential reversible causes such as hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, tamponade, thrombosis, and toxins. For asystole, the priorities are high-quality CPR, identifying and correcting reversible causes, and considering termination of efforts if no electrical activity is present after initial treatment. For PEA, the best chance of return of spontaneous circulation is through quick treatment of reversible causes such
Cardiovascular Imaging

Cardiovascular ImagingMuhammad Ayub Non-invasive imaging plays an important role in the management of cardiovascular diseases. Different imaging modalities have advantages and limitations. Echocardiography is useful for assessing cardiac structure and function but limited for coronary artery disease evaluation. Nuclear imaging can evaluate perfusion and function but not coronary anatomy directly. CT and MRI can assess coronary anatomy in addition to function but CT involves radiation. The appropriate choice of imaging modality depends on the clinical question and no single test can replace all others for evaluating cardiovascular diseases. Integrating complementary information from different tests provides the most comprehensive assessment.
ECG in Emergency Department - Advances in ACS ECG

ECG in Emergency Department - Advances in ACS ECGDr.Mahmoud Abbas ECG in Emergency Department -Advances in ACS ECG. Lecture presented by Dr Hesham Ibrahim at the Egyptian Critical Care Summit , the leading educational event and medical exhibition in Egypt.
St elevation myocardial infarction

St elevation myocardial infarctionsalaheldin abusin This document defines STEMI and describes the presentation, diagnosis, and management of a patient experiencing an ST elevation myocardial infarction through electrocardiogram findings, fibrinolytic therapy, percutaneous coronary intervention, and post-procedure care. Reperfusion therapy options like fibrinolysis with streptokinase or alteplase and primary PCI are discussed. Guidelines for long-term secondary prevention with medications and lifestyle changes are also reviewed.
X-Ray in Heart diseases

X-Ray in Heart diseaseshttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/ This document discusses the stages of pulmonary edema seen on chest x-rays and associated wedge pressures. Stage I shows early signs like deer antler sign and Kerley B lines with pressures of 12-18 mmHg. Stage II shows interstitial edema on x-ray with pressures of 19-25 mmHg. Stage III is alveolar edema appearing as bat wing shadowing on x-ray associated with pressures over 25 mmHg.
ACC/AHA 2013 STEMI GUIDELINES - SUMMARY & NEW ADDITIONS

ACC/AHA 2013 STEMI GUIDELINES - SUMMARY & NEW ADDITIONSImran Ahmed The 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of STEMI provides recommendations for reperfusion therapy. It recommends that patients with cardiogenic shock or severe heart failure be transferred for immediate cardiac catheterization. It also recommends ECG assessment by emergency medical services. Primary PCI is the preferred reperfusion strategy for STEMI when it can be performed within 12-24 hours of symptom onset. The guidelines recommend the use of drug-eluting stents in primary PCI and antiplatelet therapy to support PCI. It also provides recommendations for fibrinolytic therapy, PCI after fibrinolysis, and adjunctive antithrombotic therapies.
2015 ESC NSTEMI guidelines

2015 ESC NSTEMI guidelinesPlease hit like if you really liked my PPTs Anginal pain in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) can present in several ways, including prolonged chest pain at rest lasting over 20 minutes, new onset chest pain classified as Canadian Cardiovascular Society class II or III, recently destabilized previously stable angina with class III characteristics, or chest pain following a myocardial infarction. The document provides recommendations on diagnosis, treatment strategies, timing of invasive procedures, and long-term management of patients presenting with NSTE-ACS.
Acute coronary syndrome(STEMI GUIDELINES AND RECENT ADVANCES)

Acute coronary syndrome(STEMI GUIDELINES AND RECENT ADVANCES)Aditya Sarin This document summarizes guidelines for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It discusses epidemiology trends showing declining incidence of STEMI but increasing non-ST elevation ACS. Key recommendations include establishing regional STEMI systems, performing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) over fibrinolysis when possible within 120 minutes of first medical contact, and giving antiplatelet therapies like aspirin, clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor to support primary PCI. Recent advances in thrombus aspiration, drug-eluting stents, and antiplatelet agents are also summarized.
Chest x ray pathology

