Hul
- 1. INTRODUCTION FMCG Industry: • FMCG products are products that have quick shelf turnover, at relatively low cost and don’t require a lot of thought, time and financial investment to purchase. • FMCG Industry mainly deals with production, distribution & marketing of packaged goods to all consumers
- 2. FMCG Industry in India: • Present – Fourth largest sector in the economy – Size - US$13.1 billion – Strong MNC Presence – Well established distribution network – Competition between organized and unorganized sector – Low Costs of labour and Easy availability of key raw materials
- 3. FMCG – Major Domestic Players • Domestic Players – Britannia India Ltd (BIL) – Dabur India Ltd – Indian Tobacco Corporation Ltd (ITCL) – Marico – Nirma Limited
- 4. FMCG – Major Foreign Players • Foreign Players – Cadbury India Ltd (CIL) – Cargill – Coca Cola – Colgate-Palmolive India – H J Heinz Co – Hindustan Unilever Ltd (HUL) – Nestle India Ltd (NIL) – PepsiCo – Procter & Gamble Hygiene and Health Care Limited
- 5. Hindustan Unilever Ltd • HUL touches the lives of two out of every three Indians everyday • Part of the €40 billion Unilever Group. The Group has more than 400 brands spanning 14 categories of home, personal care and food products • Presence in over 100 countries and employs more than 174,000 people worldwide • The Company was incorporated in 1933 but its products have been sold in India since 1888
- 6. Hindustan Unilever Ltd • India’s largest FMCG Company • Headquartered in Mumbai • Over 700 million consumers • More than 15,000 employees, including 1,300 managers • More than 200 highly qualified scientists and technologists • Shares listed at BSE (Stock code - 500696) and NSE (Stock code – HINDUNILVR) • Shareholder base of over 3.5 lakh
- 7. HUL – The Journey so far… 1931: HUL set up its first subsidiary 1956: HUL offered 10% of its equity to the Indian public 1972: Lipton Acquisition 1984: Brooke Bond Acquisition 1986: Pond’s Acquisition 2000: Modern Foods Acquisition
- 8. HUL – Mission Mission Unilever's mission is to add Vitality to life. We meet everyday needs for nutrition, hygiene, and personal care with brands that help people feel good, look good and get more out of life.
- 9. HUL – Geographic Presence • Production More than 35 manufacturing locations across India, with major hubs being Assam, Uttaranchal, Himachal Pradesh, Pondicherry and Dadra & Nagar Haveli • Marketing – All States in India, Project Shakti
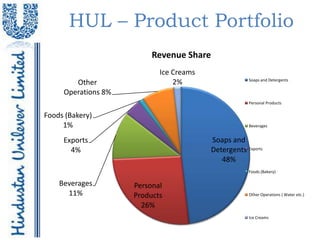
- 10. HUL – Product Portfolio Revenue Share Ice Creams Soaps and Detergents Other 2% Operations 8% Personal Products Foods (Bakery) 1% Beverages Exports Soaps and 4% Detergents Exports 48% Foods (Bakery) Beverages Personal 11% Products Other Operations ( Water etc.) 26% Ice Creams
- 11. SWOT - HUL
- 12. STRENGTHS Strong parentage and R&D, healthy cash coffers to support innovation Strong position in most of the categories of its presence Unmatched distribution network , a must to cater rural markets STRENGTHS Presence across price points to straddle across entire income pyramid Healthy Shareholder Returns in the form of RoE and dividend yield Native Know How
- 13. WEAKNESSES 49% of HUVR's sales come from detergents and personal wash WEAKNESSES Increase in Ad Spending, which may affect the margins
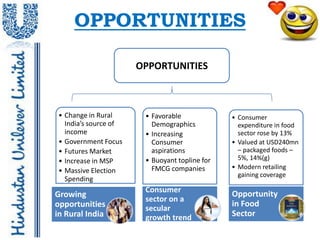
- 14. OPPORTUNITIES OPPORTUNITIES • Change in Rural • Favorable • Consumer India’s source of Demographics expenditure in food income • Increasing sector rose by 13% • Government Focus Consumer • Valued at USD240mn • Futures Market aspirations – packaged foods – • Increase in MSP • Buoyant topline for 5%, 14%(g) FMCG companies • Modern retailing • Massive Election gaining coverage Spending Consumer Growing Opportunity sector on a opportunities in Food secular in Rural India growth trend Sector
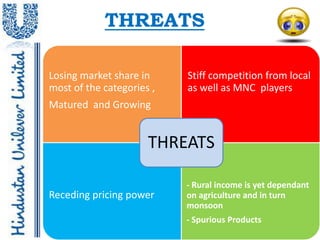
- 15. THREATS Losing market share in Stiff competition from local most of the categories , as well as MNC players Matured and Growing THREATS - Rural income is yet dependant Receding pricing power on agriculture and in turn monsoon - Spurious Products
- 16. FIVE FORCE MODEL
- 17. PORTER’S FIVE FORCE MODEL… Threat of New Entrant Supplier Power •Time and Cost of Entry •Specialist Knowledge • Number of •Economies of Scale Suppliers •Cost Advantage •Size of Suppliers •Technology Protection •Your Ability to •Barriers to Entry Change •Cost of Changing Threat of Substitution •Substitute Performance •Cost of Change Buyer Power Competitive Rivalry • Number of Customers • Number of Competitors • Size of Each Order •Quality Differences • Differencebetween •Other Differences Competition •Switching Costs • Price Sensitivity •Customer Loyalty • Ability to Substitute •Costs of Leaving Market • Cost of Changing
- 18. THREAT OF NEW ENTRANT • In early 2000, HUL decided to enter Retail Market through direct selling brand (B2C) by the name SANGAM direct • Started in Bombay…with 2 stores, Sangam has vision to grow to 15stores. • With highly competitive retail market, Sangam faced 3 problems: – Specialized knowledge • Space constraints • Cost disadvantage (No disc on competitor’s product) • Time and Cost
- 19. COMPETITIVE RIVALRY • Number of Competitors • Quality Differences • Other Differences • Switching Costs • Customer Loyalty
- 20. SUPPLIER POWER • Large economies of scale • HUL adopts Backward Integration, therefore – No. of suppliers are less – Size of Suppliers are moderate – Ability to Change is Flexible – Cost of Changing is Low
- 21. BUYER POWER • No. of customer’s is moderate • Size of Each Order is in Bulk quantity • Price Sensitivity • Ability to substitute • Cost of changing • Tie-ups with local complementary product manufacturer to get products at cheaper and minimal rates
- 22. HUL VALUE CHAIN
- 23. HUL VALUE CHAIN • Business optimisation through Technology • Integrating suppliers and distributers through SAP • Best marketing talent from top B schools • TPM and product flexibility in Operations • Emotional buying of satisfied customer
Editor's Notes
- #2: FMCG IndustryFMCG products are products that have quick shelf turnover, at relatively low cost and don’t require a lot of thought, time and financial investment to purchaseFMCG Industry mainly deals with production, distribution & marketing of packaged goods to all consumers.
- #3: FMCG Industry in IndiaPresentFourth largest sector in the economySize - US$13.1 billionStrong MNC PresenceWell established distribution networkCompetition between organized and unorganized sectorLow Costs of labour and Easy availability of key raw materials.