Chest x ray pathologyhai2all2000 yahoo The document provides an overview of the pathology of lung diseases as seen on chest x-rays, including signs, appearances and common causes of conditions such as consolidation, pleural effusion, atelectasis, pneumothorax, lung masses, fibrosis and infections like tuberculosis. Differential diagnoses are also provided for various lung abnormalities seen on x-rays.
Localization of MI on ECG

Localization of MI on ECGNooh Khushal The document discusses localization of myocardial ischemia, injury, and infarction based on electrocardiogram (ECG) findings. It provides information on interpreting ST segment changes and T-wave abnormalities in different leads to localize occlusion in the left anterior descending, right coronary artery, or left circumflex arteries. Reciprocal changes are also discussed as indicators of occlusion location.
Diagnostic radiology of cardiovascular 2009

Diagnostic radiology of cardiovascular 2009Sumit Prajapati This document summarizes diagnostic radiology techniques for imaging the cardiovascular system. It describes normal appearances and abnormalities seen on x-rays, CT, MRI, echocardiography and nuclear medicine imaging. Key sections outline normal cardiac anatomy and sizes seen on x-ray, as well as abnormalities such as heart enlargement, pulmonary blood flow changes, aortic abnormalities like aneurysms and dissections. Imaging methods for evaluating these conditions are also mentioned.
basics of chest X- ray interpretation

basics of chest X- ray interpretationMaha Yousif This document discusses chest x-ray interpretation and provides guidance on evaluating x-rays. It explains that tissue density determines how an x-ray beam penetrates, with denser tissues appearing whiter and less dense tissues appearing blacker. It also outlines different chest x-ray views and factors to consider like patient orientation, age, gender, and rotation. Abnormalities are described as appearing too white, too black, too large, or in the wrong place. The document stresses a systematic approach of identifying, localizing, describing lesions, and providing differential diagnoses.
Similar to Stemi criteria (20)
ECG: LBBB and Acute MI

ECG: LBBB and Acute MIStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine The document discusses an ECG of a 75-year-old female patient presenting with chest pain. The initial ECG showed left bundle branch block (LBBB) and signs of an acute myocardial infarction (MI) in the left anterior descending artery. A repeat ECG after 24 hours showed signs of left ventricular hypertrophy and anterior and inferior wall ischemia. The document then discusses various criteria for diagnosing MI in patients presenting with LBBB, including the Sgarbossa criteria. It also describes different subtypes and variants of LBBB that can complicate the diagnosis of MI.
ECGcheatsheet52.pdf

ECGcheatsheet52.pdfTirumalaRao41 The document provides guidance on electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation, including how to identify abnormalities related to hypertrophy, rhythm, rate, axis deviation, ST segments, T waves, and myocardial infarction patterns. Key signs of left atrial enlargement include a P wave duration over 0.12 seconds in lead II and bifid P waves. Right atrial enlargement presents as a P wave amplitude over 0.25mV in lead II. Pathological Q waves indicate prior myocardial infarction. ST segment elevation in two contiguous leads of over 0.1mV (or higher thresholds in some leads) suggests acute ischemia.
ECG IN STEMI.ppt

ECG IN STEMI.pptcmarosdi This document discusses the role of electrocardiograms (ECGs) in diagnosing ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It describes how ECGs can be used to:
1) Diagnose acute STEMI based on specific ST elevation patterns and cardiac marker changes.
2) Determine candidates for reperfusion therapy.
3) Assess the success of reperfusion therapy by observing the resolution of ST elevation.
It then outlines the typical ECG patterns seen in different types of STEMI based on the affected coronary artery.
ST SEGMENT IN ECG,ST ELEVATION AND ST DEPRESSION

ST SEGMENT IN ECG,ST ELEVATION AND ST DEPRESSIONDR Venkata Ramana The document discusses the ST segment of the ECG and various abnormalities that can occur. It notes that the ST segment represents the interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. ST segment elevation or depression can indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction. Various conditions are described that can cause ST segment changes, including myocardial infarction in different coronary artery territories, coronary vasospasm, pericarditis, early repolarization, and others. The morphology and patterns of ST segment abnormalities are discussed for evaluating these conditions.
Mi in lbbb i.tammi raju

Mi in lbbb i.tammi rajuTammiraju Iragavarapu This document discusses the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) in the presence of bundle branch blocks. It notes that bundle branch blocks can make ECG diagnosis of MI more difficult by altering depolarization patterns. For right bundle branch block, the criteria for diagnosing a Q-wave MI are the same as normal conduction. For left bundle branch block, the Sgarbossa criteria (ST elevation concordant with QRS, ST depression in V1-V3, discordant ST elevation ≥5mm) have high specificity but low sensitivity for acute MI diagnosis. Certain ECG patterns like abnormal Q waves may suggest prior infarction despite left bundle branch block.
LBBB

LBBBAswin Rm 1. Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality caused by impaired conduction in the left bundle branch or its fascicles.
2. LBBB can be chronic or intermittent and is often caused by coronary artery disease or hypertension.
3. On ECG, LBBB is characterized by a QRS duration ≥120ms and other abnormalities including broad R waves and abnormal ST-T wave patterns.
4. LBBB can make ECG diagnosis of myocardial infarction difficult and criteria like Sgarbossa scores are used to help identify MI in the setting of LBBB.
Lethal ECG pattern reading and diagnosis.pptx

Lethal ECG pattern reading and diagnosis.pptxHussein Alwais This document contains a series of ECGs with clinical scenarios and questions. It discusses various cardiac conditions that can be diagnosed based on abnormalities seen on ECGs, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, hyperkalemia, sodium channel blockade, Brugada syndrome, myocardial infarction, and pericardial effusion. The document uses ECGs to test the reader's ability to identify key abnormalities and determine the underlying cardiac diagnosis suggested by the ECG pattern.
Part 1 ecg 2019 slide share

Part 1 ecg 2019 slide sharehospital The document provides an overview of how to read and interpret electrocardiograms (ECGs). It discusses the normal conduction system including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and bundle of His. It describes lead placement and what different leads represent. It outlines the 10 rules for a normal ECG, including details on intervals, wave directions, and segment morphologies. It also discusses axis determination and provides examples of calculating heart rate from the ECG tracing.
2 Minute 12 Leads V5

2 Minute 12 Leads V5John Bray The document discusses how to obtain and interpret a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) to diagnose acute myocardial infarction (AMI), explaining the anatomy, waveform components, localization of ST elevations, and reciprocal changes seen with different types of AMI such as inferior, anterior, lateral, and posterior infarcts. It emphasizes that ST elevation is the most important indicator of AMI and timely treatment is critical, as AMI appears within 1-2 hours on ECG and delays increase damage. Bundle branch blocks and other conditions can obscure ECG findings, so new or presumed new bundle branch blocks are treated as potential AMI.
ECG LOCALIZTION OF CULPRIT VESSEL IN MI.pptx

ECG LOCALIZTION OF CULPRIT VESSEL IN MI.pptxruhailbhat ECG Localization of culprit vessel i myocardial infraction
Ecg that you cannot missed as emergency doctors

Ecg that you cannot missed as emergency doctorsssusere8a415 Just a summary about ecgs that you must not missed while practicing in ed
TCAD - Multi-lead ECG

TCAD - Multi-lead ECGTCADClinical This document provides guidance on performing and interpreting multi-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs). It aims to improve patient outcomes by reducing time to percutaneous coronary intervention through early ECG acquisition and transmission. Proper lead placement is emphasized for 12- and 15-lead ECGs. A systematic approach to ECG interpretation is outlined, including identifying the underlying rhythm, assessing the axis and potential hemiblocks or bundle branch blocks, using the ISAL method to determine infarct location, and evaluating for atrial abnormalities. Key waves, intervals, and criteria for identifying ventricular tachycardia, ischemia, injury, and infarction are defined.
Making Sense Through series of ECG signs.pptx

Making Sense Through series of ECG signs.pptxSadanand Indi bundle branch blocks with LBBB and diagnosis of Myocardial infarction
Indiana ENA 2013 Lead aVr

Indiana ENA 2013 Lead aVrAndrew J Bowman Lead aVr on EKGs is often overlooked but can provide important information. STE in lead aVr along with other leads could indicate LMCA stenosis or proximal LAD stenosis, suggesting acute coronary syndrome requiring emergent treatment. STE in aVr with SVT may indicate Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. VT can be distinguished from SVT in wide complex tachycardia based on the morphology in lead aVr. Lead aVr may also demonstrate findings suggestive of pericarditis or tricyclic antidepressant overdose. Careful examination of lead aVr is encouraged to identify potentially life-threatening conditions.
3rd part ECG Basics QRS complex Dr Salah Mabrouk Khallaf

3rd part ECG Basics QRS complex Dr Salah Mabrouk KhallafDr Salah Mabrouk Khallaf This document provides an overview of QRS complexes and abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It defines the components of the QRS complex and discusses causes of low or high voltage QRS complexes. Specific conditions that can cause left or right ventricular hypertrophy are described. Various conduction abnormalities are also summarized, including right and left bundle branch blocks, fascicular blocks, and bifascicular blocks. Causes of wide QRS complexes like hyperkalemia and certain drugs are mentioned. The document aims to educate on interpreting and analyzing QRS complexes on ECGs.
STEMI Mimic WHAT IS IT AND HOW TO IDENTIFY IT ?

STEMI Mimic WHAT IS IT AND HOW TO IDENTIFY IT ?Haitham Habtar The document discusses several STEMI mimics that can present with ST segment elevation on ECG but are not actually caused by an acute myocardial infarction. These include early repolarization, left bundle branch block, electrolyte abnormalities, left ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonary embolism, left ventricular aneurysm, Brugada syndrome, pericarditis, and hypothermia. It provides details on the characteristic ECG patterns and clinical features that can help differentiate these conditions from a true STEMI.
Topik 3 - ECG in ACS, chamber dilation and special conditions.pdf

Topik 3 - ECG in ACS, chamber dilation and special conditions.pdfanggelinathendry Explanatiin about ECG in ACS patient
Electrocardiogram in myocardial infarction 

Electrocardiogram in myocardial infarction https://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/ In a myocardial infarction transmural ischemia develops. In the first hours and days after the onset of a myocardial infarction, several changes can be observed on the ECG. First, large peaked T waves (or hyperacute T waves), then ST elevation, then negative T waves and finally pathologic Q waves develop.
Bundle branch blocks by Dr Sujith Chadala

Bundle branch blocks by Dr Sujith ChadalaDr Sujith Chadala Right bundle branch block,Left bundle branch block,Fasicular blocks,Intraventricular conduction blocks,hemiblocks,bifasicular blocks,trifasicular blocks,qRBBB ecg,causes of rbbb,causes of lbbb,Sgarbossa criteria,incomplete blocks,LAFB,LPFB,RAD,LAD
Ecg Part 1

Ecg Part 1hospital The document discusses electrocardiography (ECG) and how it is used to diagnose myocardial infarction (MI). It provides details on:
1) How 12 leads are used to view the heart electrically from different angles and locations, and which 10 electrodes are used.
2) The typical signs seen on an ECG during an MI, including ST segment elevation, pathological Q waves, reduced R waves, and inverted T waves.
3) The sequence of ECG changes that occur during an evolving MI, from initial onset through later stages.
4) How different leads on the ECG can indicate the location of an infarct, such as anterior vs inferior walls.
More from chricres (20)
Random ECGs 2

Random ECGs 2chricres 1. The document contains a series of ECG interpretations and management plans provided by Dr. Chris Cresswell for various patient presentations including chest pain, altered mental status, palpitations, and cardiac arrest.
2. Cases involve interpreting ECGs for conditions like STEMI, hyperkalemia, ventricular arrhythmias, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, and atrial flutter.
3. Management plans focus on revascularization, electrolyte abnormalities, electrical cardioversion, antiarrhythmics, and other treatments depending on the patient's condition and ECG findings.
Random ECGs 1

Random ECGs 1chricres This document contains summaries of ECG findings for various patients. Key cases include:
- A 95-year-old patient with faintness and a systolic murmur, whose ECG and murmur were suggestive of critical aortic stenosis.
- A 13-year-old with sudden palpitations found to have sinus tachycardia from rheumatic fever.
- A 10-year-old Māori boy with joint pain and swelling found to have myocarditis from acute rheumatic fever, shown on his ECG.
- A 35-year-old with chest pain and palpitations found to have Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
The document
Blood gases for nurses

Blood gases for nurseschricres The document discusses several cases presenting with blood gas results. Case 1 shows a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with relative hypoxia and hypoperfusion. Case 2 has a patient with life-threatening hyperkalemia, hypoxia, and severe acidosis requiring treatment. Case 3 is a toddler with gastroenteritis and life-threatening hypokalemia needing IV potassium replacement.
Introduction to head ct

Introduction to head ctchricres This document discusses various types of head injuries and conditions that appear on CT scans of the head. It describes acute subdural hematomas, which can cause midline shift. It also mentions chronic and subacute subdural hematomas, extradural hematomas, subarachnoid bleeds from trauma or aneurysms, and intraventricular hemorrhages that are usually secondary to hypertension. The document provides guidance on evaluating ring enhancing lesions and old lacunar or cortical infarcts. It concludes with general care recommendations for acute head injuries, such as maintaining normal oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydration and avoiding pressure areas.
Blood gases. Worked examples

Blood gases. Worked exampleschricres This patient presents with respiratory alkalosis and hypokalemia. They likely have a primary respiratory pathology causing hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. The hypokalemia needs urgent repletion through an IV route given its severity. The underlying cause of the respiratory issue needs to be determined through further history, exam, and testing to guide appropriate treatment and management.
Lbbb + sgarbossa

Lbbb + sgarbossachricres The document discusses the Law of Discordance for left bundle branch block (LBBB), stating that in a normal LBBB the ST segments should be isoelectric or go in the opposite direction from the dominant part of the QRS. It then outlines the Modified Sgarbossa Criteria for diagnosing STEMI in the presence of LBBB, including concordant ST changes or discordant ST elevation greater than 1/4 the amplitude of the S wave. Finally, it notes that these criteria also apply to ventricular paced rhythms and stresses the importance of documentation for ECG interpretations.
Military trauma

Military traumachricres This document discusses principles of combat casualty care, including:
1. The goals of Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) are to save preventable deaths, prevent additional casualties, and complete the mission.
2. About 60% of combat deaths are from hemorrhage from extremity wounds, 33% from tension pneumothorax, and 6% from airway obstruction - all of which can potentially be prevented with the right interventions.
3. There are three categories of casualties on the battlefield - those who will live regardless, those who will die regardless, and those who could be saved from preventable deaths with proper medical intervention. The goal is to target interventions to the correct mechanisms
Mass casualty and hazardous substances 2014

Mass casualty and hazardous substances 2014chricres This document outlines procedures for a mass casualty hazardous substances incident at a hospital. It describes locking down the hospital, declaring a mass casualty event, activating the mass casualty plan by calling in additional staff, and setting up an incident command structure. It also provides guidelines for patient decontamination and flow through hot, warm, and cold zones, as well as staff protection and hospital operations during the response. The goal is to treat patients while preventing spread of contamination within the hospital.
Rmo mil trauma

Rmo mil traumachricres This document discusses principles of combat casualty care, including:
1. The goals of Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) are to save preventable deaths, prevent additional casualties, and complete the mission.
2. About 60% of combat deaths are from hemorrhage from extremity wounds, 33% from tension pneumothorax, and 6% from airway obstruction - all largely preventable causes if immediate lifesaving interventions are provided on the battlefield.
3. There are three categories of casualties - those who will live regardless, those who will die regardless, and those who could be saved by timely intervention to stop hemorrhage, relieve airway obstruction, or treat tension
Sumatra assist1

Sumatra assist1chricres The document discusses the medical response to the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami in Sumatra, Indonesia. It notes that Australian medical teams performed over 270 operations in 6 weeks, with a third of cases not related to the tsunami and a third involving dressings and other treatments. The majority of acute cases were seen in the first 3 weeks, and medical issues included 93 cases of tetanus, with 30% of those experiencing aspiration pneumonia. Tuberculosis was also highly prevalent.
Ct head, nz_guidelines,_ed_presentation

Ct head, nz_guidelines,_ed_presentationchricres This document summarizes guidelines for head CT scans in adults and children presenting to the emergency department with head trauma. It outlines criteria for when to CT scan based on factors like Glasgow Coma Scale score, loss of consciousness, age, mechanism of injury, vomiting, and neurological symptoms. It also provides recommendations for when to perform a repeat CT scan if symptoms worsen or change. The guidelines aim to identify clinically significant traumatic brain injuries requiring intervention while avoiding unnecessary radiation exposure from CT scans.
ECG 101

ECG 101chricres The ECG provides a window into the heart, lungs, electrolytes, body temperature and sometimes the brain. It is important to systematically interpret the ECG by examining features like the rate, rhythm, axes, QRS complex, ST segment, T waves and QTc interval. Interpreting ECGs helps identify conditions like myocardial ischemia, electrolyte imbalances and long QT syndrome. It is important to record the time and name on the ECG and order repeat ECGs as needed to monitor patients.
Anaphylaxis. Dr Tom Francis

Anaphylaxis. Dr Tom Francischricres This document provides information on the treatment of anaphylaxis. It begins by defining anaphylaxis as an acute hypersensitivity reaction and describes the pathophysiology involving the release of histamine. The mainstay treatment is identified as adrenaline (epinephrine) injected intramuscularly. Common causes and signs/symptoms are outlined involving the airways, breathing and circulation. Additional treatment steps are described including IV fluids, antihistamines, steroids, and monitoring. Guidance is provided on discharge instructions and managing pediatric cases.
Corneal abrasions and f bs

Corneal abrasions and f bschricres Corneal abrasions are common eye injuries caused by trauma, foreign bodies, or improper contact lens use. Patients experience severe eye pain and a foreign body sensation. Examination involves assessing visual acuity, examining the cornea under fluorescein dye for abrasions, and evertiing the lids to check for foreign bodies. Treatment consists of topical antibiotic drops and pain medication. Most abrasions heal within 24 hours, but deep or infected abrasions require follow up.
Diabetes mx

Diabetes mxchricres This document describes several clinical scenarios involving patients with diabetes. The first scenario describes a 42-year-old Māori man presenting with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. The second discusses an 80-year-old man with unstable blood sugars on his current insulin regimen. The third involves a 20-year-old man newly diagnosed with latent autoimmune diabetes of adults. The fourth outlines a 69-year-old man with unstable blood sugars while tapering prednisone. Each scenario provides background on the patient's history and current treatment, with blood glucose readings and considerations for modifying insulin therapy.
Obstetric emergency communication and teamwork

Obstetric emergency communication and teamworkchricres The document discusses effective communication and teamwork during obstetric emergencies. It emphasizes the importance of clear leadership, role assignment, situation awareness, and closed-loop communication to ensure procedures are performed quickly and lead to better outcomes for mother and baby. Key aspects of managing emergencies as a team include mindful focus, declaring the situation, assigning a leader, providing handovers, voicing a shared plan of action, and managing any disagreements constructively.
Swarm based medical education

Swarm based medical educationchricres The document discusses how free open-access medical education (FOAM) through platforms like podcasts, blogs, and social media can significantly reduce the time it takes for new medical knowledge to be implemented in practice. It provides examples of how techniques learned from medical research publications or podcasts were put into practice within months, compared to the traditional 10 year lag. It also explains how the online medical community acts as a "swarm" that identifies high quality sources and provides peer feedback, helping to validate information and more quickly influence guidelines and practices.
Surgical emergencies. Dr Rebecca Thomas

Surgical emergencies. Dr Rebecca Thomaschricres This document provides guidelines from a surgical registrar on when and how to contact them regarding surgical emergencies that present to the emergency department. It outlines some key situations that should prompt a call, such as a hole or blockage in something, something in the wrong place, or significant infection or inflammation. It also provides advice on what information to provide when calling, including who you are, where you're calling from, and what you need from the registrar. The document gives some brief overviews of specific conditions like hernias, pancreatitis, ischemic gut and limb, and massive GI bleeds.
Wound care in ER. Dr Erik Adler

Wound care in ER. Dr Erik Adlerchricres This document provides guidance on evaluating and managing lacerations requiring closure. It discusses factors to consider when determining if primary closure is appropriate, steps for wound preparation including irrigation, and various closure methods. High-pressure irrigation with saline or tap water is recommended. Clean wounds within 8 hours can often be closed primarily, except on the face or scalp where longer time frames may apply. A physical exam alone is inadequate for ruling out a foreign body, so further imaging may be needed.
ED Urology. Dr Dan Morrissy

ED Urology. Dr Dan Morrissychricres This document discusses urinary tract infections, renal/ureteral calculi, and urinary retention. It provides information on signs, symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment for these conditions. For urinary tract infections, it outlines diagnostic criteria and treatment recommendations based on patient characteristics like age, sex, and pregnancy status. For renal calculi, it discusses etiology, diagnostic studies like ultrasound and CT, and medical expulsive and surgical treatment options. For acute urinary retention, it identifies pharmacological, neurological, infectious, and obstructive causes and recommends immediate catheterization for decompression of the bladder.
Recently uploaded (20)
IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE

IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy.
Dr. Jaymee Shell’s Perspective on COVID-19

Dr. Jaymee Shell’s Perspective on COVID-19Jaymee Shell Dr. Jaymee Shell views the COVID-19 pandemic as both a crisis that exposed weaknesses and an opportunity to build stronger systems. She emphasizes that the pandemic revealed critical healthcare inequities while demonstrating the power of collaboration and adaptability.
Shell highlights that organizations with gender-diverse executive teams are 25% more likely to experience above-average profitability, positioning diversity as a business necessity rather than just a moral imperative. She notes that the pandemic disproportionately affected women of color, with one in three women considering leaving or downshifting their careers.
To combat inequality, Shell recommends implementing flexible work policies, establishing clear metrics for diversity in leadership, creating structured virtual collaboration spaces, and developing comprehensive wellness programs. For healthcare providers specifically, she advocates for multilingual communication systems, mobile health units, telehealth services with alternatives for those lacking internet access, and cultural competency training.
Shell emphasizes the importance of mental health support through culturally appropriate resources, employee assistance programs, and regular check-ins. She calls for diverse leadership teams that reflect the communities they serve and community-centered care models that address social determinants of health.
In her words: "The COVID-19 pandemic didn't create healthcare inequalities – it illuminated them." She urges building systems that reach every community and provide dignified care to all.
Evidence - Based Practice - Nursing Research

Evidence - Based Practice - Nursing ResearchDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy Evidence-Based Practice - Nursing Research
PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...

PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...ABHAY INSTITUTION Personality theory is a collection of ideas that explain how a person's personality develops and how it affects their behavior. It also seeks to understand how people react to situations, and how their personality impacts their relationships.
Key aspects of personality theory
Personality traits: The characteristics that make up a person's personality.
Personality development: How a person's personality develops over time.
Personality disorders: How personality theories can be used to study personality disorders.
Personality and environment: How a person's personality is influenced by their environment.
Characteristics and Criteria of Good Research.pptx

Characteristics and Criteria of Good Research.pptxDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy Characteristics and Criteria of Good Research
physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation سؤال.pptx

physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation سؤال.pptxamralmohammady27 لو عندك لاب توب أو تابلت فال
power point show
هينفعك جدا في مراجعة سريعة ليلة الامتحان
واللي يقدر يعمل حاجة يعملها
وشكرا للدكتورة نوال على تجميعة أسئلة البيو
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptx

Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptxDr Punith Kumar Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing clinical microbiology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, automating workflows, and improving patient outcomes. This presentation explores the key applications of AI in microbial identification, antimicrobial resistance detection, and laboratory automation. Learn how machine learning, deep learning, and data-driven analytics are transforming the field, leading to faster and more efficient microbiological diagnostics. Whether you're a researcher, clinician, or healthcare professional, this presentation provides valuable insights into the future of AI in microbiology.
Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptx

Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptxdribnibrahem164 neurological complications of infective endocarditis
Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...

Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education Chair, Grzegorz (Greg) S. Nowakowski, MD, FASCO, discusses diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in this CME activity titled “Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic Assessment and Off-the-Shelf Immunotherapy Strategies.” For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aid, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/49JdxV4. CME credit will be available until February 27, 2026.
Increased Clinical Trial Complexity | Dr. Ulana Rey | MindLumina

Increased Clinical Trial Complexity | Dr. Ulana Rey | MindLuminaUlana Rey PharmD Increased Clinical Trial Complexity. By Ulana Rey PharmD for MindLumina. Dr. Ulana Rey discusses how clinical trial complexity—endpoints, procedures, eligibility criteria, countries—has increased over a 20-year period.
Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...

Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...KHUSHAL CHAVAN This presentation provides an in-depth understanding of solubilization and its critical role in pharmaceutical formulations. It covers:
Definition & Mechanisms of Solubilization
Role of surfactants, micelles, and bile salts in drug solubility
Factors affecting solubilization (pH, polarity, particle size, temperature, etc.)
Methods to enhance drug solubility (Buffers, Co-solvents, Surfactants, Complexation, Solid Dispersions)
Advanced approaches (Polymorphism, Salt Formation, Co-crystallization, Prodrugs)
This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical scientists, formulation experts, regulatory professionals, and students interested in improving drug solubility and bioavailability.
Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy | Causes, Risks & Management

Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy | Causes, Risks & ManagementDr.Laxmi Agrawal Shrikhande Explore the impact of thyroid disorders in pregnancy, including causes, risks, diagnosis, and management strategies to ensure maternal and fetal health.
Research Hyopthesis and Research Assumption

Research Hyopthesis and Research AssumptionDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy Research Hyopthesis and Assumption
Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptx

Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptxKafrELShiekh University Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.
legal Rights of individual, children and women.pptx

legal Rights of individual, children and women.pptxRishika Rawat A legal right is a claim or entitlement that is recognized and protected by the law. It can also refer to the power or privilege that the law grants to a person. Human rights include the right to life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and education
ISPE Baseline PEG Volumen 7 Risk-Based Manufacture Pharmaceutical Products 2n...

ISPE Baseline PEG Volumen 7 Risk-Based Manufacture Pharmaceutical Products 2n...alokksharma18 guidelines for pharma products
Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...

Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Stemi criteria
- 1. STEMI on ECG • New ST elevation at J-point in 2 contiguous leads with cut-points: • ≥ 0.2 mV in men ≥ 40 years in leads V2 - V3 • ≥ 0.25 mV in men < 40 years in leads V2 - V3 • ≥ 0.15 in women in leads V2 - V3 • ≥ 0.1 mV in all other leads • In the absence of LVH and LBBB examples of ST-elevation in MI
- 3. 3rd Universal Definition of MI (2012)
- 4. STEMI on ECG • New ST elevation at J-point in 2 contiguous leads with cut-points: • ≥ 0.2 mV in men ≥ 40 years in leads V2 - V3 • ≥ 0.25 mV in men < 40 years in leads V2 - V3 • ≥ 0.15 in women in leads V2 - V3 • ≥ 0.1 mV in all other leads • In the absence of LVH and LBBB examples of ST-elevation in MI
- 5. General pitfalls • Beware of baseline ECG abnormalities that may obscure interpretation • LBBB • refer to Sgarbossa’s criteria • LVH • J-point elevation syndromes eg, Brugada • PE • Peri/myocarditis • Cardiomyopathy, including Takotsubo • Cocaine use • Cardiac pacing
- 6. STEMI location • septal • V1, V2 • inferior • II, III, aVF • reciprocal changes: I, aVL • lateral • I, aVL, V5, V6 • reciprocal changes: II, III, aVF • anterior • V3, V4 • anteroseptal • V1, V2, V3, V4 • anterolateral • I, aVL, V3, V4, V5, V6 • reciprocal changes: II, III, aVF • posterior • V7, V8, V9 • reciprocal changes: V1, V2, V3, V4
- 9. ECG 3 Inferolateral STEMI + Horizontal ST depression V1-3 + Tall R waves, upright T-waves V2-3
- 10. ECG 3 + posterior leads Inferior-lateral-posterior STEMI
- 11. References • Bax, Jeroen J., et al. "Third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction." Journal of the American College of Cardiology 60.16 (2012): 1581-1598.